
Gene (DNA) is capable of following three functions:
- Duplication of its genetic material by faithful replication and its precise distribution among new cells by cell division.
- It should be able to undergo mutation and such a change should be stably inherited.
- It should be able to express in genetic information by transcription to mRNA and finally to produce proteins.
Full Answer
What is the purpose of a gene?
Genes Genes are functional units of heredity as they are made of DNA. The chromosome is made of DNA containing many genes. Every gene comprises of the particular set of instructions for a particular function or protein-coding. Speaking in usual terms, genes are responsible for heredity. There are about 30000 genes in each cell of the human body.
What is a gene best defined as?
Gene = The gene is the basic physical unit of inheritance. Genes are passed from parents to offspring and contain the information needed to specify traits. Genes are arranged, one after another, on structures called chromosomes. A chromosome contains a single, long DNA molecule, only a portion of which corresponds to a single gene.
What are genes responsible for?
May 30, 2018 · “A gene is a functional- hereditary unit made up of nucleotides which forms proteins.” Genes are located on chromosomes.” Or we can say, “A gene is an inheritance unit of a cell”- is a globally and universally accepted definition of a gene. But actually, it’s not a complete one or we can say scientifically it isn’t accepted fully.
What is the purpose of genes?
Sep 28, 2016 · Most simply, a gene is a specific area of DNA on a chromosome that codes for the production of certain proteins that influence a particular trait (e.g., hair color). However, to understand what a...
What is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity?
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes are made up of DNA. Some genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins. However, many genes do not code for proteins. In humans, genes vary in size from a few hundred DNA bases to more than 2 million bases.
Is a gene the same in all people?
Most genes are the same in all people, but a small number of genes (less than 1 percent of the total) are slightly different between people. Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases. These small differences contribute to each person’s unique physical features.
How long is a gene?
Narration. A gene could be as short as a few hundred base pairs or as long as many thousands. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, for instance, are very long and huge. The beta-globin gene, on the other hand, is only a few hundred of these nucleotides. A gene, in a common way of thinking about it, is a packet of information coding generally for a protein.
What is the basic physical unit of inheritance?
The gene is the basic physical unit of inheritance. Genes are passed from parents to offspring and contain the information needed to specify traits. Genes are arranged, one after another, on structures called chromosomes.
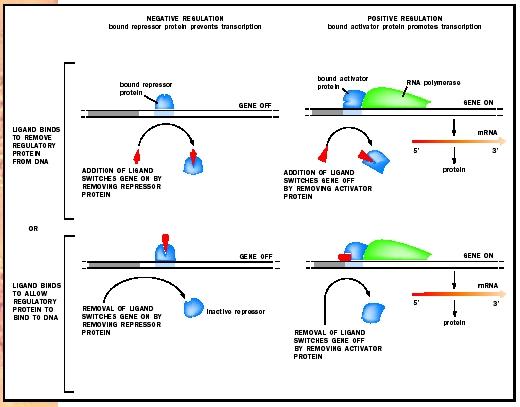
What are the processes that regulate gene expression?
This entire mechanism is known as the regulation of gene expression. Now, this is for pro–. Methylation, histone modification, chromatin remodeling, RNA interference are some of the processes that help in controlling genes.
Where are genes located?
Genes are located on chromosomes. ”. “A gene is an inheritance unit of a cell”- is a globally and universally accepted definition of a gene. But actually, it’s not a complete one or we can say scientifically it isn’t accepted fully. Defining a “gene” is actually intricate.
What are some examples of gene symbols?
Let’s look at some of the examples of gene symbol: 1 ACOT1– acyl-CoA thioesterase 1 2 ABCA1– ATP= binding cassette sub-family A (ABC1), member 1. 3 SRY– a sex-determining region on Y 4 HBA– human beta-globin A
What are the elements that make up the nucleotides of DNA?
Key information– only ~2.2% of human DNA are coding sequences. In general, the gene structure consists of two types of elements: core elements and regulatory elements.
Who coined the term "gene"?
The term gene was coined by Wilhelm Johannsen in 1909. However, their function was reported by Mendel during the 1800s. Notably, the chemical structure of genes is almost similar in prokaryotes as well as eukaryotes although their location and regulation differ.
What are the introns and exons of a gene?
Introns are intervening non-coding sequences removed from the final transcript. Exons are coding part of a gene which are joined after splicing and constructs the final transcript. Regulatory elements are located on the extreme ends of a gene. The molecular structure of a gene.
Where does mRNA come from?
The mRNA is constructed from a gene. After that, post-transcriptional modifications happen, followed by the migration of mRNA to the cytoplasm. At the ribosome, in the cytoplasm, the mRNA translated into the chain of amino acids. That is how the entire mechanism of protein formation occurs in a cell.
What is a gene?
Most simply, a gene is a specific area of DNA on a chromosome that codes for the production of certain proteins that influence a particular trait (e.g., hair color). However, to understand what a gene is, some understanding of basic genetics is necessary, including what DNA, chromosomes, and traits are. To do that, we'll take a look ...
How many genes are there in humans?
Monogenic and Polygenic Traits. It is estimated that humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes in their 23 chromosome pairs. Interestingly, less than 2% of the DNA on chromosomes are part of identified genes. The Human Genome Project is an attempt to map those genes so that their impact can be better understood.
What is the chemical compound that tells the cell's machinery to produce specific proteins?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is a chemical compound found in all eukaryotic cells that tells the cell's machinery to produce specific proteins. It has a 'code' that gets translated into proteins. Every one of Emma's cells has the exact same DNA as every other cell.
How many genes are in chromosome 11?
It is also where Emma's sickle cell anemia comes from. It is estimated that human chromosome 11 contains nearly 1,500 genes, coding for the proteins that influence many different traits, including sickle-cell anemia and many of the olfactory (smell) receptor genes in humans.
What is the human genome project?
The Human Genome Project is an attempt to map those genes so that their impact can be better understood. Human chromosome 11 provides a good example to describe the relationship between genes, traits, and chromosomes. It is also where Emma's sickle cell anemia comes from.
What are some examples of polygenic traits?
There are many polygenic traits, and some examples of these in humans include height and skin color . It is a misnomer to say, 'Emma has the sickle cell gene.'. All people have the area of chromosome 11 (i.e., 'the gene') that codes for the proteins that determine whether or not someone has sickle-cell anemia.
Is gene therapy still in its infancy?
Gene therapy is still in its infancy, but is looked to as a potential therapy for all kinds of diseases and genetic disorders, including cancers. Lesson Summary. Genes are specific areas of DNA on a chromosome that code for certain protein production that influences particular traits.
Definition
A gene is a DNA segment or small portion. Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) are the bases that make up DNA, which is a double-stranded molecule (G).
History of genes
It was the Mendel who first discovered the concept of the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring, however, he failed to describe it or find out the role of genes.
Work Mechanism of Genes
Each gene is made up of a specific base sequence that holds the information (code) needed to make specific proteins and so perform specified functions. They may, for example, provide instructions for a person’s eye colour, hair colour, skin colour, body height, and other characteristics.
Composition of genes
Gene is a short section or segment of DNA which itself is made of millions of chemicals called nitrogenous bases. These bases are of four types; Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Guanine (G).
Structure of Genes
A gene is a short segment of DNA strand (a chain made of nucleotides). So, the entire DNA is a chain of genes or we can say that genes are units of DNA strands. The genes may vary in size based on the size of proteins for which they code.
Promoter region
There are some regions on DNA or gene that contain certain sequences that provide the signal to enzymes about the start point of a gene from where enzymes are supposed to start transcription.
Structural region
The structural region of a gene is the section of a gene that is transcripted to generate mRNA, or the part of a gene that includes the actual code that forms mRNA.
What is a gene in biology?
A gene is a tiny section of a long DNA double helix molecule, which consists of a linear sequence of base pairs. A gene is any section along the DNA with instructions encoded that allow a cell to produce a specific product – usually a protein, such as an enzyme – that triggers one precise action.
What are the genes in the human body?
All living beings have genes. They exist throughout the body. Genes are a set of instructions that determine what the organism is like, its appearance, how it survives, and how it behaves in its environment. Genes are made of a substance called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.
How many chromosomes are in a human?
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or a total of 46. A donkey has 31 pairs of chromosomes, a hedgehog has 44, and a fruit fly has just 4. DNA contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. DNA is passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction.
What is the human genome project?
The Human Genome Project (HGP) is a major scientific research project. It is the largest single research activity ever carried out in modern science. It aims to determine the sequence of the chemical pairs that make up human DNA and to identify and map the 20,000 to 25,000 or so genes that make up the human genome.
What is the layer of genetic data that is not held in the genome?
In recent years, geneticists have found another layer of heritable genetic data that is not held in the genome, but in the “epigenome, ” a group of chemical compounds that can tell the genome what to do.
What is genetic engineering?
A geneticist is a person who studies genes and how they can be targeted to improve aspects of life. Genetic engineering can provide a range of benefits for people, for example, increasing the productivity of food plants or preventing diseases in humans.
How do genes affect a living thing?
Genes decide almost everything about a living being. One or more genes can affect a specific trait. Genes may interact with an individual’s environment too and change what the gene makes.
A GENE NAME
From the NCBI home page, click on the Search pull-down menu to select the Gene database, type the Gene Name in the text box and click Go. See Gene Help for tips searching Gene.
A PROTEIN SEQUENCE
Go to the BLAST home page and click "protein blast" under Basic BLAST.
A NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE
Go to the BLAST home page and click "nucleotide blast" under Basic BLAST.
Where do tRNA genes occur?
Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRNA genes in the ITS. In eukaryotes, genes encoding ribosomal RNA and spacers occur in tandem repeats that are thousands of copies long, each separated by regions of non-transcribed DNA termed intergenic spacer ...
What is the ITS region?
The ITS region is the most widely sequenced DNA region in molecular ecology of fungi and has been recommended as the universal fungal barcode sequence. It has typically been most useful for molecular systematics at the species to genus level, and even within species (e.g., to identify geographic races).
Where is the internal transcribed spacer located?
Internal transcribed spacer ( ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript.
Is ITS2 conserved?
ITS2 is known to be more conserved than ITS1 is. All ITS2 sequences share a common core of secondary structure, while ITS1 structures are only conserved in much smaller taxonomic units. Regardless of the scope of conservation, structure-assisted comparison can provide higher resolution and robustness.
