
The endopelvic fascia is the extraperitoneal cellular tissue of the uterus (the parametrium), vagina, bladder and rectum. Within this endopelvic fascia are three important condensations of connective tissue which sling the pelvic viscera from the pelvic walls.
What is the difference between endopelvic and pelvic fascia?
Pelvic fascia is the term applied to the connective tissue floor of the pelvis covering levator ani and obturator internus. The endopelvic fascia is the extraperitoneal cellular tissue of the uterus (the parametrium), vagina, bladder and rectum.
What is another name for the pelvis fascia?
pa·ri·e·tal pel·vic fas·ci·a. [TA] including the obturator fascia, covers the pelvic walls formed primarily by muscles that pass from the interior of the pelvis to the thigh. Synonym(s): fascia pelvis parietalis [TA], endopelvic fascia ☆ , fascia endopelvina ☆.
Is there any fatty tissue in The endopelvic fascia?
The endopelvic fascia does not contain any fatty tissue. 38 Only in the region of the uterosacral ligament do the strands of fibrous tissue run in a fan-like shape in a large area through the subperitoneal adipose tissue. There is a variable amount of fatty tissue outside the adventitia of the urinary bladder and rectum.
What are the two components of the pelvic fascia?
Patrick C Walsh, 1998. The pelvic fasciae consist of two components: (i) the endopelvic fascia, which primarily covers the pelvic muscles; and (ii) the visceral fascia which covers the pelvic organs and the supplying vessels and nerves. – Together, they support and define the structures in the pelvis.
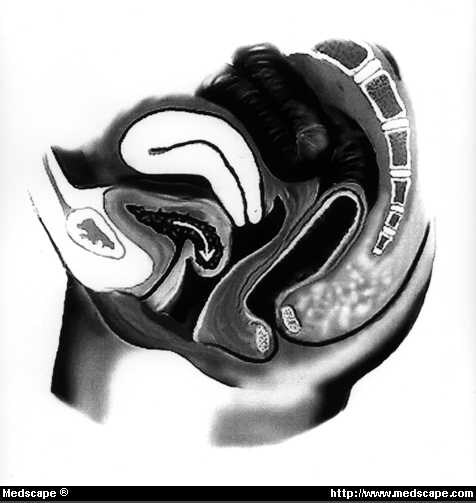
Where is the Endopelvic fascia?
pelvisThe pelvic fasciae consist of two components: (i) the endopelvic fascia, which primarily covers the pelvic muscles; and (ii) the visceral fascia which covers the pelvic organs and the supplying vessels and nerves. Together, they support and define the structures in the pelvis.
What does Endopelvic mean?
The endopelvic fascia is the enveloping connective tissue network for the pelvic viscera, suspending, supporting and fusing the pelvic organs to the arcus tendineus fasciae pelvis, which itself inserts onto the pelvic sidewalls and pubic bones.
What is the fascia of the uterus?
Results: The endopelvic fascia has the shape of a semifrontally oriented septum, which surrounds the vagina and part of the uterine cervix and divides the pelvic floor into the anterior and posterior compartments.
What is the fascia of the pelvic floor?
The parietal pelvic fascia is a membranous layer of variable thickness that lines the pelvic aspect of muscles forming the walls and floor of the pelvis. This layer is continuous superiorly with the transversalis fascia of the abdominal wall.
What muscle originates Endopelvic fascia?
The internal sheet of the internal obturator muscle fascia is part of the parietal endopelvic fascia that continues covering the piriformis and the coccygeus muscles and has a thickening on which the levator anis muscle is attached (ATLA) [9].
What is Pubocervical fascia?
The pubocervical fascia has been described as extending from the symphysis along the anterior vaginal wall to blend with the fascia that surrounds the cervix. It is continuous laterally with the pubococcygeus and also suspended to the arcus tendineus of the pelvic fascia.
How do you release pelvic fascia?
0:524:53Easy Pelvic Fascia Exercise to Release Tension and Tightness ♂️YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we'll start with the pelvis facing the leg. Then we will slide our hand over the inside of theMoreSo we'll start with the pelvis facing the leg. Then we will slide our hand over the inside of the thigh like that and if you pull a little bit you might feel that connection. Into the pelvic floor.
What ligaments are cut during hysterectomy?
Explanation of Procedure The sites that are most likely to cause ureteral injury when cutting the ligaments are: (1) vesicouterine ligament, (2) cardinal ligament, (3) sacrouterine ligament, (4) infundibulopelvic ligament, and (5) round ligament.
What holds the uterus in position?
The pelvic diaphragm supports all the viscera. The round ligament helps maintain the anteversion position of the uterus during pregnancy. The cardinal ligaments support the uterus.
How do you strengthen fascia?
How to improve your fascia healthStretch for 10 minutes a day. Share on Pinterest. ... Try a mobility program. ... Roll out your tight spots. ... Visit the sauna, especially after the gym. ... Apply cold therapy. ... Get your cardio on. ... Try yoga. ... Keep you and your fascia hydrated.More items...
How do I strengthen my pelvic floor?
To strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, sit comfortably and squeeze the muscles 10 to 15 times. Do not hold your breath or tighten your stomach, bottom or thigh muscles at the same time. When you get used to doing pelvic floor exercises, you can try holding each squeeze for a few seconds.
Do sit ups strengthen your pelvic floor?
Exercises that strongly engage the upper abdominal muscles such as sit-up or abdominal curl exercises increase downward pressure on the pelvic floor.
What are the three layers of the endometrium?
The endometrium undergoes changes in the late secretory phase with the development of the spiral arteries. The endometrium has three layers: the outer (superficial) compact layer, the larger middle spongy layer, and the inner basal layer.
What are the layers of the uterus?
The uterus has three tissue layers which include the following:Endometrium: the inner lining and consists of the functional (superficial) and basal endometrium. ... Myometrium: the muscle layer and is composed of smooth muscle cells.Serosa/Perimetrium: the thin outer layer composed of epithelial cells.
What surrounds the uterus?
The peritoneum covers the uterus and is separated from the uterine musculature by a thin layer of periuterine fascia, which is a continuation and extension of the transversalis fascia.
What is the function of endometrium?
The physiological functions of the uterine endometrium (uterine lining) are preparation for implantation, maintenance of pregnancy if implantation occurs, and menstruation in the absence of pregnancy. The endometrium thus plays a pivotal role in reproduction and continuation of our species.
What is the pelvic fascia?
Pelvic fascia is the term applied to the connective tissue floor of the pelvis covering levator ani and obturator internus. The endopelvic fascia is the extraperitoneal cellular tissue of the uterus (the parametrium), vagina, bladder and rectum. Within this endopelvic fascia are three important condensations of connective tissue which sling ...
Which ligament extends forward from the pubis on either side of the bladder?
3 The pubocervical fascia extends forward from the cardinal ligament to the pubis on either side of the bladder, to which it acts as a sling. These three ligaments act as supports to the cervix of the uterus and the vault of the vagina, in conjunction with the important elastic muscular foundation provided by levator ani.
What are the three condensations of connective tissue that sling the pelvic viscera from the pelvic
Within this endopelvic fascia are three important condensations of connective tissue which sling the pelvic viscera from the pelvic walls. 1 The cardinal ligaments (transverse cervical, or Mackenrodt's ligaments), which pass laterally from the cervix and upper vagina to the side walls of the pelvis along the lines of attachment of levator ani, ...
What is the broad ligament?
1 The broad ligament is a fold of peritoneum connecting the lateral margin of the uterus with the side wall of the pelvis on each side. The uterus and its broad ligaments, therefore, form a partition across the pelvic floor dividing off an anterior compartment, containing bladder (the uterovesical pouch), from a posterior compartment, ...
How long is a procidentia ligament?
In prolapse these ligaments lengthen (in procidentia — complete uterine prolapse—they may be 6 in (15 cm) long) and any repair operation must include their reconstitution. Two other pairs of ligaments take attachments from the uterus.
What is the endopelvic fascia?
The endopelvic fascia is a confluent suspensory apparatus of the female pelvic organs. The aim of the study was to construct a three-dimensional model of the endopelvic fascia, defining its shape and its connections to the surrounding parietal structures. METHODS: .
Where does the endopelvic fascia insert?
The endopelvic fascia inserts into these surrounding structures: Pubic bone: The anterosuperior leaf of the endopelvic fascia (the “pubocervical fascia”) in its most anterior part inserts into the body of the pubic bone (Fig. 4A, 5A). This attachment is interrupted at the midline for approximately 4–6 mm.
What is the perineural connective tissue that arises from the fascia of the piriformis muscle
The perineural connective tissue that arises from the fascia of the piriformis muscle, together with the errigent nerves, creates the “neural portion” of the uterosacral ligament. This stalk lies inferomedially from the “vascular portion” and is also not attached to the bone (Fig. 7b).
What is the confluent septum?
This confluent septum has specific connections to the pubic bone, anterior perineal membrane, perineal body, and superior fascia of the levator ani muscle. Additionally, the uterosacral part of the septum has three subdivisions— the “vascular part,” the “neural part,” and the true uterosacral ligament.
What is the vagina surrounded by?
The vagina is, therefore, circularly surrounded by the endopelvic fascia. The adventitia of the base of the urinary bladder is connected to the “pubocervical fascia” by the left and right “bladder pillar.”. These structures contain terminal branches of the middle and inferior vesical artery.
What is the neural part of the uterosacral ligament?
The "neural" part of the uterosacral ligament: The pelvic splanchnic nerves (the “erigent nerves”) proceed from the ventral aspect of the sacral plexus, and together with fibers of inferior hypogastric nerves and fibers from the sympathetic chain, create the neural pelvic plexus (plexus hypogastricus inferior).
Which direction does the endopelvic fascia increase?
The density and stronghold of the endopelvic fascia is not uniform in all regions. The tissue density increases in the craniocaudal direction. The tissue is strongest and most dense, and its surface is best defined in the region of the distal pubocervical and distal rectovaginal fascia.
What is the pelvic fascia?
The pelvic fasciae are the fascia of the pelvis and can be divided into: (a) the fascial sheaths of. the Obturator internus muscle ( Fascia of the Obturator internus) the Piriformis muscle ( Fascia of the Piriformis) the pelvic floor. (b) fascia associated with the organs of the pelvis.
Which muscle is located on the pelvic floor?
The part of the pelvic fascia on the pelvic floor covers both surfaces of the Levatores ani muscle. The layer covering the upper surface of the pelvic diaphragm follows, above, the line of origin of the Levator ani and is therefore somewhat variable.
What is the inferior layer of the urogenital diaphragm?
The inferior layer is known as the anal fascia. It is attached above to the obturator fascia along the line of origin of the Levator ani, while below it is continuous with the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, and with the fascia on the Sphincter ani internus .
Which layer of the pelvic organ is known as the vesical layer?
The fascia which covers pelvic organs can be divided according to the organs that are covered: The front is known as the "vesical layer". It forms the anterior and lateral ligaments of the bladder.
Where is the symphysis attached to the pubic symphysis?
In front it is attached to the back of the pubic symphysis about 2 cm above its lower border. It can then be traced laterally across the back of the superior ramus of the pubis for a distance of about 1.25 cm, when it reaches the obturator fascia .
