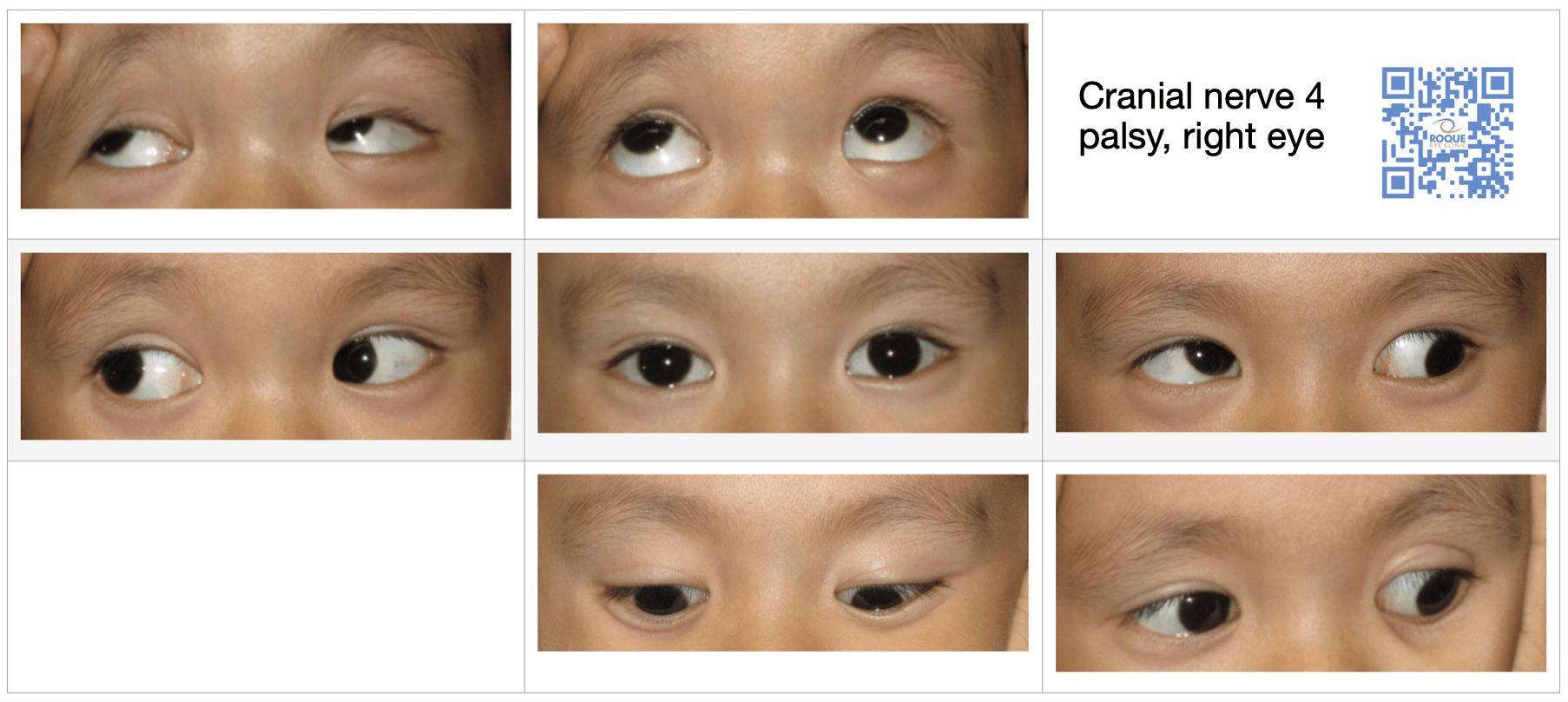
Fourth cranial nerve palsy impairs the superior oblique muscle, causing paresis of vertical gaze, mainly in adduction. (See also Overview of Neuro-ophthalmologic and Cranial Nerve Disorders.) Fourth cranial (trochlear) nerve palsy is often idiopathic. Few causes have been identified.
What is CN 6 palsy?
Sixth cranial nerve palsy is weakness of the nerve that innervates the lateral rectus muscle. The lateral rectus muscle rotates the eye away from the nose and when the lateral rectus muscle is weak, the eye crosses inward toward the nose ( esotropia ). The esotropia is larger when looking at a distant target and looking to same side as the affected lateral rectus muscle.
What are the 4 cranial nerves?
These Are the 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions The 12 Cranial Nerves I. Olfactory nerve II. Optic nerve III. Oculomotor nerve IV. Trochlear nerve V. Trigeminal nerve VI. Abducens nerve VII....
What is congenital 4th nerve palsy?
Fourth nerve palsy refers to a congenital defect or an acquired injury to the fourth cranial nerve, which is responsible for eye movement. When the nerve is damaged or malformed, the superior oblique muscle in the skull behind the eye cannot keep it aligned straight ahead. The affected eye tends to drift vertically, horizontally, or both from ...
What happens in third nerve palsy?
Third nerve palsy, also called oculomotor palsy, occurs when the third cranial nerve becomes injured or diseased. The third cranial nerve controls the actions of four external eye muscles. These muscles are responsible for turning the eye inward, moving the eye upward and downward, and rotating the eye downward and outward toward the ear.

What happens when cranial nerve 4 is damaged?
Effects of a Cranial Nerve 4 Palsy Inability to move the eye down and in toward the nose. Double vision (because the two eyes are not pointed in the same direction). This double vision is vertical and torsional (tilted) Tilting of the head to compensate for the double vision.
What are the symptoms of 4th nerve palsy?
Fourth nerve palsy generally affects only one eye, but it can affect both eyes as well. The most common symptoms of fourth nerve palsy include: Double vision (diplopia) when both eyes are open. Strabismus, or an eye turn that causes the affected eye to turn upward.
What does cranial nerve 4 palsy look like?
Fourth cranial nerve palsy may affect one or both eyes. Because the superior oblique muscle is paretic, the eyes do not adduct normally. Patients see double images, one above and slightly to the side of the other; thus, going down stairs, which requires looking down and inward, is difficult.
What is cranial nerve palsy symptoms?
Cranial nerve issues can affect a motor nerve, called cranial nerve palsy, or affect a sensory nerve, causing pain or diminished sensation. Individuals with a cranial nerve disorder may suffer from symptoms that include intense pain, vertigo, hearing loss, weakness or paralysis.
What is the treatment for 4th nerve palsy?
Eye muscle surgery is generally recommended as the treatment for fourth nerve palsy in children and adults. Following corrective eye muscle surgery for fourth nerve palsy, the associated abnormal head tilt usually disappears.
Will 4th nerve palsy go away?
Treatment of fourth nerve palsy depends on its cause. Idiopathic fourth nerve palsies tend to go away on their own. Palsies caused by injury can also get better with time. If something is pressing on the fourth cranial nerve, you may need surgery to ease the pressure.
Is 4th nerve palsy serious?
People with fourth nerve palsy often have one iris that is higher than the other, tilt their head, and have double vision. Some types of fourth nerve palsy may go away on their own. You may need surgery if the palsy does not go away.
Does 4th nerve palsy get worse with age?
A person may adapt an abnormal head position, usually tilting of the head to one side, which allows better alignment of the eyes and helps prevent double vision. The head tilt may get progressively worse with age.
How is 4th nerve palsy diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Fourth Cranial Nerve Palsy Usually, 4th cranial nerve palsy is suspected if a person has characteristic limited eye movement. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain may be done to identify the cause.
How do you get cranial nerve palsy?
A cranial nerve palsy can occur due to a variety of causes. It can be congenital (present at birth), traumatic, or due to blood vessel disease (hypertension, diabetes, strokes, aneurysms, etc.). It can also be due to infections, migraines, tumors, or elevated intracranial pressure.
Is cranial nerve palsy curable?
In many patients, 6th cranial nerve palsies resolve once the underlying disorder is treated. Treatment of infection, inflammation, or tumor when present may result in improvement. Idiopathic palsy and ischemic palsy usually abate within 2 months.
How do you test for cranial nerve palsy?
3:539:34How to do the Cranial Nerve Examination - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipInclude forehead cheek and chin bilaterally. Ask the patient whether the same stimulus feels theMoreInclude forehead cheek and chin bilaterally. Ask the patient whether the same stimulus feels the same on both sides. Equal. Equal test cold sensation using the metal tuning fork.
How do you test for 4th nerve palsy?
Measure the patient's vertical misalignment while in the upright position. Then, measure again while the patient is supine. A decrease of more than 50% in supine is a positive result. The vertical misalignment caused by skew deviation depends on head position, whereas it would not change in trochlear nerve palsy.
How is 4th nerve palsy diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Fourth Cranial Nerve Palsy Usually, 4th cranial nerve palsy is suspected if a person has characteristic limited eye movement. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain may be done to identify the cause.
Does 4th nerve palsy get worse with age?
A person may adapt an abnormal head position, usually tilting of the head to one side, which allows better alignment of the eyes and helps prevent double vision. The head tilt may get progressively worse with age.
How do you test the 4th cranial nerve?
0:462:434th cranial nerve examination - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay we ask the patient to look on my hand my finger. Then bring his right sides with into the nose.MoreOkay we ask the patient to look on my hand my finger. Then bring his right sides with into the nose. And we put it down.
What causes 4th cranial nerve palsy?
Causes of Fourth Cranial Nerve Palsy. Often, the cause of 4th cranial nerve palsy cannot be identified. The most common identified cause is. A head injury, often due to a motorcycle accident but sometimes even relatively minor head trauma .
What causes palsy in the brain?
Occasionally, diabetes causes this palsy by damaging small blood vessels that carry blood to the nerve. Rarely, the cause is a tumor, a bulge ( aneurysm) in an artery in the skull, or multiple sclerosis.
What nerve affects vertical eye movements?
A palsy of the 4th cranial nerve affects vertical eye movements. Often doctors cannot identify the cause, but when they can, the cause is usually a head injury, sometimes a minor one. People see double images, but tilting the head to the side opposite the affected eye can eliminate them. Doctors suspect palsy of the 4th cranial nerve based on ...
How to stop double vision in palsy?
Thus, going down stairs, which requires looking inward and down, is difficult. However, tilting the head to the side opposite the affected eye muscle can compensate and eliminate the double images. This position can eliminate the double images because people use eye muscles that are unaffected by the palsy to focus both eyes on an object.
Can you turn your eyes inward with 4th cranial nerve palsy?
Symptoms of Fourth Cranial Nerve Palsy. One or both eyes may be affected. The affected eye cannot turn inward and down. As a result, people see double images, one above and slightly to the side of the other. Thus, going down stairs, which requires looking inward and down, is difficult.
What is the 4th cranial nerve palsy?
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Usually, 4th cranial nerve palsy is suspected if a person has characteristic limited eye movement. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain may be done to identify the cause.
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
Overview of the Cranial Nerves Twelve pairs of nerves—the cranial nerves—lead directly from the brain to various parts of the head, neck, and trunk. Some of the cranial nerves are involved in the special senses (such as seeing... read more
What nerve affects vertical eye movements?
A palsy of the 4th cranial nerve affects vertical eye movements. Often doctors cannot identify the cause, but when they can, the cause is usually a head injury, sometimes a minor one. People see double images, but tilting the head to the side opposite the affected eye can eliminate them. Doctors suspect palsy of the 4th cranial nerve based on ...
What causes palsy in the brain?
Occasionally, diabetes causes this palsy by damaging small blood vessels that carry blood to the nerve. Rarely, the cause is a tumor, a bulge ( aneurysm) in an artery in the skull, or multiple sclerosis.
What nerve is involved in the facial muscles?
Bell palsy is sudden weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face due to malfunction of the seventh cranial nerve. This nerve moves facial muscles, stimulates salivary and tear glands, detects tastes, and controls a muscle involved in hearing. Which of the following is often the first symptom of Bell palsy?
How to stop double vision in palsy?
Thus, going down stairs, which requires looking inward and down, is difficult. However, tilting the head to the side opposite the affected eye muscle can compensate and eliminate the double images. This position can eliminate the double images because people use eye muscles that are unaffected by the palsy to focus both eyes on an object.
Can you turn your eyes inward with 4th cranial nerve palsy?
Symptoms of Fourth Cranial Nerve Palsy. One or both eyes may be affected. The affected eye cannot turn inward and down. As a result, people see double images, one above and slightly to the side of the other. Thus, going down stairs, which requires looking inward and down, is difficult. However, tilting the head to the side opposite ...
How long does it take for 4th nerve palsy to resolve?
Fourth nerve palsy secondary to microvascular disease will frequently resolve within 4-6 months spontaneously. Idiopathic In a small subset of patients with acquired trochlear palsy, no etiologic cause can be established even after extensive testing.
What is a CN IV palsy?
Congenital Trochlear nerve palsy is a common cause of congenital cranial nerve (CN) palsy. Patients with congenital CN IV palsies may compensate for diplopia with variable head positioning; chin-down head posture is seen in bilateral CN IV palsy and contralateral head tilt is typically seen in unilateral CN IV palsy. Later in life, these patients may experience decompensation of their previously well controlled CN IV palsy from the gradual loss of fusional amplitudes that occurs with aging or after illness or other stress event. Congenital CN IV palsies can have very large hypertropias in the primary position (greater than 10 prism diopters) despite the lack of diplopia or only intermittent diplopia symptoms. These large vertical fusional ranges characteristic of congenital cases.
What causes trochlear nerve palsy?
Trochlear nerve palsy can also occur as part of a broader syndrome related to causes like trauma, neoplasm, infection, and inflammation. These etiologies are further categorized based on the anatomic location of involvement (midbrain, subarachnoid space, cavernous sinus, orbit).
Which nerve has the longest intracranial course?
The trochlear nerve has the longest intracranial course of all of the cranial nerves. There are four anatomic regions which can be responsible for non-isolated CN IV palsies :
Which nerve passes adjacent to the trigeminal nerve?
The trochlear nerve passes adjacent to the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve and the two share a connective tissue sheath. The trochlear nerve gains entry to the orbit via the superior orbital fissure, passes outside the tendinous ring of Zinn and innervates the SOM.
What is the cause of paralytic strabismus?
Dysfunction of the fourth cranial nerve (trochlear nerve), which innervates the superior oblique muscle (SOM), is one cause of paralytic strabismus. The SOM has different (primary, secondary, and tertiary) actions dependent on mechanical position of the eye. In the primary position, the primary action of the superior oblique muscle is intorsion.
Can 4th cranial nerve palsy affect ipsilateral hypertropia?
History. Fourth cranial nerve palsies can affect patients of any age or gender. They can present with vertical diplopia, torsional diplopia, head tilt, and ipsilateral hypertropia. Determining the onset, severity, and chronicity of symptoms can be vital in delineating between the various etiologies of a CN 4 palsy.