The CT scanner gantry is the doughnut-shaped part of the CT scanner that houses the apparatus necessary to produce and detect x-rays in order to create a CT image. The x-ray tube and detectors are positioned exactly opposite each other and rotate around the CT scanner gantry aperture.
What is gantry aperture in CT scan?
The gantry aperture is the opening in which the patient is positioned during scanning procedure. Most scanners have a 70cm aperture that facilitates patient positioning and helps provides access to patients in emergency situation. The CT gantry must be capable of tilting to accommodate all patients and clinical examinations.
What is a gantry in Xray?
Gantry is a rotating scan frame onto which the x-ray generator, x-ray tube and others components are mounted. The generator is usually a small solid-state high frequency generator. It is located close to the x-ray tube; only a short high tension cable (HTC) is required to couple the x- ray tube and generator.
What size CT scanner gantry do I Need?
CT scanner gantry aperture diameters generally range from 50 – 85 cm. In general, larger CT scanner gantry diameters, 70 – 85 cm, are necessary for CT scanner departments that do a large volume of biopsy procedures.
How does a gantry scanner work?
The gantry also include a laser light that is used to position the patient within the scanner. Control panels located on either side of the gantry opening allow the radiologic technologist to control the alignment lights, gantry tilt, and movement of the table. In most scanners, these functions may also be controlled via the operator’s console.

What is a gantry radiology?
Definition: gantry. gantry. A frame housing the x-ray tube, collimators, and detectors in a CT or radiation therapy machine, with a large opening into which the patient is inserted; a mechanical support for mounting a device to be moved in a circular path.
What are the parts of CT gantry?
On 27 March 2020, this CT gantry was opened and sampled in each of the following components: (a) gantry case; (b) inward airflow filter; (c) gantry motor; (d) x-ray tube; (e) outflow fan; (f) fan grid; (g) detectors; and (h) x-ray tube filter.
What is gantry angle?
The actual gantry angle could then be defined as the angle between vertical, as indicated by a plumb bob, and the direction of the beam axis that could be indicated by the position of a BB placed in the central axis and its shadow.
What is gantry size?
The gantry height is the vertical distance between the tip of the nozzle to the XY axis gantry that carries the printhead. Sequential printing is when multiple models are printed on the buildplate one after the other.
What is are the importance of a gantry in obtaining CT images?
The movement of the table through the gantry allows a complete scanning of the desired part of the patient. The degree of X-ray beam absorption (also called attenuation) differs according to the density of each anatomical structure through which the beam passes.
What is CT collimator?
The collimator is located immediately in front of the detectors to protect them from scattered X-rays. Ideally, each detector in a CT scanner measures intensity of X-rays that reach the detector after traveling along a straight-line path from the X-ray source to the detector.
What does a gantry do?
Gantry cranes are generally used for lifting extremely heavy objects. Because of this, they are often employed during shipbuilding, where the crane straddles the ship to allow for very large jobs, such as lifting the engines into the ship.
What does a gantry look like?
0:071:57What Does A Gantry Look Like? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThat is holding a bracket with the HMR B size 18 side mounted on this bracket. We can also do otherMoreThat is holding a bracket with the HMR B size 18 side mounted on this bracket. We can also do other configurations depending on your application requirements.
How many detectors does a CT scan have?
Detector Array Now all scanners are multi-slice and have 8-64 rows of detectors. There are generally 1000-2000 detectors in each row.
What are the components of CT scan?
CT scanners are composed of three important elements: an X-ray tube, a gantry with a ring of X-ray sensitive detectors, and a computer.
What is the diameter of a CT scan machine?
Computed tomography scanners do vary in their gantry aperture, with more modern scanners typically 75–85 cm in diameter 1. This information should be available from radiology staff, or alternatively a simple tape measure may be enough to prevent a wasted journey to CT.
What is aperture in CT?
A CT scanner looks like a big, square doughnut. The patient aperture (opening) is 60 cm to 70 cm (24" to 28") in diameter. Inside the covers of the CT scanner is a rotating frame which has an x-ray tube mounted on one side and the banana shaped detector mounted on the opposite side.
What are slip rings in CT?
Slip-ring CT is the technology which enables power and data to be transferred without physical cables connecting the stationary and rotating portions of the CT gantry.
What are the major components used for data acquisition in CT?
-The major components used for data acquisition are the scanning gantry, x-ray generator, and patient table.
What is Hounsfield unit in a CT scan?
The Hounsfield unit (HU) is a relative quantitative measurement of radio density used by radiologists in the interpretation of computed tomography (CT) images. The absorption/attenuation coefficient of radiation within a tissue is used during CT reconstruction to produce a grayscale image.
What are the types of CT scan?
CT Angiography. CT Scan Arthrography. CT Scan Bones. CT Scan Brain/ CT Scan Head.
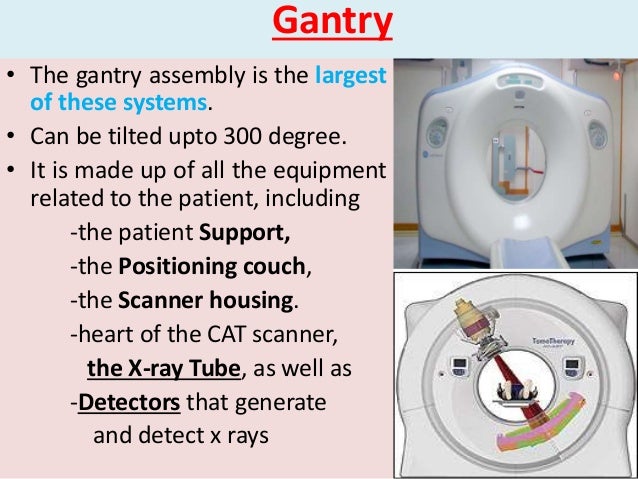
What is the gantry of a CT scanner?
The gantry of a computed tomography scanner (CT) is a ring or cylinder, into which a patient is placed. The x-ray tube and x-ray detector spin rapidly in the gantry, as the patient is moved in and out of the gantry. The CT scanner produces 3-dimensional x-ray images of the patient.
What is gantry in medical?
Gantry (medical) In a medical facility, such as a hospital or clinic, a gantry holds radiation detectors and/or a radiation source used to diagnose or treat a patient's illness. Radiation sources may produce gamma radiation, x-rays, electromagnetic radiation, or magnetic fields depending on the purpose of the device.
How does an MRI gantry work?
An MRI gantry remains fixed, and contains cryogenically cooled superconducting electromagnets and radio transmitters that flip protons in hydrogen atoms in the human body via proton nuclear magnetic resonance. The machine then listens and processes the signals given off by the hydrogen atoms as the protons flip back in order to produce a 3D image of the interior of the patient's body.
What is the gantry of a radiotherapy machine?
The gantry of an external beam radiotherapy machine moves a radiation source around a patient . A linear accelerator (linac) is built into the top part of the gantry in the photo at the right. The rectangular screen on the right side of the gantry is a cone beam x-ray detector, which is used to help position a patient prior to treatment.
How wide is a gantry?
The diameter of the opening or aperture varies in size, as does the gantry as a whole. The aperture range size is usually 70-90 cm. The gantry can be tilted forward or backward as needed to accommodate a variety of patients and examination protocols, usually 15-30 degrees. This, too, can vary between manufacturers.
What is CT scanner?
CT Scanners are complicated medical imaging devices, with each component contributing to the creation of successful images. However, different manufacturers don’t always use the same component design, which makes things even more complicated.
What is post patient collimation CT scan?
There are CT Scan systems that use predictor collimation or post patient collimation. The scan occurs below the patient and above the detector array. This collimate shapes the beam after it has passed through the patient. This approach ensures the beam is the proper width as it enters the detector and prevent scatter radiation from reaching the detector.
What generator is used in CT scanners?
CT Scanners currently use high frequency generator s. They’re designed to be small enough to fit within the gantry. In the past, highly stable three-phase generators were used. These stand-alone units were located near the gantry and required cables.
How does a generator affect xrays?
Generators produce high voltage and transmit it to the x-ray tube. The power capacity of the generator (listed in kilowatts or kW) determines the range of exposure techniques like kV and mA settings, which are available on a particular system. The generator usually produces high kV (120-140 kV) to increase the beam intensity and reduce patient dose. A higher kV setting helps reduce the heat load on the x-ray tube by allowing a lower mA setting. By reducing the heat load on the tube the life of the tube will be extended.
What is gantry in CT?
The gantry is the donut like or ring shaped part of the CT scanner. It houses many of the components necessary to produce and detect xrays. These components are mounted on a rotating scan frame.
How does a gantry work?
Component of the gantry are mounted on a rotating scan frame. Gantries vary in total size as well as in the diameter of the opening or aperture. The range size of aperture is typically 70 to 90 cm. The gantry is designed to be tilted either forward or backward as needed to accommodate a variety of patients and examination protocols. The gantry can be tilted varies among systems, but more or less 15 degrees to 30 degrees is usual. The gantry also include a laser light that is used to position the patient within the scanner. Control panels located on either side of the gantry opening allow the radiologic technologist to control the alignment lights, gantry tilt, and movement of the table. In most scanners, these functions may also be controlled via the operator’s console. A microphone is installed in the gantry to allow communication between the patient and the radiologic technologist throughout the scanning procedure.
Why do we need a compensating filter for a CT scan?
Compensating filters are used to shape the xray beam. They reduce the radiation dose to the patient and help to minimize image artifact. As our teachers tough us that, radiation emitted by CT scan xray tube is polychromatic. Filtering the xray beam helps to reduce the range of xray energies that reach the patient by removing the long wavelength or soft xrays. These long-wavelength xrays are readily absorbed by the patient, therefore they do not contribute to the CT image but do contribute to the radiation dose to the patient. In addition, creating a more uniform beam intensity improves the CT image by reducing artifacts that result from beam hardening.
What is a CT scanner?
CT scanners are composed of many different connected parts, with many different components involved in the process of creating an image. More to the complexity, different CT scan manufacturers often modify the design of various components. To understand the basic function of each components, and some of the major variations in their design. From a broad perspective, all make and models of CT scanner are similar in that they consist of a scanning gantry, x-ray generator, computer system, operator’s console or the console panel and physician’s viewing console. Although hard copy filming has largely been replaced by workstation viewing and electronic archiving, most CT system still include a laser printer for transferring CT images to film.
Why do we use body scanning filters?
Hence, body scanning filters are used to reduce the beam intensity at the periphery of the beam , corresponding to the thinner areas of a patient’s anatomy.
Do long wavelength xrays help with CT?
These long-wavelength xrays are readily absorbed by the patient, therefore they do not contribute to the CT image but do contribute to the radiation dose to the patient. In addition, creating a more uniform beam intensity improves the CT image by reducing artifacts that result from beam hardening.
What is CT SCAN?
Is a method of acquiring and reconstructing the image of a thin cross section on the measurement of attenuation. Ct is also called as the following name; Computed Tomography, Computed Axial Tomography and Body Section Roentgenography. It is came from the greek word TOMOS which means a slice or section, and GRAPHIA means describing. A binary system is use to construct a diagnostic images of the ct scan provided by the computer.
What is binary system in a CT scan?
A binary system is use to construct a diagnostic images of the ct scan provided by the computer. CT scan is an x-ray source and has detectors across from each other located in about 180 degrees from tube to end, it move 360 degrees around the patient, continuously and sends information about attenuation of x-rays as x-ray pass through the body.
What is the difference between a 4th generation CT scanner and a 3rd generation CT scanner?
Disadvantage of this ct scanner is a drawback patient dose, as the detectors are not coupled to the xray source and hence it cannot focus and make use of SEPTA to reject the scattered radiation. However, the detectors are program to a self-calibrating system, the detectors are calibrating twice during each rotation. While the 3rd generation scanner are automatically callibrating once only in every fer hours.
What is the 2nd generation CT scanner?
The 2nd generation ct scan is Rotate - Translate scanners. It has a narrow fan beam with multiple detector installed ranges from 5 to 30 detectors. The disadvantage of the is scanners is that, it has a drawback effect of increase scatter radiation.
When was the first CT scanner installed?
1974 - 1976 - First clinical ct scanners were installed. 1979 - Both Hounsfield and Cormark shared the nobble prize in medicine. 1980 - CT scan machine became widely available and its the first Ct scan system that can produced a ct images of any part of the body without requiring a water tank for scanning.
How long does it take to scan a CT scanner?
The First generation of ct is a Rotate - Translate type of scanner. It has a Pencil beam and has only one detector, it is slow scanning and took around 5 minutes to complete one scan (a 180° rotation).
Why is a restricted beam used in x-rays?
Restriction of the useful x-ray beam to reduce patient dose and improve image contrast.
What is a CT scan?
The term “ computed tomography ”, or CT, refers to a computerized x-ray imaging procedure in which a narrow beam of x-rays is aimed at a patient and quickly rotated around the body, producing signals that are processed by the machine’s computer to generate cross-sectional images—or “slices”—of the body. These slices are called tomographic images ...
What is a dedicated breast CT scanner?
Dedicated Breast CT Scanner: NIBIB is funding research for development of a dedicated breast CT scanner that allows the breast to be imaged in 3D and could help radiologists detect hard-to-find tumors. The scanner produces a radiation dose comparable to that of a standard x-ray mammogram and doesn’t require compression of the breast. In this breast CT scanner, a woman lies prone in a specially designed large table with her breast suspended in a special opening in the scanning bed. The scanner rotates around the breast, without passing through the chest, thus reducing the radiation that would be delivered to the chest in a conventional CT scanner. Listen to a podcast about the scanner.
How does CT work?
Unlike a conventional x-ray—which uses a fixed x-ray tube—a CT scanner uses a motorized x-ray source that rotates around the circular opening of a donut-shaped structure called a gantry. During a CT scan, the patient lies on a bed that slowly moves through the gantry while the x-ray tube rotates around the patient, shooting narrow beams of x-rays through the body. Instead of film, CT scanners use special digital x-ray detectors, which are located directly opposite the x-ray source. As the x-rays leave the patient, they are picked up by the detectors and transmitted to a computer.
What is a CT contrast agent?
As with all x-rays, dense structures within the body—such as bone—are easily imaged, whereas soft tissues vary in their ability to stop x-rays and, thus, may be faint or difficult to see. For this reason, intravenous (IV) contrast agents have been developed that are highly visible in an x-ray or CT scan and are safe to use in patients. Contrast agents contain substances that are better at stopping x-rays and, thus, are more visible on an x-ray image. For example, to examine the circulatory system, a contrast agent based on iodine is injected into the bloodstream to help illuminate blood vessels. This type of test is used to look for possible obstructions in blood vessels, including those in the heart. Oral contrast agents, such as barium-based compounds, are used for imaging the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, and GI tract.
Why do we need a CT scan of the heart?
A CT scan of the heart may be ordered when various types of heart disease or abnormalities are suspected. CT can also be used to image the head in order to locate injuries, tumors, clots leading to stroke, hemorrhage, and other conditions.
How thick is a CT scan?
The thickness of the tissue represented in each image slice can vary depending on the CT machine used, but usually ranges from 1-10 millimeters. When a full slice is completed, the image is stored and the motorized bed is moved forward incrementally into the gantry.
Can a CT scan be life threatening?
CT scans can diagnose possibly life-threatening conditions such as hemorrhage, blood clots, or cancer. An early diagnosis of these conditions could potentially be life-saving. However, CT scans use x-rays, and all x-rays produce ionizing radiation.