
What is fortification in history? A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis (“strong”) and facere (“to make”).
What does the term fortification mean?
fortification ( ˌfɔːtɪfɪˈkeɪʃən) n 1. the act, art, or science of fortifying or strengthening 2. (Fortifications) a. a wall, mound, etc, used to fortify a place b. such works collectively 3. (Fortifications) any place that can be militarily defended
What does fortifying mean?
To fortify is defined as to make something stronger. An example of to fortify is to add extra support to a building. To strengthen and secure (a position) with fortifications. To reinforce by adding material. To impart physical strength or endurance to; invigorate. To give emotional, moral, or mental strength to; encourage.
What does fortify mean?
fortify. ( ˈfɔːtɪˌfaɪ) vb ( mainly tr) , -fies, -fying or -fied. 1. (Fortifications) ( also intr) to make (a place) defensible, as by building walls, digging trenches, etc. 2. to strengthen physically, mentally, or morally. 3. to strengthen, support, or reinforce (a garment, structure, etc) 4.
What does fortified means?
fortified. ( ˈfɔːtɪˌfaɪd) adj. 1. (of a place) defensible, due to walls, trenches, etc. 2. strengthened physically, mentally, or morally. 3. (of a garment, structure, etc) strengthened, supported, or reinforced. 4. (of wine) having spirits or alcohol added in order to produce sherry, port, etc.
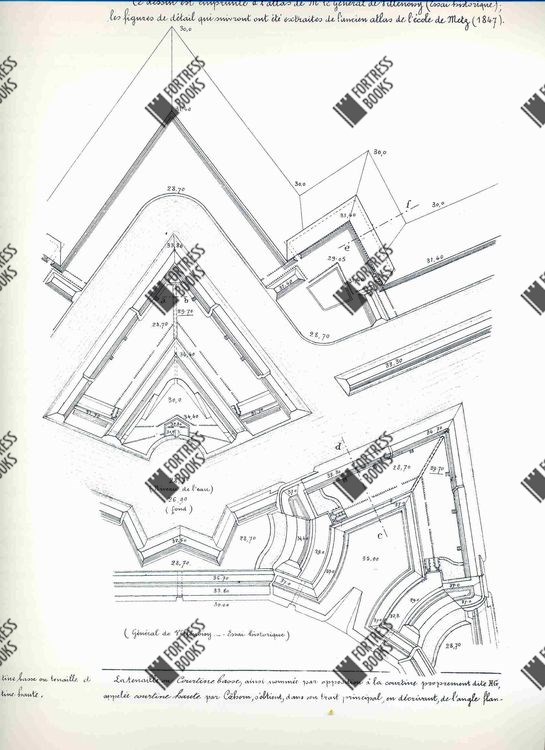
What does fortification mean in history?
A fortification is a strong wall, building, or other reinforced structure that's used to defend against attack. In medieval times, castle fortifications protected them from invading armies.
What was fortification in ww2?
The Maginot Line was fortified with reinforced concrete and 55 million tons of steel embedded deep into the earth. It was designed to withstand heavy artillery fire, poison gas and whatever else the Germans could throw against it.
What does fortified mean in war?
fortification, in military science, any work erected to strengthen a position against attack. Fortifications are usually of two types: permanent and field. Permanent fortifications include elaborate forts and troop shelters and are most often erected in times of peace or upon threat of war.
What are fortification used for?
Fortification is the practice of deliberately increasing the content of one or more micronutrients (i.e., vitamins and minerals) in a food or condiment to improve the nutritional quality of the food supply and provide a public health benefit with minimal risk to health.
How were fortifications used in the Civil war?
They served as observation points and a first line of defensive positions. Angle: Point where two faces of a fortification met. A reentrant angle pointed away from the enemy, a salient angle pointed toward the enemy.
What food was eaten in ww2?
meat (Mar 1940)jam (Mar 1941)biscuits ( Aug 1942),fishtea (Jul 1940)breakfast cereals,cheese (May 1941)eggs (June 1941)milk,tinned tomatoes (Feb. 1942)peas (Feb. 1942)dried fruit Jan 1942rice (Jan 1942)canned fruit,cooking fat (Jul 1940)
What fortification means?
1 : an act or process of fortifying. 2 : something that fortifies, defends, or strengthens especially : works erected to defend a place or position.
What fortified means?
for·ti·fied ˈfȯr-tə-ˌfīd. : made stronger or more secure. a fortified city. fortified bridges. : improved or enhanced through the addition of one or more ingredients: such as.
What is an example of fortification?
Fortified foods are those that have nutrients added to them that don't naturally occur in the food. These foods are meant to improve nutrition and add health benefits. For example, milk is often fortified with vitamin D, and calcium may be added to fruit juices.
What are the types of fortification?
Fortification is usually divided into two branches: permanent fortification and field fortification. There is also an intermediate branch known as semi-permanent fortification.
What are the effects of fortification?
In many cases, fortification targets restoring nutrients lost during processing, enhancing nutrients lost during processing, enhancing nutrient levels of food vehicles that have limited content than what is required, and adding nutrients not usually present in food to some commonly consumed food vehicles for the ...
What is the best fortification?
5 of the world's strongest fortifications everMasada, Israel. On a rocky plateau situated on a hill in southern Israel near the edge of the Judean desert, one can find the fortress of Masada. ... Great Wall of Gorgan, Parthian/Sassanid Empire. ... Hadrian's Wall, England/Scotland. ... Walls of Constantinople. ... Great Wall of China.
How did they preserve food in ww2?
Wartime canning and victory gardens were symbols of patriotism and heavily promoted by the government. Home canning during World War II offered families on the home-front a way to supplement their food supplies when rationing was in effect. As an import, sugar, a home canning staple, was among the rationed items.
What was the powder sprinkled on wounds in ww2?
If you watch a World War II movie like Band of Brothers, you'll see medics sprinkling a yellow powder on wounds—that's sulfa powder, or sulfanilimade. The ubiquitous bandage packs given to soldiers in the war years were coated in it.
What did they use bones for in ww2?
Bones were made into glue for airplane construction as well as being used in munitions. Housewives were asked to save the fat from the cooking of meat and fowl for the making of dynamite.
What were German and French trenches fortified with?
Trenches were longer, deeper, and better defended by steel, concrete, and barbed wire than ever before. They were far stronger and more effective than chains of forts, for they formed a continuous network, sometimes with four or five parallel lines linked by interfacings.