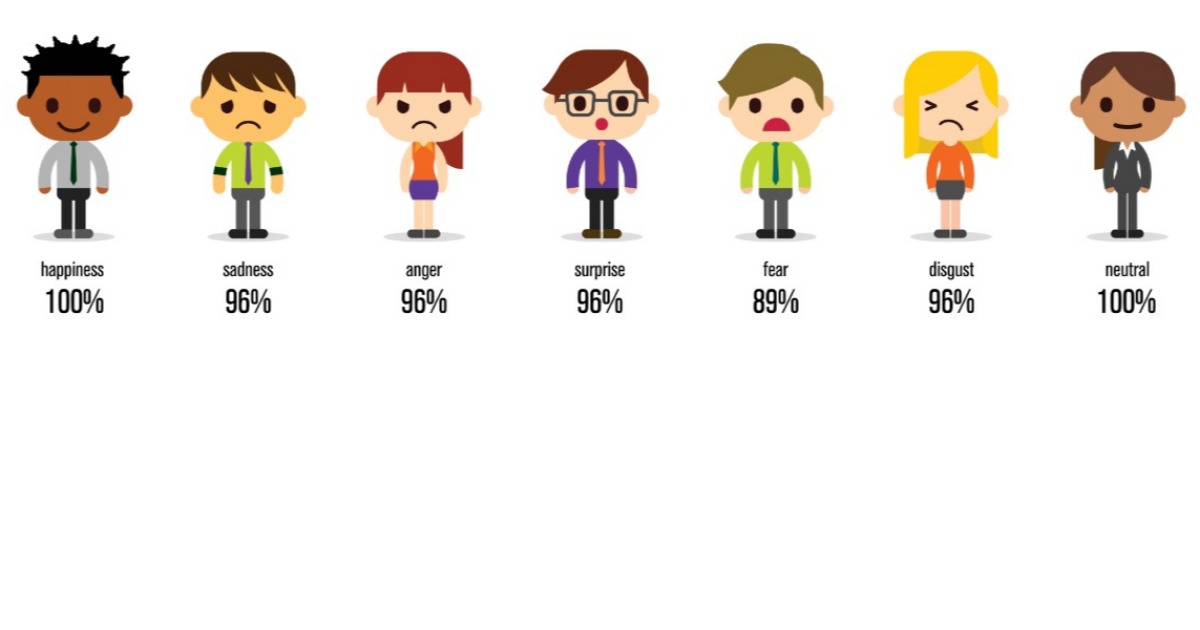
What are the six basic facial expressions?
- Anger + Anticipation = Aggressiveness
- Anticipation + Joy = Optimism
- Joy + Trust = Love
- Trust + Fear = Submission
What are some examples of facial expressions?
Just a few examples of emotions that can be expressed via facial expressions include:
- Happiness
- Sadness
- Anger
- Surprise
- Disgust
- Fear
- Confusion
- Excitement
- Desire
- Contempt
How to understand body language and facial expressions?
When evaluating body language, pay attention to the following mouth and lip signals:
- Pursed lips. Tightening the lips might be an indicator of distaste, disapproval, or distrust.
- Lip biting. People sometimes bite their lips when they are worried, anxious, or stressed.
- Covering the mouth. When people want to hide an emotional reaction, they might cover their mouths in order to avoid displaying smiles or smirks.
- Turned up or down. ...
What are the 7 universal emotions?
What are the Basic Emotions?
- Universal, underlying psychological triggers or antecedents
- Unique physiological signatures
- Pan-cultural cognitive gating
- Cross-cultural feelings and experiences
- Universal nonverbal expressions in the face, voice and body.
What is the meaning of facial expression?
A facial expression is one or more motions or positions of the muscles beneath the skin of the face. According to one set of controversial theories, these movements convey the emotional state of an individual to observers. Facial expressions are a form of nonverbal communication.
What are the 4 main facial expressions?
These seven are: Happiness, Sadness, Fear, Disgust, Anger, Contempt and Surprise.
What are the different types of facial expression?
Past research on facial expressions of emotion has focused on the study of six basic categories—happiness, surprise, anger, sadness, fear, and disgust.
What are the 7 main facial expressions?
Facial expressions that give clues to a person's mood, including happiness, surprise, contempt, sadness, fear, disgust, and anger.
Why is facial expression important?
Facial expressions of emotion are probably the most important signal of the face because they tell us about people's personalities, emotions, motivations, or intent. They are not only signs of people's internal states; they are also signals to others to act in certain ways, providing messages for social coordination.
What is an example of facial expression?
Facial expressions are also among the most universal forms of body language. The expressions used to convey fear, anger, sadness, and happiness are similar throughout the world.
What are the elements of facial expression?
Thus there is strong evidence for the universal facial expressions of seven emotions – anger, contempt, disgust, fear, joy, sadness, and surprise (see Figure 1). Figure 1: The Seven Basic Emotions and their Universal Expressions.
What is another word for facial expression?
1. expressionface.visage.twinkle.spark.countenance.light.aspect.sparkle.More items...
What are the six main facial expressions?
Basic facial expressions of emotion are universal; Ekman and Friesen [13] reported that six (anger, happiness, fear, surprise, disgust and sadness) are readily recognized across very different cultures.
How do you identify facial expressions?
Look out for:A dropped jaw (which signals surprise)Open mouth (showing fear)One side of the mouth raised (which could indicate hate or contempt)Raised corners (meaning happiness)Corners that are drawn down (conveying sadness)
What are 21 facial expressions?
Here is the full list of emotional states identified by the scientists from facial expressions: Happy, Sad, Fearful, Angry, Surprised, Disgusted, Happily Surprised, Happily Disgusted, Sadly Fearful, Sadly Angry, Sadly Surprised, Sadly Disgusted, Fearfully Angry, Fearfully Surprised, Fearfully Disgusted, Angrily ...
What is a good facial expression?
Nodding while listening is the positive facial expression This people normally use when the speaker is speaking about something which the listener does not like. Nodding while listening: The speaker feels good and speaks more only if the listener nodes the head.
What are the 6 facial expressions?
Basic facial expressions of emotion are universal; Ekman and Friesen [13] reported that six (anger, happiness, fear, surprise, disgust and sadness) are readily recognized across very different cultures.
What are the 8 facial expressions?
In our work, we mainly focused on generating facial expression for eight emotions: happy, sad, fear, surprise, anger, disgust, irony, and determined.
What are the 9 facial expressions?
Example facial expressions for each of the nine emotion categories (from the top left corner per row: anger, disgust, fear, sadness, embarrassment, contempt, happiness, pride, surprise) and a neutral blank stare (last image bottom right corner) included in the study.
What are the six common facial expressions?
Psychological research has classfied six facial expressions which correspond to distinct universal emotions: disgust, sadness, happiness,fear,anger, surprise[Black,Yacoob,95]. It is interesting to note that four out of the six are negative emotions.
Why do we use facial expressions?
Facial expressions and gestures in communication with others play a huge role. They help to enhance, fully reveal feelings. With the help of facial expressions, we express emotions that we are not talking about. Our body is very insidious, we may not notice how we say one thing, and body language shows something completely different.
When interrogating a suspect or witness, a specialist can track certain facial characteristics, by which it is answer?
When interrogating a suspect or witness, a specialist can track certain facial characteristics, by which it is easy to calculate whether a person is lying or telling the truth. Our body will not let itself be deceived. A person can, without suspecting it, betray himself through gestures and facial expressions.
What is the dictionary of symbolic psychoanatomy?
The Dictionary of Symbolic Psychoanatomy is a kind of deciphering of sign language. Based on it, you can find out what certain gestures mean in the current situation. This section is considered purely on specific examples since, in different situations, the same gesture can be interpreted in different ways. The ergonomics of facial expressions and gestures is a section that describes the ability to adapt body language to specific tasks. For example, to influence the human psyche with the help of positive beliefs transmitted through gestures.
What is a gesture refrain?
A gesture refrain is a repetitive gesture that always has the same meaning.
What does it mean to understand a topic?
A person who understands the topic will be able to personally show and explain how everything works and how to apply the knowledge gained in life.
Is facial expressions a good topic to study?
The psychology of facial expressions and gestures is not an easy topic to study and master. But how interesting and exciting it is! Just think, interpreting simple elements of behavior helps to literally read a person like a book. This is a very valuable ability.
Is facial expression intertwined?
Facial expressions and gestures are very strongly intertwined with each other, so they are always considered in one bundle.
Why do people use embarrassment facial expressions?
The appeasement hypothesis states that when an individual violates a social norm , this elicits anger in group members. By displaying the embarrassment facial expression after violating a norm, people acknowledge that they are aware of their violation and exhibit submission to maintain the social order. Yet, Keltner acknowledged the DFA task is one unique situation that elicited embarrassment and that some of the touching displays could be due to the physiological attachments and not really to embarrassment.
What are the three facial expressions that represent guilt?
To test for a unique guilt facial expression, researchers displayed facial expressions of self-contempt, sympathy, and pain. Keltner and colleagues believed these three facial expressions could represent guilt. Why? Well self-contempt could be similar to anger toward the self for committing a violation. After harming another person, we may feel sympathy toward that person (i.e., care, concern, feel bad for them). Finally, pain is a subjective feeling often reported with guilt and shame experiences (Tangney et al., 1996).
Which facial change lasts the longest?
The duration of each facial change is from the left edge of the photograph to the end of the arrow. Thus, downward gaze is the facial change that last the longest, followed by head away. It is interesting to note that the embarrassment facial expression comprises several facial changes over a period of six seconds.
Does embarrassment affect facial expressions?
Overall these studies provide some initial evidence of embarrassment facial changes, including averting gaze, shifting gaze, head down, and touching the face. More recent evidence by Widen et al. (2011) suggests the recognition rates for shame and embarrassment might be inflated due to the forced choice method used in past research. In fact, Russell found participants did not do a great job at correctly free labeling shame and embarrassment. So, this might suggest that shame and embarrassment are not basic emotions. This could also mean that because the embarrassment facial expressions change over a short period of time, identifying the emotion in still photos could be more difficult. Unfortunately, we do not have much evidence on cross-cultural differences in facial expressions. Some of this new research will be discussed in the pride section here.
Why are facial expressions important?
Facial expressions, especially microexpressions, can be signs of these emotions and the ability to detect them may be important for individuals working in law enforcement, national security, intelligence, or the legal system.
How can facial expressions help people?
Findings concerning the universality of facial expressions of emotion and the existence of microexpressions can help people in a range of professions requiring face-to-face interactions improve their skills in reading the emotions of others. Reading facial expressions of emotion, and especially microexpressions, can aid the development of rapport, trust, and collegiality; they can be useful in making credibility assessments, evaluating truthfulness and detecting deception; and better information about emotional states provides the basis for better cooperation, negotiation, or sales. Health professionals can develop better rapport with patients, interact humanely with empathy and compassion, and make the right diagnosis by obtaining complete information. Teachers can read the emotions of their students to obtain cues about the progress of their lesson plans so they can adjust accordingly and deliver them more effectively. School administrators who read the emotions of their teachers can reduce burnout and maintain and improve teacher effectiveness. Businesspersons and negotiators who can read the emotions of others can nurture mutually beneficial collaborations. Product researchers can improve the qualitative data they obtain from consumers by reading consumer’s emotions when evaluating products, giving hints as to what they truly feel despite what they say about it. Parents, spouses, friends, and everyone with an interest in building strong and constructive relationships can benefit from improving their ability to read emotions.
What was Darwin's theory of facial expressions?
Early research testing Darwin’s ideas, however, was inconclusive (Ekman, Friesen, & Ellsworth, 1972), and the dominant perspective in psychology was that facial expressions were culture-specific – that is, just as every culture had its own verbal language, it had its own language of facial expressions. Darwin’s claims were resurrected by Tomkins ...
Why do microexpressions occur so fast?
They are so fast that if you blink you would miss them. Microexpressions are likely signs of concealed emotions. (They may also be signs of rapidly processed but unconcealed emotional states.) They occur so fast that most people cannot see or recognize them in real time.
What is the most important contribution to understanding emotion?
Arguably the most important contribution basic science has made to our understanding of emotion concerns the universality of facial expressions of emotion. Darwin (1872) was the first to suggest that they were universal; his ideas about emotions were a centerpiece of his theory of evolution, suggesting that emotions and their expressions were biologically innate and evolutionarily adaptive, and that similarities in them could be seen phylogenetically. Early research testing Darwin’s ideas, however, was inconclusive (Ekman, Friesen, & Ellsworth, 1972), and the dominant perspective in psychology was that facial expressions were culture-specific – that is, just as every culture had its own verbal language, it had its own language of facial expressions. Darwin’s claims were resurrected by Tomkins (1962, 1963), who suggested that emotion was the basis of human motivation and that the seat of emotion was in the face. Tomkins conducted the first study demonstrating that facial expressions were reliably associated with certain emotional states (Tomkins & McCarter, 1964).
How long do microexpressions last?
When single emotions occur and there is no reason for them to be modified or concealed, expressions typically last between 0.5 to 4 seconds and involve the entire face (Ekman, 2003).
What are the seven universal emotions?
Thus there is strong evidence for the universal facial expressions of seven emotions – anger, contempt, disgust, fear, joy, sadness, and surprise (see Figure 1). Figure 1: The Seven Basic Emotions and their Universal Expressions. Other bodies of evidence provide support for the biological and genetic sources of facial expressions of emotion.
Where do facial expressions originate?
Our facial expressions therefore often have origins within the primary motor region, which receives signals from the thalamus, and the supplementary motor cortex [10, 11]. This pathway can be elucidated further, but essentially leads to a wider and wider network of brain areas that can activate facial expressions at various stages.
How does facial expression analysis work?
The oldest of these three methods, facial electromyography (fEMG) involves recording the electrical activity from facial muscles.
How does affectiva work?
Software may then differ in how the images are processed, but Affectiva uses algorithms trained through deep learning to analyze these landmarks, and subsequently predict facial expressions.
Why is FACS important?
While the importance of FACS for the field of facial expression analysis is hard to overstate, the practical application of its methods is not without difficulty. To properly quantify facial expressions according to the FACS method, officially certified and trained FACS coders need to determine which muscles are moving, and the intensity of the movement. This means in practical terms that a video of an interaction must be viewed essentially frame-by-frame and processed – which can clearly take a lot of time.
What nerve innervates facial muscles?
Almost all facial muscles are innervated by a single nerve, the facial nerve, which is also known as cranial nerve VII. The facial nerve emerges from deep within the brainstem (the pons), leaves the skull slightly below the ear (the facial canal), and branches off to all the facial muscles [8]. The facial nerve is also wired up with the primary motor region of our neocortex, which controls all the muscle movements of our body (a representative image of how this is organised is shown below; [9]).
Why is understanding the emotional state of people important?
It’s clear that understanding the emotional state of people can be useful for a range of applications – from developing a better understanding of human psychology, to investigating behavior for improved user experiences, to developing productive advertising campaigns, and beyond.
How many muscles are there in the face?
Our face is an intricate, highly differentiated part of our body – in fact, it is one of the most complex signal systems available to us. It includes 43 structurally and functionally autonomous muscles, each of which can be triggered independently of each other [7].
Why is facial expression important?
The ability to understand facial expressions is an important part of nonverbal communication. If you only listen to what a person says and ignore what their face is telling you, then you really won't get the whole story. Often, words do not match emotions, and the face betrays what a person is actually feeling.
How many facial expressions are there?
Research by Dr. Paul Ekman tells us that there are seven universal facial expressions that we all use, even across cultural divides. These expressions show: 2
What does it mean when you have a hard time paying attention to facial expressions?
If you have social anxiety disorder (SAD), you might have a hard time paying attention to facial expressions. You might have trouble with eye contact or read too much into negative expressions on other people's faces.
Why do we look at our faces?
We look at the eyes to determine if someone is sad or angry, for example, and at the mouth to check if someone is happy. 7
Why do people use their mouths?
The mouth can convey more than just a smile. People often use their mouths to mask other emotions their face is conveying— for example, a forced smile might cover up an eye micro-expression showing someone's true feelings. 12
What does it mean when you look at micro expressions?
Micro-expressions are often connected with emotions that a person is trying to conceal, and looking at micro-expressions could reveal whether someone is being truthful or lying. 5
Can a person with SAD see negative facial expressions?
People with SAD often interpret facial expressions more negatively (even if they're neutral), and they may even avoid looking at negative facial expressions altogether. 1. Although it is important to pay attention to facial expressions, remember that knowing the emotion doesn't tell you the cause.
What is facial expression?
3 . Facial expressions are also among the most universal forms of body language. The expressions used to convey fear, anger, sadness, and happiness are similar throughout the world.
What is body language?
Body language refers to the nonverbal signals that we use to communicate. According to experts, these nonverbal signals make up a huge part of daily communication. From our facial expressions to our body movements, the things we don't say can still convey volumes of information. 1 .
What does a smile mean?
Think for a moment about how much a person is able to convey with just a facial expression. A smile can indicate approval or happiness. A frown can signal disapproval or unhappiness.
Why are eyes called windows to the soul?
The eyes are frequently referred to as the "windows to the soul" since they are capable of revealing a great deal about what a person is feeling or thinking. As you engage in conversation with another person, taking note of eye movements is a natural and important part of the communication process.
What are some of the most direct and obvious body language signals?
Gestures can be some of the most direct and obvious body language signals. Waving, pointing, and using the fingers to indicate numerical amounts are all very common and easy to understand gestures.
What does it mean when you chew on your lip?
For example, chewing on the bottom lip may indicate that the individual is experiencing feelings of worry, fear, or insecurity.
What do you notice when you look at someone's eyes?
Some common things you may notice include whether people are making direct eye contact or averting their gaze, how much they are blinking, or if their pupils are dilated . When evaluating body language, pay attention to the following eye signals.
