How to calculate equilibrium price.?
Calculating the equilibrium price becomes simple when you know the supply function, demand function, and equilibrium price formula. The linear supply function is-Qs = x + yP, where Qs= supplied quantity, x= quantity, P= price. The demand function is-Qd = x + yP, where Qd= demanded quantity, x= quantity, P= price. Finally, the equilibrium price formula is-Qs = Qd
How to find the equilibrium price and quantity algebraically?
So the steps are:
- Get functions solved for Qs (quantity supplied) and Qd (quantity demanded).
- Set Qs equal to Qd
- Solve for P (equilibrium price)
- Plug your P back into your Qs and Qd functions to get equilibrium quantity
Which factor determines the equilibrium price?
- Introduction. Price is dependent on the interaction between demand and supply components of a market. ...
- Equilibrium price. When a product exchange occurs, the agreed upon price is called an equilibrium price, or a market clearing price.
- Price stability. ...
- Price level. ...
- Summary. ...
What is the price at which equilibrium is achieved?
The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agree—that is, where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy (quantity demanded) is equal to the amount producers want to sell (quantity supplied). This mutually desired amount is called the equilibrium quantity.

What is the equilibrium quantity?
3 days agoEquilibrium quantity is when there is no shortage or surplus of a product in the market. Supply and demand intersect, meaning the amount of an item that consumers want to buy is equal to the amount being supplied by its producers.
What is equilibrium price and quantity graph?
On a graph, the intersection of the demand and supply curves shows the equilibrium price. Any price above or below this price creates a surplus or shortage respectively. It's formula is Sq=Dq or quantity supplied=quantity demanded.
How do you find the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity?
Here is how to find the equilibrium price of a product:Use the supply function for quantity. You use the supply formula, Qs = x + yP, to find the supply line algebraically or on a graph. ... Use the demand function for quantity. ... Set the two quantities equal in terms of price. ... Solve for the equilibrium price.
What is meant by equilibrium price?
An equilibrium price, also known as a market-clearing price, is the consumer cost assigned to some product or service such that supply and demand are equal, or close to equal. The manufacturer or vendor can sell all the units they want to move and the customer can access all the units they want to buy.
What is equilibrium price formula?
The equilibrium price formula is based on demand and supply quantities; you will set quantity demanded (Qd) equal to quantity supplied (Qs) and solve for the price (P). This is an example of the equation: Qd = 100 - 5P = Qs = -125 + 20P.
How do you find equilibrium quantity?
How to calculate equilibrium quantity? It can be calculated by solving the demand and supply function (Qa – bP = x + yP). Solving the equation when the supply equals the demand gives an equilibrium price. Input the equilibrium price in the demand or supply function to determine the quantity.
What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when demand increases?
An increase in demand, all other things unchanged, will cause the equilibrium price to rise; quantity supplied will increase. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity supplied will decrease.
What is Qd and Qs?
At this price level, market is in equilibrium. Quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded ( Qs = Qd). Market is clear. If the market price (P) is higher than $6 (where Qd = Qs), for example, P=8, Qs=30, and Qd=10. Since Qs>Qd, there are excess quantity supplied in the market, the market is not clear.
How do you show equilibrium on a graph?
MARKETS: Equilibrium is achieved at the price at which quantities demanded and supplied are equal. We can represent a market in equilibrium in a graph by showing the combined price and quantity at which the supply and demand curves intersect.
How do you read equilibrium graphs?
1) At equilibrium the rates of the forward and backward reactions are equal. Remember, it is a dynamic equilibrium. Hence the rates graph should indicate that both the forward and backward rates are equal. A typical reaction rates graph when a system is at equilibrium is shown on the right at t1.
How do you create an equilibrium graph?
0:002:47How to create an Equilibrium Graph - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo what we're gonna do is we're gonna highlight three columns then we're gonna go into insert chartMoreSo what we're gonna do is we're gonna highlight three columns then we're gonna go into insert chart the chart we're gonna use for this one is going to be scatter.
How does equilibrium price and quantity change?
A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity supplied will decrease. An increase in supply, all other things unchanged, will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity demanded will increase. A decrease in supply will cause the equilibrium price to rise; quantity demanded will decrease.
1. What is the difference between Demand and Supply?
The difference between demand and supply is as follows:The equilibrium between the quantity and price for goods at a particular time is called dema...
2. What are the factors affecting Demand and Supply?
These are the following factors which affect demand and supply:Price of the goods: If the price rises then, the demand decreases. In this way, the...
3. How did the Equilibrium Theory originate?
The balance in the supply and demand levels that are competing in different markets ultimately create a price equilibrium, this phenomenon is known...
4. Do the Supply and Demand affect the Equilibrium Price?
Yes, they do. This can happen due to these certain situations:There is an upward shift, the demand stays stable, whereas the price increases, and a...
5. Do the consumers and producers agree on an equilibrium price?
Yes, the equilibrium price is the only price in the market where both, the plans of the producers and the plans of the consumers agree on. This mea...
6. Does a Supply Shock affect the Equilibrium Price and Quantity?
Yes, a supply shock does affect the equilibrium price and quantity, sometimes positively and sometimes negatively.A supply shock is an event that i...
7. Can I find more concepts related to Economics on Vedantu?
At Vedantu, we provide the students with all the important concepts in the subject of Economics that are needed to be studied by them to ace their...
How to find Equilibrium Price?
A market reaches its equilibrium when the demand equals the supply, which is when the demand and supply curve intersect in the equilibrium price graph.
When the quantity of supply of goods matches the demand for goods, it is called the equilibrium price?
When the quantity of supply of goods matches the demand for goods, it is called the equilibrium price . The market is said to be in a state of equilibrium when the main experience is in the phase of consolidation or oblique momentum. Then, it can be concluded that demand and supply are comparatively equal. Equilibrium price examples are discussed below as well.
How do supply and demand affect Equilibrium Price?
With the upward shift, the supply decreases, the equilibrium price increases and demand stays stable. With the downward change in supply, the supply increases and the equilibrium price falls.
What is the difference between supply and demand?
Ans: The difference between demand and supply is as follows: The equilibrium between the quantity and price for goods at a particular time is called demand. Conversely, the equilibrium between the amount and value of commodities is supply. The curve of demand slopes downward and the curve of supply is upward sloping.
Why do prices go down?
Generally, the reason for prices to go down is an oversupply of goods or services, resulting in higher demand for goods or services. Equilibrium price definition explains the state of equilibrium is the result of the balancing effect of demand and supply. The equilibrium price is showing through the intersection of the demand ...
Who developed the equilibrium theory?
The equilibrium theory was introduced and developed by a French economist, Leon Walras, in the late 19th century. Walras used this theory to multi-market settings by bringing in another good into his model, which then helped him to calculate price ratios.
What are the factors that affect demand and supply?
Ans: These are the following factors which affect demand and supply: Price of the goods: If the price rises then, the demand decreases. In this way, the supply increases, and demand decreases. If prices fall then demand increases automatically.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity of a commodity demanded and supplied are equal. It is the price at which there is neither a surplus nor a shortage of the commodity in the market.
Solution
From the graph above, it can be seen that at ₦15, sixty cartons of Indomie were demanded and sixty cartons of Indomie were equally supplied. ₦15 is the equilibrium price while sixty cartons of Indomie is the equilibrium quantity and the point of interaction between the supply curve and demand curve (E) is called the equilibrium point.
What is equilibrium quantity?
Equilibrium quantity refers to the point of balance in the marketplace where the supply of a given good perfectly matches the consumer demand for the good. Equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price are basic concepts within the overall macroeconomic theories of supply and demand, free markets, and capitalism.
How to understand equilibrium quantity?
To understand the concept of equilibrium quantity, one needs to understand the basics of how supply and demand interact and affect the price of available goods. The economic theory of capitalism holds that when markets can operate freely, the forces of supply and demand will naturally interact in such a way to produce market efficiency.
What is the point at which supply and demand levels meet?
The point at which supply and demand levels meet, or intersect, is the point of both equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. The equilibrium price is considered the optimal price, as it is the price level at which neither consumers nor suppliers enjoy an advantage or suffer a disadvantage relative to the other.
What is supply and demand?
Supply and Demand The laws of supply and demand are microeconomic concepts that state that in efficient markets, the quantity supplied of a good and quantity. , marketplace operations, and market efficiency. The concept of equilibrium quantity is a theoretical construct more so than a practical marketplace reality.
Why is equilibrium quantity important?
The concept of equilibrium quantity is a theoretical construct more so than a practical marketplace reality. It is unlikely that there is ever a point in time or a marketplace price point at which supply and demand precisely match up and are exactly equal. Nonetheless, the concept is useful for understanding how the forces of supply and demand interact and how markets function to create efficient pricing of goods.
What is aggregate supply and demand?
Aggregate Supply and Demand Aggregate supply and demand refers to the concept of supply and demand but applied at a macroeconomic scale. Aggregate supply and aggregate
What does it mean when a market is free?
What does it mean in practical terms? It means that in free markets, increased demand over available supply will drive prices higher, while increased supply over current demand levels will drive prices lower. The tendency will be to move toward equilibrium quantity, where supplies provided by manufacturers and retailers approximately match the quantity of a good that is demanded by consumers.
What is equilibrium quantity?
Equilibrium quantity is when there is no shortage or surplus of a product in the market. Supply and demand intersect, meaning the amount of an item that consumers want to buy is equal to the amount being supplied by its producers. In other words, the market has reached a perfect state of balance as prices stabilize to suit all parties.
What is supply and demand?
Supply and demand theory underpins most economic analysis, but economists caution against taking it too literally. A supply and demand chart only represents, in a vacuum, the market for one good or service. In reality, there are always many other factors influencing decisions such as logistical limitations, purchasing power, ...
What is the basic theory of microeconomics?
Basic microeconomic theory provides a model to determine the optimal quantity and price of a good or service. This theory is based on the supply and demand model, which is the fundamental basis for market capitalism. It assumes that producers and consumers behave predictably and consistently and there are no other factors influencing their decisions.
Why does the demand curve slope downwards?
Meanwhile, the demand curve , representing buyers, slopes downwards. This is because there is an inverse relationship between the price and quantity demanded. Consumers are more willing to purchase goods if they are inexpensive; therefore, as the price increases, the quantity demanded decreases.
What happens at the intersection of supply and demand curves?
Since the intersection occurs at a point on both the supply and demand curves, producing/buying the equilibrium quantity of a good or service at the equilibrium price should be agreeable to both producers and consumers. Hypothetically, this is the most efficient state the market can reach and the state to which it naturally gravitates.
Why does the supply curve slope upwards?
If looking from left to right, the supply curve slopes upwards. This is because there is a direct relationship between price and supply. The producer has a greater incentive to supply an item if the price is higher. Therefore, as the price of a product increases, so does the quantity supplied.
What are the factors that influence market decisions?
In reality, there are always many other factors influencing decisions such as logistical limitations, purchasing power, and technological changes or other industry developments . The theory does not account for potential externalities, which can result in market failure.
What happens when the price is below the equilibrium intersection point?
If the price is below this equilibrium intersection point, a shortage results. If the price is above the point, a surplus results.
What happens if the price is set at $7?
In the graph above, the market is at equilibrium at a price of $11 and a quantity of 9. If the price were set at $7, a shortage of 7 products results. At $7 the quantity demanded is 13 (from $7 go straight over to the demand curve) and the quantity supplied is 6 (from $7 go straight over to the supply curve). Similarly, if the price were set at $14, a surplus of 5 units (11 minus 6) results.
What are the consequences of the price ceiling?
In addition to the shortage, there are other consequences of the government’s price ceiling. Because of the increased quantity demanded landlords have less incentive and because of the lower rent they have less rental income to maintain the rental properties. This usually leads to a deterioration of the rental units. Due to the shortage of rental units in the inner city, the demand for properties not subject to rent controls increases. This increases the price of non-rent-controlled properties.
What would happen if the minimum wage was increased to $6.50?
If in another state the equilibrium (market) wage is $4.50 per hour, and the state government increases the minimum wage to $6.50 per hour, then businesses are required to pay many workers more per hour compared to what they were paying at the market wage. This will increase the incomes of workers who are able to keep their jobs. And it will lead to unemployment of workers (especially full-time workers), because the higher wage decreases the quantity demanded of labor and increases the quantity supplied.
What happens to equilibrium price when demand increases?
Both the increase in demand and the decrease in supply raise the price, so the equilibrium price rises.
How does the increase in demand affect the equilibrium price?
The increase in the demand raises the equilibrium price and the decrease in supply raises the price further .
How many boxes are there in a week at equilibrium price?
At the equilibrium price, the shortage is eliminated, and the equilibrium quantity is 1,400 boxes a week.
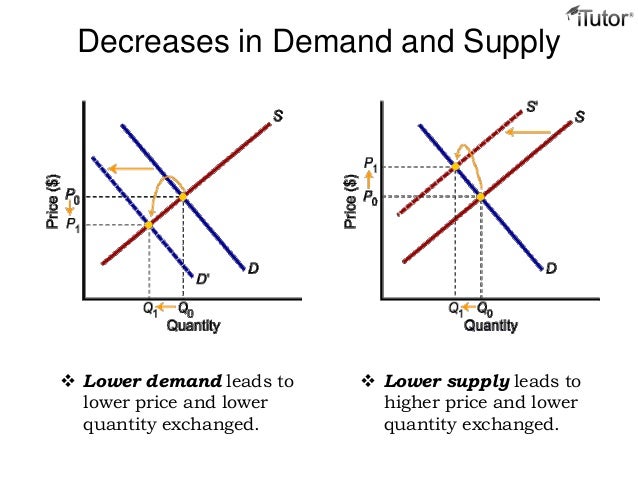
When demand decreases and supply decreases, the equilibrium quantity of theater tickets decreases?
When demand decreases and supply decreases, the equilibrium quantity of theater tickets decreases and the equilibrium price of a theater ticket rises, falls, or remains the same.
What is the new demand curve?
The new demand curve is left of the original demand curvelong dash—a decrease in demand. And the change in the quantity supplied is a decrease, shown by a movement along the supply curve from the original equilibrium point 1 to the new equilibrium point 2.
What is productivity in economics?
Productivity is output per unit of input. An increase in productivity lowers costs and increases supply. Technological change increases productivity and increases supply. A decrease in productivity has the opposite effect and decreases supply.
Does demand change along the demand curve?
There is no movement along the demand curve. The quantity of steel demanded does not change.