What direction is depth of cut in turning?
It is usually given in the third perpendicular direction (velocity, feed and depth of cut usually act in mutually perpendicular directions). Click to see full answer. In this manner, what is depth of cut in turning?
What is the depth of cut in conventional machining operations?
Usually, in conventional machining operations, depth of cut value varies between 0.1 – 1.0mm. Selection of its value requires attention on the following characteristics.
What determines the depth of cut?
Depth of cut is determined according to the required stock removal, shape of workpiece, power and rigidity of the machine and tool rigidity. 1. Changing depth of cut doesn't effect tool life greatly.
What is the maximum depth for a rough cut?
Accuracy and surface finish are not important in this operation. Therefore, max depth of .030 inch and a .020 to .030 inch feed is recommended. Workpiece is generally rough turned to within about .030 inch of the finished size in a few cuts as possible.

What is depth of cut in turning?
Depth of Cut (t): It is the total amount of metal removed per pass of the cutting tool. It is expressed in mm. It can vary and depending upon the type of tool and work material. Mathematically, it is half of difference of diameters. Depth of cut (t) = D-d/2 mm.
What is depth of cut in CNC machine?
Depth of Cut is also referred to as Axial Depth of Cut. Cut Width, also called Stepover, is the total thickness of the cut when viewing the cutting tool from above. It can be no more than 100% of the cutter's diameter. Stepover is also referred to as Radial Depth of Cut.
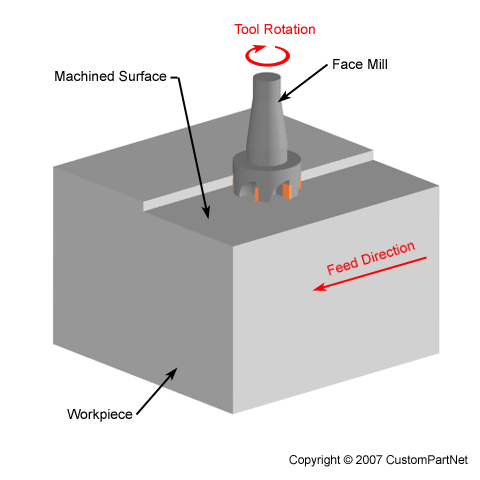
What is depth of cut in milling machine?
In milling, the depth of cut is two-dimensional. The Radial depth of cut (AE or RDOC), is the length that the tool engages a workpiece perpendicular to its axis direction and the Axial depth of cut (AP or ADOC), is the length in its axis direction. They are both measured perpendicular to the table feed direction.
How do you determine the depth of a cut?
The depth of cut is set at values found by multiplying the diameter or ball nose radius by a fixed coefficient. The image to the right shows a depth of cut standard for 2-flute, square corner, coated carbide end mill. If the workpiece materials are harder, the depth of cut should be decreased.
What is depth in machining?
Depth of cut (t)—The tertiary cutting motion that provides necessary depth of material that is required to remove by machining. It is expressed in mm. It is usually given in the third perpendicular direction (velocity, feed and depth of cut usually act in mutually perpendicular directions).
What is feed and depth of cut?
Feed, Speed, and Depth of Cut Feed rate is defined as the distance the tool travels during one revolution of the part. Cutting speed and feed determines the surface finish, power requirements, and material removal rate. The primary factor in choosing feed and speed is the material to be cut.
What is a turning operation?
Turning is the most common lathe machining operation. During the turning process, a cutting tool removes material from the outer diameter of a rotating workpiece. The main objective of turning is to reduce the workpiece diameter to the desired dimension. There are two types of turning operations, rough and finish.
What is radial depth of cut?
Radial Depth of Cut (RDOC): The distance a tool is stepping over into a workpiece. Also referred to as Stepover, Cut Width, or XY.
What is cut length?
Overall Length (OAL) & Length of Cut (LOC) Overall length is easy to decipher, as it is simply the measurement between the two axial ends of the tool.
What two terms relate to the depth of cut?
The correct answer is A & C. Congrats to all of those who got it right! Axial depth of cut, ap inch (mm), is what the tool removes in metal on the face of the workpiece.
What is axial depth of cut?
Axial Depth of Cut (ADOC): The distance a tool engages a workpiece along its centerline. Also referred to as Stepdown, or Cut Depth.
What is cut length?
Overall Length (OAL) & Length of Cut (LOC) Overall length is easy to decipher, as it is simply the measurement between the two axial ends of the tool.
What is the maximum depth of cut recommended for an end mill?
With a cut equal to the full width of the cutter, the maximum recommended depth of cut (ap) is 0.6 D. If, however, the cutting action is the cleaning up of the edge of a component, with the cut only 10 per cent of the diameter, the depth can be increased to 1.5 D.
What is cutting speed formula?
cutting speed Tangential velocity on the surface of the tool or workpiece at the cutting interface. The formula for cutting speed (sfm) is tool diameter 5 0.26 5 spindle speed (rpm). The formula for feed per tooth (fpt) is table feed (ipm)/number of flutes/spindle speed (rpm).
What is the depth of cut?
Depth of cut (t) —The tertiary cutting motion that provides necessary depth of material that is required to remove by machining. It is expressed in mm. It is usually given in the third perpendicular direction (velocity, feed and depth of cut usually act in mutually perpendicular directions).
How does depth of cut affect cutting force?
Effects of depth of cut (DOC) 1 Larger depth of cut indicates higher material removal rate (MRR), as MRR is proportional to the speed, feed and depth of cut. So productivity of machining can be enhanced by employing larger depth of cut and consequently machining cost can be reduced. 2 Cutting force depends on chip load, which is proportional to depth of cut. Thus larger value of depth of cut can increase cutting force, which may hamper machining performance and induce vibration. 3 Higher depth of cut may also break the cutting tool catastrophically, which is highly undesirable. 4 It also influences chip thickness, type of chip produces, shear deformation, etc., which are indication of machinability.
What is the most important cutting parameter?
1. Cutting velocity (Vc) —The most important cutting parameter that provides necessary cutting motion. It can be imparted either on the cutting tool or on workpiece by either rotating it or reciprocating it. In case of either rotating tool (such as milling, drilling, grinding) or rotating workpiece (such as turning), the peripheral velocity of cutter or workpiece is considered as the cutting velocity. However, where neither the workpiece nor the tool rotates, the translation velocity of cutter or workpiece gives the intended cutting velocity . Learn more about cutting speed and cutting velocity .
How does depth of cut affect productivity?
So productivity of machining can be enhanced by employing larger depth of cut and consequently machining cost can be reduced. Cutting force depends on chip load, which is proportional to depth of cut. Thus larger value of depth of cut can increase cutting force, which may hamper machining performance and induce vibration.
What is the peripheral velocity of a cutter?
In case of either rotating tool (such as milling, drilling, grinding) or rotating workpiece (such as turning), the peripheral velocity of cutter or workpiece is considered as the cutting velocity.
What is the productivity requirement of material removal?
Productivity requirement —Since material removal rate is expressed by the multiplication of cutting velocity, feed rate and depth of cut, so usage of larger depth of cut results in enhanced MRR. This, in turn, cuts down machining time and thus improves productivity.
What is quality of cut required?
Quality of cut required —For finish cut, lower depth of cut should be provided; whereas, for rough cut, larger value can be utilized to shorten machining time.
What is radial depth of cut?
Radial Depth of Cut (RDOC): The distance a tool is stepping over into a workpiece. Also referred to as Stepover, Cut Width, or XY.
How much of the cutter diameter is engaged during peripheral milling?
In heavy roughing applications, 30-50% of the tool’s cutter diameter is engaged with the part. Although heavy roughing involves a higher RDOC than finishing, the ADOC is most often smaller than for finishing due to load on the tool.
What is a single point turning tool?
A single-point turning tool moves axially, along the side of the workpiece, removing material to form different features, including steps, tapers, chamfers, and contours. These features are typically machined at a small radial depth of cut and multiple passes are made until the end diameter is reached.
What is the process of turning?
Turning is a form of machining, a material removal process, which is used to create rotational parts by cutting away unwanted material. The turning process requires a turning machine or lathe, workpiece, fixture, and cutting tool.
What is cutting feed?
Cutting feed – The distance that the cutting tool or workpiece advances during one revolution of the spindle, measured in inches per revolution (IPR). In some operations the tool feeds into the workpiece and in others the workpiece feeds into the tool. For a multi-point tool, the cutting feed is also equal to the feed per tooth, measured in inches per tooth (IPT), multiplied by the number of teeth on the cutting tool.
What is a boring tool?
The boring tool is a single-point cutting tool, which can be set to cut the desired diameter by using an adjustable boring head. Boring is commonly performed after drilling a hole in order to enlarge the diameter or obtain more precise dimensions.
What is the purpose of turning a cylinder?
Turning can be done either on the outside of the cylinder or on the inside (also known as drilling) to produce tubular components with various geometries.
What is polygonal turning?
Polygonal turning. In which non-circular forms are machined without interrupting the rotation of the raw material.
What is the purpose of drilling?
Drilling. It is used to remove material from the inside of a workpiece. This process utilizes standard drill bits held stationary in the tail stock or tool turret of the lathe. The process can be done by separately available drilling machines.
What is the operation of parallel turning?
Work that must be cut to size and have the same diameter along the entire length of the workpiece involves the operation of parallel turning. Many factors determine the amount of materials which can be removed on a lathe. A diameter should be cut to size in two cuts: an roughing cut and finishing cut.
What is rough turning?
The operation of rough turning is used to remove as much metal as possible in the shortest length of time. Accuracy and surface finish are not important in this operation. Therefore, max depth of .030 inch and a .020 to .030 inch feed is recommended. Workpiece is generally rough turned to within about .030 inch of the finished size in a few cuts as possible.
What is finish turning on a lathe?
Finish turning on a lathe, which follows rough turning , produces a smooth surface finish, and cuts the workpiece to an accurate size. Factors such as the condition of the cutting tool bit, the rigidity of the machine and workpiece and the lathe speed and feedrate, may affect the type of surface finish produced.
How to lay out shoulder on lathe?
1. With a workpiece mounted in a lathe, lay out the shoulder position from the finished end of the workpiece. In case of filleted shoulders, all sufficient length to permit the proper radius to be formed on the finished shoulder.
What is the purpose of facing a lathe?
The purpose of facing are: • To provide a true, flat surface, square with the axis of the workpieces.
How to set a lathe to the right?
1. Move the tool post to the left-hand side of the compound rest, and set the right hand facing tool bit to the right height of the lathe center point . The compound rest may be set at 30 degrees for accurate end facing.
When calculating the tail stock offset, what must be known?
When calculating the tail stock offset, the taper per foot and total length of the workpiece must be known.
How does depth of cut increase productivity?
Depth of cut is the simplest of these to increase, but improvements are possible only when there is enough material and power for it. Doubling depth of cut doubles productivity at no increase to cutting temperature, tensile strength or cutting force per cubic inch or centimeter removed (also called the specific cutting force). It doubles the required power, but so long as the tool meets tangential cutting force requirements, there is no decrease in tool life.
What is the effectiveness of cutting tools?
Cutting tools’ effectiveness depends largely on the tool’s angle in relation to the workpiece. The terms defined in this section reference inserts to define cutting and relief angles, but can also apply to brazed single-point tools.
What is a top rake angle?
Top rake angle (also called back rake angle) is the angle formed between the angle of inclination of the insert and the line perpendicular to the workpiece when viewing the tool from the side, front to back. Top rake is positive when it slopes downward from the cutting point and into the shank, neutral when the line from the top of the insert is parallel with the top of the shank, and negative when it slopes upward from the cutting point and above the shank. Inserts and toolholders are also categorized as positive or negative. Positive inserts have angled sides and mount into toolholders with positive top and side rake angles. Negative inserts have square sides relative to the top face of the insert and mount into toolholders with negative top and side rake angles. Top rake angle is unique in that it is dependent on the geometry of the insert — a positive ground or a molded chipbreaker can change the effective top rake angle from negative to positive. Top rake angles also tend to be greater with softer and more ductile workpiece materials, which require high positive shearing angles, while harder and tougher materials are best cut with neutral or negative geometries.
How does feed rate affect cutting force?
This change lowers tool life, but does not halve it. Specific cutting force (the cutting force in relation to the amount of material removed) also decreases with increased feed rate. The additional force imposed on the cutting edge with increased feed rates can result in the cratering of the top rake insert surface due to the increased temperature and friction generated during the cut. Operators must monitor this variable carefully to avoid catastrophic failure where the chip becomes stronger than the insert.
Why use positive rake angle cutting tool?
Positive rake angle cutting tools are preferable for most boring operations in order to reduce cutting forces. However, the smaller clearance angles of positive rake angle tools require operators to plan for the possibility of contact between the tool and the workpiece. It is especially important to ensure an adequate clearance angle when boring small diameter holes.
How to determine surface finish?
Once rigidity is assured, the relationship between the machine feed (in./rev or mm./rev) and the nose contour of the insert or cutting tool can be used to determine the workpiece’s surface finish. The nose contour is expressed as a radius — up to a certain point, a larger radius translates to better surface finish, but too large of a radius can introduce chatter. For machining operations where a smaller-than-optimum radius is required, feed rate may need to be reduced for the desired finish.
What is the difference between cutting speed and feed rate?
Turning is a combination of linear (tool) and rotational (workpiece) movement. Thus, cutting speed is defined as the rotational distance (recorded as sfm — surface feet per minute — or smm — square meters per minute — traveled in one minute by a point on the part surface). Feed rate (recorded in inches or millimeters per revolution) is the linear distance that the tool travels along or across a workpiece surface. Feed is also sometimes expressed as the linear distance the tool travels in a single minute (in./min or mm/min).
Why do you need to increase the depth of cut?
2. Small depths of cut result in friction when cutting the hardened layer of a workpiece. Thus tool life is shortened. 3. When cutting uncut surfaces or cast iron surfaces, the depth of cut needs to be increased as much as the machine power allows in order to avoid cutting impure hard layers with the tip of cutting edge to prevent chipping ...
What are the conditions for cutting?
Ideal conditions for cutting are short cutting time, long tool life, and high cutting accuracy. In order to obtain these conditions, selection of efficient cutting conditions and tools, based on work material, hardness, shape and machine capability is necessary.
How does cutting speed affect tool life?
Cutting speed effects tool life greatly. Increasing cutting speed increases cutting temperature and results in shortening tool life. Cutting speed varies depending on the type and hardness of the work material. Selecting a tool grade suitable for the cutting speed is necessary.