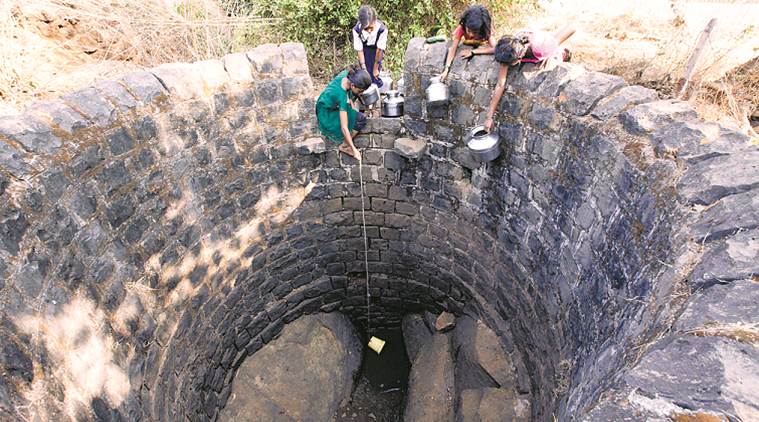
groundwater extraction Definition The process, deliberate or inadvertent, of extracting ground water from a source at a rate so in excess of the replenishment that the ground water level declines persistently, threatening exhaustion of the supply or at least a decline of pumping levels to uneconomic depths.
How does man extract the groundwater?
14.3 Groundwater Extraction. Except in areas where groundwater comes naturally to the surface at a spring (a place where the water table intersects the ground surface), we have to construct wells in order to extract it. If the water table is relatively close to the surface, a well can be dug by hand or with an excavator, but in most cases we ...
What we can all do to reduce groundwater pollution?
What is the easiest way to reduce water pollution?
- Use Less Plastic. It is very difficult to break down plastic after it is produced. …
- Reuse Items. …
- Recyclable Options. …
- Do Not Dispose of Oils in the Sink. …
- Cleaning Chemicals. …
- Handle Toxic Chemicals Properly. …
- Shop to Stop Water Pollution. …
- Do Not Throw Away Medicines.
What are some facts about groundwater?
- The top of the subsurface ground-water body, the water table, is a surface, generally below the land surface, that fluctuates seasonally and from year to year in response to changes ...
- Ground water commonly is an important source of surface water. ...
- Ground water serves as a large subsurface water reservoir. ...
How do hydrologists locate groundwater?
How Do Hydrologists Locate Groundwater? Using scientific methods to locate water. To locate groundwater accurately and to determine the depth, quantity, and quality of the water, several techniques must be used, and a target area must be thoroughly tested and studied to identify hydrologic and geologic features important to the planning and ...

Why do we extract groundwater?
Groundwater Wells In many places wells provide a reliable and ample supply of water for home uses, irrigation, and industries. Where surface water is scarce, such as in deserts, people couldn't survive and thrive without groundwater, and people use wells to get at underground water.
What is the meaning of water extraction?
Water extraction is the process of taking water from any source, either temporarily or permanently, for flood control or to obtain water for, for example, irrigation. The extracted water could also be used as drinking water after suitable treatment.
Why is groundwater extraction bad?
A related effect of groundwater pumping is the lowering of groundwater levels below the depth that streamside or wetland vegetation needs to survive. The overall effect is a loss of riparian vegetation and wildlife habitat. The basic cause of land subsidence is a loss of support below ground.
What is the process of extracting water?
6 Steps for Proper Water Extraction & Home RestorationShut Down the Source of Water. The first step in proper water extraction is to find the water source and shut it down. ... Protect Against Health Issues. ... Remove All Standing Water. ... Dry Out the Area and All Materials. ... Cleaning. ... Remove Any Lingering Odors.
What are some examples of water extraction?
Here we present results of an intercomparison of five common lab-based soil water extraction techniques: high pressure mechanical squeezing, centrifugation, direct vapor equilibration, microwave extraction, and cryogenic extraction.
Where do we extract ground water?
Water in aquifers is brought to the surface naturally through a spring or can be discharged into lakes and streams. Groundwater can also be extracted through a well drilled into the aquifer. A well is a pipe in the ground that fills with groundwater. This water can be brought to the surface by a pump.
What are the effects of water extraction?
Accordingly, the most common effect of extraction from a groundwater system is to reduce the discharge of groundwater to surface water, which decreases the flow in receiving rivers and streams and in some cases causes them to dry up completely.
How can we save groundwater?
At homeproperly dispose of all waste; don't dump chemicals down drains or on the ground.test underground fuel oil tanks for leaks; if possible, replace them above ground.safely store all chemicals and fuels.minimize the use of chemicals; always use according to directions.More items...
How does the extraction of water affect the environment?
Diverting river water or groundwater through the built infrastructure for discharge elsewhere alters the surface water quantity and quality and thereby disrupts the natural flows through streams, rivers, and lakes. This can destroy habitat and disrupt wildlife that depend on that habitat.
What are examples of groundwater?
The definition of groundwater, or ground water, is water located beneath the surface of the earth. The water that your well draws from under the ground is an example of groundwater. Water that exists beneath the earth's surface in underground streams and aquifers.
What are the types of wells used for extraction of groundwater?
There are three types of private drinking water wells.Dug/Bored wells are holes in the ground dug by shovel or backhoe. ... Driven wells are constructed by driving pipe into the ground. ... Drilled wells are constructed by percussion or rotary-drilling machines.
Why water extraction is important?
Why is Water Extraction so Necessary? The reason speedy water extraction is so vital is that standing water can start to seep into the grounds of your property. This water can damage the foundations of your home or building and put you and your family or employees at risk of health issues.
What is water extract in chemistry?
Water extract: The process of taking off the water, temporarily or permanently to control flood. It can also be used for drinking. Original salt solution: It is a process in which salt is dissolved in water to form a solution.
What are the effects of water extraction?
Accordingly, the most common effect of extraction from a groundwater system is to reduce the discharge of groundwater to surface water, which decreases the flow in receiving rivers and streams and in some cases causes them to dry up completely.
How is water extracted from the environment?
When a well is pumped, the water around the well itself is drawn down the furthest, with the groundwater table forming a cone of depression around the well. Surrounding groundwater then flows by gravity to fill the void, which can pull water from nearby streams and lakes.
How does groundwater extraction affect the flow rate?
For instance, the rise and fall of groundwater levels resulting from seasonal changes can alter groundwater recharge and discharge rates. The addition or deletion of capture wells within a given flow net also affects the volume of water that the extraction system can pump. Similarly, agricultural, industrial, and domestic water usage can influence the rate of groundwater extraction. Withdrawal rates also may be varied as part of the overall groundwater remediation or control strategy.
Where was groundwater extraction in California?
Groundwater extraction near Pixley in California caused some 0.75 m of settlement between 1958 and 1963, the surface depression being mainly over the area pumped, with the effect decreasing with distance. In the Houston/Galveston region, the presence of faults has restricted the area affected by the dewatering such that a face up to a metre high has developed over a length of almost 17 km.
What is microwatershed level water balance?
Microwatershed level water balance was estimated on the basis of groundwater recharge and groundwater extraction for the year 2004 in Kundi basin. The groundwater recharge and groundwater extraction were estimated using the estimated values of average water-level fluctuations in wells during monsoon (FLWL ), the specific yield of the aquifer ( Sy ), and the geographical area of the watershed ( A) to arrive at the net recharge ( RECHNET ). To the net recharge figures, the estimated groundwater draft during kharif ( PUMPWELL) was added to arrive at the actual monsoon recharge.
How much groundwater is used in the MDB?
Across the MDB, groundwater extraction fluctuates between 700 GL per year for wet periods and 1800 GL per year for dry periods. Groundwater use is an important drought contingency measure as groundwater aquifers provide greater water storage than surface water reservoirs. The large groundwater storage creates interest in the application of managed aquifer recharge (MAR), using surface water, stormwater, recycled water, and even desalinated water and then using it at times of demand. While a number of MAR schemes are proposed within the Basin, MAR is currently practiced in only two groundwater resource units: one in South Australia and the other in the Australian Capital Territory for a total supply of about 1 GL per year ( MDBA, 2019d ).
What is the use of groundwater in India?
About 90% of our annual groundwater extraction is used for agriculture. Other societal uses include that consume remaining 10% are domestic consumption and also industrial demand that include manufacturing industries, packaged drinking water, infrastructures, and mining activities. CGWB estimates groundwater resource availability of entire India at regular interval (cgwb.gov.in ). The latest resource estimation as on 2017 reveals that out of 6584 groundwater assessment units in the country, 1034 are overexploited, annual extraction is more than annual recharge ( Saha et al., 2019 ). In another 253 units, extraction exceeds 90% of annual recharge. In total, 4520 units are such that extraction is less than 70% of the recharge, which is considered as “safe” as per the Govt. of India Guidelines ( GEC, 1997 ).
How much groundwater has been extracted in 2017?
An analysis of data of groundwater extraction for groundwater resources assessment since 2004, 2009, 2011, 2013, and 2017 reveals that groundwater extraction has increased from 231 BCM in 2004 to 249 BCM in 2017 ( Table 35.2 ). The groundwater extraction for irrigation has, however, marginally reduced over the years. If we consider the groundwater draft for irrigation in percentage of total extraction, it has reduced from 92% in 2004 to 90% in 2013 and further to 89% in 2017 ( Fig. 35.5 ).
How to manage multiple water resources?
Generally, optimal management of multiple water resources is driven by an SSP, and augmenting groundwater extraction with any number of alternatives reduces scarcity. Consequently, a variety of tools have been implemented in recent years to enhance or supplement existing groundwater resources. In Orange County (California), for example, recycled wastewater is currently being injected deep underground both to augment the coastal aquifer resource and to create a buffer against saltwater intrusion. However, policies driven by the desire to sustain groundwater resources at their current level often fail to account for the resulting temporal patterns of associated benefits and costs. Optimal management, on the other hand, generates a larger PV while typically sustaining groundwater resources in the long run. In this sense, managing for sustainability is unlikely to achieve optimality, but managing optimality typically assures sustainability. Although optimizing across multiple dimensions (e.g., space and time) necessarily increases modeling and computational requirements, continual advances in algorithm design and data processing power are allowing researchers to include more details of the entire water system.
Why is groundwater important in a watershed?
support populations of salmon that live in the stream for part of their life cycle or return to their home stream for spawning. Groundwater forms a part of the baseflow in a watershed , and is therefore an important part of the environmental flow needs.
How does a well get water from the ground?
That is how a well gets water from the ground. The water table , or potentiometric surface, will slope in toward the well where the water is being withdrawn. That indicates the energy gradient that is allowing water to flow toward the well. This creates a shape known as a cone of depression surrounding the well, as illustrated in Figure 14.11.
How does a well pump work?
Pumping water from the well removes water from inside the well at first. That lowers the water level inside the well. This means that water will flow from the surrounding aquifer (higher groundwater head) toward the pumping well where the groundwater head is now lower. That is how a well gets water from the ground.
How to dig a well?
If the water table is relatively close to the surface, a well can be dug by hand or with an excavator, but in most cases we need to use a drill to go down deep enough. There are many types of drills that can be used; an example is shown in Figure 14.10. A well has to be drilled at least as deep as the water table, but in fact must go much deeper; first, because the water table may change from season to season and from year to year, and second, because when water is being pumped, the water level will drop, at least temporarily.
How to check water level in BC?
Ministry of the Environment observation well website at: http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/wsd/data_searches/obswell/map/ and use the map to find an observation well near you. When you click on a point, a window pops up with a link that says, “Click for details about this well.” Click on that link and then choose one of the options available. The “Graphs” tab will show you a graph of the water levels, and you should be able to tell if the level is generally increasing or decreasing. If there isn’t much data to see, choose a different well.
What is the water sustainability act?
This comes into effect in January 2016. The new Act also includes provisions for determining “environmental flow needs” — the amount of water that must be in surface water streams at different times of the year to meet the needs of the ecosystem that depends on the streamflow . For example, many streams in B.C. support populations of salmon that live in the stream for part of their life cycle or return to their home stream for spawning. Groundwater forms a part of the baseflow in a watershed, and is therefore an important part of the environmental flow needs. Careful work is needed in the coming years to ensure that the amount of water licensed to be extracted from surface water and groundwater for human use does not interfere with the amount of water needed for the natural water-dependent ecosystems to function.
How does groundwater affect water flow?
High levels of groundwater in a well can cause contaminated water to flow toward other bodies of water. Groundwater can be extracted through a well drilled into the aquifer. A well is a pipe in the ground that fills with groundwater. This water can be brought to the surface by a pump.
What is a QED pump?
QED pumps are ideal for landfill pumping, with its fluctuating flow rate and discharge head requirements, challenging down-well environments and special hazards that make other pumps unsuitable. Ever since users first adapted our monitoring well purge pumps to collect leachate, a continuous program of customer-driven engineering advances has created the industry's most complete, highest performance landfill pumping product line.
What is groundwater?
Groundwater is water that exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. The upper surface of the saturated zone is called the water table. Contrary to popular belief, groundwater does not form underground rivers. It fills the pores and fractures in underground materials such as sand, gravel, and other rock, ...
How much groundwater was withdrawn in 2015?
In 2015, about 84,600 million gallons per day (Mgal/d) of groundwater were withdrawn in the United States for various uses including public supply, self-supplied domestic, industrial, mining, thermoelectric power, aquaculture, livestock, and irrigation.
How many people rely on groundwater for drinking water?
The quality of our Nation's waters: Water quality in principal aquifers of the United States, 1991-2010. About 130 million people in the United States rely on groundwater for drinking water, and the need for high-quality drinking-water supplies becomes more urgent as our population grows.
What is the purpose of the USGS?
USGS scientist tests groundwater samples for water quality. The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling.
How long does groundwater stay in an aquifer?
As a result, water could remain in an aquifer for hundreds or thousands of years. Groundwater is the source of about 40 percent of water used for public supplies and about 39 percent of water used for agriculture in the United States.
What is the USGS?
The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling. The latest results from five regional aquifers are now available.
When did groundwater levels change in the aquifer?
The report presents water-level change data in the aquifer for two separate periods: from 1950 – the time prior to significant groundwater irrigation development – to 2013, and 2011 to 2013.
Why are surfactants injected in groundwater?
Surfactants are injected in the contaminated zone, recovered with contaminated groundwater, and are separated and reused to increase the economic feasibility of the technology. The contaminant type, its concentration levels, and the extraction flow rates influence above-ground treatment options and design.
What is the best way to design extraction and treatment systems?
Design of extraction and treatment systems should be based on longer duration field pump or pilot tests as opposed to engineering estimates or "worst-case" projections, which can lead to inaccurate input data and over-design of treatment equipment.
Why is the contaminant mass recovered by a pump and treat system limited?
Because of the tendency of many contaminants to sorb to the heterogeneous soil types making up a typical aquifer, the contaminant mass recovered by a pump and treat system can quickly become limited by the slow pace of contaminant back-diffusion from soil into groundwater.
What is reinjection in water treatment?
Reinjection may require a state permit, 1 and a demonstration that the water will be captured by the pump and treat system and will not push contaminated water from the treatment area , may be required. Oftentimes, reinjection is used to constrain the plume boundary and flush contaminants toward the recovery wells.
What are the effects of heterogeneity and transmissivity on the aquifer?
Heterogeneity and transmissivity of the aquifer will influence the production rate and capture influence, propensity for prolonged back-diffusion of contaminants from fine-grained soil types, and potential for preferential migration pathways. Detailed logging of stratigraphy to facilitate evaluation of lithologic influences on the distribution and mobility of site contaminants and impacts of the pump and treat system on them should be performed.
Why is it important to have a detailed characterization of the aquifer and contaminant characteristics?
Sufficiently detailed characterization of the aquifer and contaminant characteristics must be performed to allow design of the pumping component and the treatment component. An inadequate conceptual site model can lead to an ineffective design and application and unreasonable remediation timeframe.