Glossary of microbiology terms Meaning and definition of etiology : etiology The study of the cause of a disease. For the term etiology may also exist other definitions and meanings, the meaning and definition indicated above are indicative not be used for medical and legal or special purposes.
What is the meaning of etiology?
eti·ol·o·gy | \ˌē-tē-ˈä-lə-jē \. plural etiologies. 1 : cause, origin specifically : the cause of a disease or abnormal condition. 2 : a branch of knowledge concerned with causes specifically : a branch of medical science concerned with the causes and origins of diseases.
What is the etiology of a bacterial infection?
Lesson Summary. Bacterial infections are caused when pathogenic bacteria invade a human host. When a bacterial infection is suspected, the etiology, or cause of the infection must be established. Doctors take a sample of the bacteria and culture it, using growth conditions, dyes, and morphology to determine the identity of the bacteria.
What is the difference between epidemiology and etiology?
When comparing and contrasting between epidemiology vs etiology, know that epidemiology refers to how diseases are spread and controlled, as well as other factors. Etiology simply desires to find the causes of diseases. Both of these scientific studies are important regarding learning about how diseases can affect human beings.
What is bacterial pathology?
Bacterial Pathology. Pathology is the study of causes and effects of a disease on the body. In bacterial infections, pathology focuses on how bacteria make us sick and what damage occurs in the body.

What does etiology mean in microbiology?
the study of the cause or origin of disease.
What is etiology with example?
When a cause of a disease is determined, this is called its etiology. For example, the etiology of cholera is known to be a bacterium that contaminates food and drinking water in places with poor sanitation.
What do u mean by etiology?
Etiology (pronounced /iːtiˈɒlədʒi/; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination.
What is etiology vs epidemiology?
The term “etiology” means the science of causes; from a scientific perspective, all diseases must have causes. A cause is something that produces an effect; in epidemiology it is customary to distinguish necessary cause, sufficient cause, proximal cause, and distal cause.
What is etiology of a disease?
Etiology describes the cause or causes of a disease.
What are etiological factors?
We define environmental etiological factors as non-genetic factors that have been associated with the disease from an "etiological" point of view in MEDLINE. As a result, diseases that are predisposing factors to other diseases are included.
What is the difference between etiology and pathogen?
The terms “etiology” and “pathogenesis” are closely related to the questions of why and how a certain disease or disorder develops. Models of etiology and pathogenesis therefore try to account for the processes that initiate (etiology) and maintain (pathogenesis) a certain disorder or disease.
What does etiology unknown mean?
'Unknown' is meant to be viewed neutrally and to designate that the nature of the underlying cause of the epilepsy is as yet unknown; it may have a fundamental genetic defect at its core or there may be a separate as yet unrecognized disorder.
What is the concept of etiology in modern science?
Etiology in medicine is defined as the determination of a cause of disease or pathology. Its influence on the development of civilization can be traced back to several impressive findings, ranging from the germ theory of pathology to the modern understanding of the source of diseases and their control.
What is etiology and pathology?
Pathology is that field of science and medicine concerned with the study of diseases, specifically their initial causes (etiologies), their step-wise progressions (pathogenesis), and their effects on normal structure and function.
Does etiology include risk factors?
In etiological studies, the ultimate goal of identifying risk factors is either to cure the patient, to prevent the occurrence of an outcome, or to prevent disease progression by preventing or intervening on these risk factors. This kind of research typically addresses the aetiology—or cause—of the outcome.
What is social etiology?
In the social etiology model, people with disorders other than the one particular disorder singled out for investigation are implicitly classified as "well." This disorder-specific model is inappropriate for the more general sociological task of identifying the consequences of various social arrangements, such as ...
What is etiology the study of?
Etiology in medicine is defined as the determination of a cause of disease or pathology. Its influence on the development of civilization can be traced back to several impressive findings, ranging from the germ theory of pathology to the modern understanding of the source of diseases and their control.
What is the difference between etiology and pathogenesis?
The terms “etiology” and “pathogenesis” are closely related to the questions of why and how a certain disease or disorder develops. Models of etiology and pathogenesis therefore try to account for the processes that initiate (etiology) and maintain (pathogenesis) a certain disorder or disease.
What is etiology in psychology?
n. 1. the causes and progress of a disease or disorder. 2. the branch of medical and psychological science concerned with the systematic study of the causes of physical and mental disorders.
What does etiology unknown mean?
'Unknown' is meant to be viewed neutrally and to designate that the nature of the underlying cause of the epilepsy is as yet unknown; it may have a fundamental genetic defect at its core or there may be a separate as yet unrecognized disorder.
What is Etiology?
When the questions "What is etiology ?" or "What does etiology mean?" are posed, the answer is "the cause of something in particular." When specifically asked, "What is the etiology of disease ?" the answer one is looking for is "What is the cause of disease?" The definition of etiology, when pertaining to the biological sciences or medicine, is the study of the cause of disease..
Epidemiology vs. Etiology
When comparing and contrasting between epidemiology vs etiology, know that epidemiology refers to how diseases are spread and controlled, as well as other factors. Etiology simply desires to find the causes of diseases. Both of these scientific studies are important regarding learning about how diseases can affect human beings.
Categories of a Disease's Etiology
There are three main types of disease etiologies that will be expounded upon in this lesson. These categories of disease etiologies are intrinsic etiology, extrinsic etiology, and idiopathic etiology.
Etiology of Disease
The etiology of disease examines possible causes for the development of a particular disease. These causes can be intrinsic, extrinsic or Idiopathic. The questions below will help you gain a better understanding using specific examples. Read the scenarios below and do your best to answer the questions.
What is the medical definition of etiology?
Medical Definition of etiology. 1 : the cause or causes of a disease or abnormal condition some types of cancer have a viral etiology a multiple etiology in which biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors all play a role — M. E. Jackson et al.
What is viral etiology?
1 : the cause or causes of a disease or abnormal condition some types of cancer have a viral etiology a multiple etiology in which biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors all play a role — M. E. Jackson et al. 2 : a branch of medical science dealing with the causes and origin of diseases.
What does "cause" mean in medical terms?
1 : cause, origin specifically : the cause of a disease or abnormal condition. 2 : a branch of knowledge concerned with causes specifically : a branch of medical science concerned with the causes and origins of diseases.
What Is a Bacterial Infection?
Pathogens are organisms that cause an infection. Sometimes pathogens are viruses, like what causes the flu or a cold. Bacterial infections are caused by pathogenic bacteria. Not all bacteria cause infections, but some can be very dangerous to humans. Today, we're going to look at how to distinguish the etiology, pathology and pathogenesis of different examples of bacterial infections.
What is the process of bacteria infecting a human host?
Doctors take a sample of the bacteria and culture it, using growth conditions, dyes, and morphology to determine the identity of the bacteria. Pathogenesis is the steps a bacteria takes to infect a host and pathology is the resulting effects on the body, such as changes in intestinal structure or cell death in E.coli O157:H7 poisoning.
How to identify Streptococcus pyogenes?
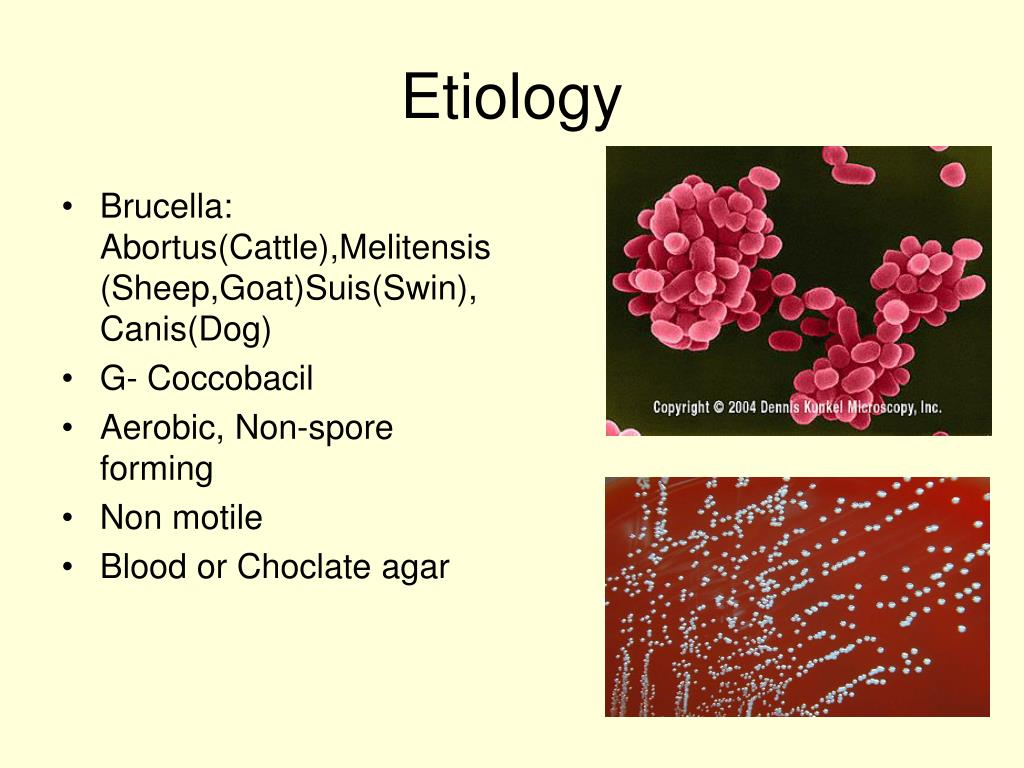
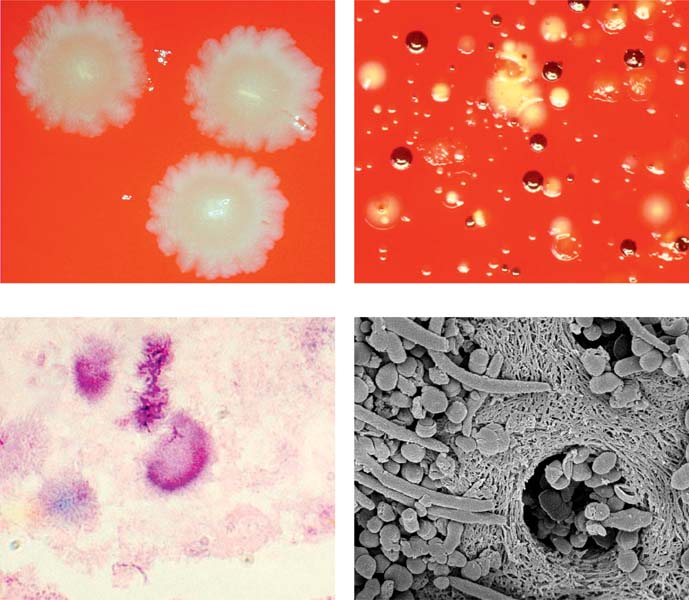
Using a sample provided by the doctor from the patient's throat, you grow the bacteria and look for characteristics of Streptococcus pyogenes. Different types of stains, or dyes can differentiate between types of bacteria. Also, different growth conditions and morphology of bacteria can be used to establish etiology. Streptococcus pyogenes is known for it's hemolytic activity on blood agar plates.
What is the hemolytic activity of Streptococcus pyogenes?
Streptococcus pyogenes is known for it's hemolytic activity on blood agar plates . Samples from a sore throat are cultured on blood agar to determine if Streptococcus pyogenes is the infective agent.
What is the cause of a red throat?
Her throat is red, with inflamed tonsils and white spots of pus. These symptoms indicate a possible infection of Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria that causes 'strep throat'. However, identifying symptoms isn't enough to establish etiology of the infection, or the cause.
How does Clostridium enter the body?
Once inside the body, the toxin circulates through the blood to the neuromuscular junction, where neurons attach to muscles to tell them to contract or relax. Presence of Clostridium bacteria in the blood indicates a more advanced infection.
What is the difference between pathogens and bacteria?
Pathogens are organisms that cause an infection. Sometimes pathogens are viruses, like what causes the flu or a cold. Bacterial infections are caused by pathogenic bacteria. Not all bacteria cause infections, but some can be very dangerous to humans. Today, we're going to look at how to distinguish the etiology, ...
What Is Etiology?
Etiology in medicine is defined as the determination of a cause of disease or pathology. Its influence on the development of civilization can be traced back to several impressive findings, ranging from the germ theory of pathology to the modern understanding of the source of diseases and their control.
What is intrinsic etiology?
Intrinsic — coming from within. Extrinsic — originating from external factors. Idiopathic — cause unknown. Etiology is not only disease specific but also person specific. While a particular cause may lead to a disease manifesting in an individual, a similar set of factors could lead to a different illness being manifested in another individual.
What do nurses need to know about disease?
Nurses are on the front line of disease outbreaks, so they need to understand the basics of epidemiology and etiology and apply them where necessary. The journal Family Practice explores the idea of primary care epidemiology, including prevention, diagnosis, and etiology of a disease as a significant benefit to all physicians having to deal with the outbreak. Nurses may be the first responders to a disease occurrence, and determining the etiology of the disease and its method of containment as fast as possible can be crucial to avoid its spread.
What is advanced research methods for EBP?
Advanced Research Methods for EBP I — the implementation of evidence-based practice and how it applies to using factual information to determine etiology and epidemiology of an outbreak
What is epidemiology in health?
According to the World Health Organization, epidemiology is the study of the spread of disease and factors affecting states of health. Generally, epidemiology doesn’t just focus on illness; it primarily studies wellness and how to maintain it. In essence, it can be considered the basic science of public health.
When was epidemiology first used?
In essence, it can be considered the basic science of public health. Epidemiology was initially coined in the mid-19th century to refer to the study of epidemics. Today, it’s applied to all factors affecting the health and wellness of a particular demographic.
Is etiology the same as epidemiology?
Etiology and epidemiology cover similar approaches to the study of diseases, but they’re distinct medical terms that shouldn’t be used interchangeably. While both fields offer valuable insight into diseases and the maintenance of health, each has an area of focus. Understanding the differences between etiology vs. epidemiology and how each is applied can help shape how a nursing student deals with real-world scenarios.
Which bacteria are most common in aerobic bacteria?
Escherichia coli, Klebsiella and Streptococcus faecalis dominate among aerobic bacteria, whereas Bacteroides fragilis and clostridia are commonly encountered anaerobes. Mixed infections are prevalent. Bactibilia occurs in at least 60% of the early stage of acute cholecystitis and is particularly prevalent in the elderly.
How long should you take antimicrobial prophylaxis?
Prophylactic courses should not exceed one or two days, one single preoperative dose is probably adequate.
Is cholecystitis a microbiological disease?
Cholecystitis--etiology and treatment--microbiological aspects. Acute cholecystitis is initially a chemical inflammation, but regularly complicated by bacterial invasion from the gut. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella and Streptococcus faecalis dominate among aerobic bacteria, whereas Bacteroides fragilis and clostridia are commonly encountered ...
What is the etiology of an illness?
In medicine, the etiology of an illness or condition refers to the frequent studies to determine one or more factors that come together to cause the illness. Relatedly, when disease is widespread, epidemiological studies investigate what associated factors, such as location, sex, exposure to chemicals, and many others, ...
What is the study of the causes, origins, or reasons behind the way that things are, or the way they?
More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins, or reasons behind the way that things are, or the way they function, or it can refer to the causes themselves. The word is commonly used in medicine (pertaining to causes of disease) and in philosophy, but also in physics, psychology, government, geography, spatial analysis, theology, ...
What is a disease where the cells of the body grow out of control?
Neoplastic disorders or cancer where the cells of the body grow out of control.
What is the origin of myth?
Thus, an etiological myth, or origin myth, is a myth that has arisen, been told over time or written to explain the origins of various social or natural phenomena. For example, Virgil 's Aeneid is a national myth written to explain and glorify the origins of the Roman Empire. In theology, many religions have creation myths explaining the origins of the world or its relationship to believers.