Do athletes require a higher tidal volume?
Tidal volume (Vt) for ALI/ARDS is 6 ml/kg. However, professional athletes have higher forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) than predicted for the same body weight and thus a higher Vt could be required.
How do you measure tidal volume?
Measure Tidal Volume Take a normal breath in, hold your nose and take a normal breath out into the lung volume bag mouthpiece. Slide a paper towel along the bag to push all the air to the lower end and measure the volume of air it contains. (The bag has liter and 1/10 liter graduations.) Record this as tidal volume.
What causes tidal volume to increase?
what causes tidal volume to increase? During exercise, tidal volume increases as the depth of breathing increases and the rate of breathing increases too. This has the effect of taking more oxygen into the body and removing more carbon dioxide.
What is normal tidal volume?
Tidal volume is the measure of the amount of air inhaled during a normal breath. Safe tidal volumes can be determined based on patient’s height and gender and the rule of thumb, when lung-protective ventilation is required, is setting the tidal volume at 6-8 mL/kg ideal body weight. Target tidal volume ranges from 6 to 8 mL/kg IBW, where:

What do high tidal volumes mean?
High tidal volumes have been associated with an increase in local and systemic inflammation and a decrease in mean arterial pressure compared with protective ventilation.13Another study has shown that protective ventilatory strategies decrease systemic and local inflammation, cardiac dysfunction, perivascular edema, ...
What is a normal tidal volume?
approximately 500 ml per inspirationTidal volume (symbol VT or TV) is the volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during a normal breath. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 ml per inspiration or 7 ml/kg of body mass.
Is high or low tidal volume good?
Mechanical ventilation with higher tidal volumes contributes to the development of lung injury in patients without ALI at the onset of mechanical ventilation. Ventilation with low tidal volumes is associated with a lower risk of development of pulmonary complications in patients without ARDS.
What is a bad tidal volume?
High tidal volumes (greater than 10 mL/kg) can be harmful and may delay advancement to independent breathing. Using low tidal volumes on a ventilator has been shown to improve the survival rate in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
What is the maximum tidal volume in humans?
It is the maximum volume of air the lungs can accommodate or sum of all volume compartments or volume of air in lungs after maximum inspiration. The normal value is about 6,000mL(4‐6 L). TLC is calculated by summation of the four primary lung volumes (TV, IRV, ERV, RV).
What is the tidal volume of a 70kg person?
roughly 840-1050mlThat works out to be roughly 840-1050ml for a 70kg person.
What happens if tidal volume is low?
Low tidal volumes can lead to atelectasis and, of course, that can lead to shunt. But the Bendixon study didn't use PEEP. They used zero end-expiratory pressure, or ZEEP. When patients exhaled, their lung pressure fell to atmospheric pressure levels.
Does increasing tidal volume increase oxygenation?
Increasing tidal volume improves oxygenation, whereas a decrease in tidal volume from its normocapnic value causes a rapid decrease in oxygenation during HFOV compared to CV.
Why is increased tidal volume good?
During exercise, tidal volume increases as the depth of breathing increases and the rate of breathing increases too. This has the effect of taking more oxygen into the body and removing more carbon dioxide.
Why is increasing tidal volume good?
Since the problem in obstructive lung disease is expiratory, breathing with higher tidal volumes helps overcome airway resistance.
Does decreasing tidal volume increase pH?
Minute volume is calculated by multiplying tidal volume and respiratory rate. Increasing minute volume eliminates more carbon dioxide from the blood, increasing pH, and decreasing minute volume allows the patient to retain more carbon dioxide, decreasing their pH.
Does increased tidal volume increase dead space?
Alveolar dead space increases with tidal volume so that the sum of anatomical and alveolar (= physiological) dead space remains about 32% of tidal volume (Fig. 20.17).
What are the consequences of high tidal volume?
HIGH tidal volumes in mechanically ventilated patients with acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) lead to baro- and bio-trauma 1 , 2 and increased mortality. 3, 4 Few studies have investigated patients without ALI/ARDS, but several suggest that high tidal volumes may also be deleterious for them. 5, –, 9 It has recently been shown that ventilation with high tidal volumes is a risk factor for acquired ALI in a medical population. 5, 6, 10 Some authors plead for the generalization of a protective ventilatory strategy to many mechanically ventilated patients, especially in those at risk of developing lung injury. 11 In the case of cardiac surgery, most patients have normal lungs before surgery. Although mechanical ventilation is usually delivered for several hours, respiratory mechanics are transiently affected within the first few hours of surgery. 12 In addition, systemic inflammation because of different causes (cardiopulmonary bypass, multiple transfusions) is frequent after cardiac surgery and may be further aggravated by injurious ventilation, even if it is only delivered for a few hours. 13 However, low tidal volumes are not recommended in surgical settings 14, 15 because a reduction in tidal volume is associated with hypoxemia, probably by promoting atelectasis. 16, 17 The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical impact of high tidal volumes after cardiac surgery. Our hypothesis was that use of high tidal volumes delivered immediately after cardiac surgery increases organ failure.
What are the effects of tidal volume after cardiac surgery?
Traditional tidal volumes (10–12 ml/kg of predicted body weight) and high tidal volumes (more than 12 ml/kg of predicted body weight) were associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation, hemodynamic instability, renal failure, and prolonged stay in the ICU among patients who underwent cardiac surgery, compared with low tidal volumes (less than 10 ml/kg of predicted body weight). Use of high tidal volume was an independent risk factor for prolonged mechanical ventilation, hemodynamic instability, multiple organ failure, and prolonged ICU stay. Women and obese patients were more at risk of receiving injurious ventilation.
What is tidal volume reduction?
Tidal volume reduction is a standard of care for patients with ALI and ARDS. 19 There is no consensus for other patients, but some authors advocate broader applicability of protective ventilation. 11 Several studies have demonstrated a link between high tidal volumes and the development or aggravation of local and systemic inflammation in patients with normal lungs. 8, 9, 13, 20, –, 22 However, several studies did not observe such an effect. 23, –, 26 The studies suggesting that tidal volume reduction has a protective effect included patients who underwent surgery with one-lung ventilation, 7, 8 prolonged surgical procedures, 9, 20 and cardiac surgery. 13, 21, 22 In a recently published paper by Kor et al. it was shown that this latter group was at risk to develop early postoperative acute lung injury. 27 In the present study we showed that tidal volume was independently associated with patient outcomes after cardiac surgery. In this population, several studies showed that a protective ventilatory strategy can reduce systemic and pulmonary inflammation. 13, 21, 22 In a group of 40 patients who underwent coronary artery bypass graft surgery, Zupancich et al. demonstrated that pulmonary and systemic proinflammatory cytokines levels increase in patients ventilated with high tidal volumes but not in those ventilated with low tidal volumes. 13 In a recently published study, Sundar et al. compared ventilation with 10 versus 6 ml/kg tidal volumes after cardiac surgery. 28 The authors demonstrated that in the small tidal volumes group, fewer patients were intubated after 6 h, which may be related to the significantly higher PaCO 2 levels in this group. Also, fewer patients were reintubated in this group. 28 However, this study did not include enough patients to demonstrate differences on ICU length of stay, and data on organ dysfunction were not reported. It is likely that in the high tidal volume group, inflammation was increased as previously demonstrated. 13 Recently, it was demonstrated that increased inflammatory markers were independent predictors of major adverse cardiac events after cardiac surgery. 29 The present study is the first to demonstrate that high tidal volumes have an impact on cardiac surgery outcomes.
What is the risk of tidal volume?
Tidal volumes of more than 10 ml/kg are risk factors for organ failure and prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery. Women and obese patients are particularly at risk of being ventilated with injurious tidal volumes.
What does CABG mean in a flow chart?
Fig. 3. Flow chart of the study and the study groups based on the initial tidal volume. CABG = coronary artery bypass graft; CPB = cardiopulmonary bypass; PBW = predicted body weight.
How are continuous variables expressed?
Continuous variables are expressed as means (SD) and categorical variables as percentages. Group comparisons were analyzed using one-way ANOVA for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. Post hoc comparisons were performed using the Tukey post hoc test. A logistic regression analysis was performed to identify variables independently associated with organ failure definitions. Continuous variables were checked for the assumption of linearity in the logit using quartiles of the distribution and fractional polynomials before building the model in order to obtain the correct relationships. The graphic representations suggested linear relationships with the logit for all continuous variables. Variables from univariate logistic regressions with P < 0.20 were candidates for the multivariate regression model building. The variables were selected using two statistical approaches. First, stepwise and backward selections of variables were used in the multivariate regression model. Both approaches gave similar results. An alternative procedure to select variables was to use the best subset selection containing two to nine variables. Akaike and Sawa Bayesian information criteria were computed to validate the model selected. Conclusions were similar for both methods. To assess goodness-of-fit (calibration) for the model, a Hosmer-Lemeshow decile of risk test, Osius-Rojek normal approximation of the Pearson chi-square statistic distribution, and Stukel two degree-of-freedom test were performed. In order to appreciate the appropriate functional form between organ failure definitions and tidal volume/predicted body weight, a generalized additive model was built using the binary distribution. Smoothing was performed by spline fitting (df = 4). A linear regression analysis was performed to identify variables independently associated with length of ICU stay. The dependant variable was log-transformed to respect the linearity assumption with the continuous independent variables. The selection variables were performed using the stepwise and backward selections and the use of the best subset selection. Akaike and Sawa Bayesian information criteria were computed to validate the model selected, and conclusions were similar for both statistical approaches. As the statistics may vary from sample to sample and inference about the population must take into account these variations, we used the bootstrap technique to approximate the sampling distribution; 1,000 samples with replacement were performed. Kaplan–Meier analysis was used to examine differences in unadjusted survival without or with organ failure, with the log-rank tests used for comparison. Two-tailed values of P < 0.05 were considered significant. The univariate normality assumptions were verified using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Brown and Forsythe's variation of Levene's test statistic was used to verify the homogeneity of variances. All analyses were conducted using the SAS statistical package, version 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC).
What is TV/PBW in statistics?
Statistical model of a nonparametric logistic regression showing the dose-response relationship between the tidal volume at intensive care unit admission (ml/kg of predicted body weight) and the probability of an organ failure. TV/PBW = tidal volume/predicted body weight.
What happens to the lungs when you exercise?
During exercise, your body's production of carbon dioxide goes up. Increasing tidal volume during exercise is one way for your lungs to accommodate the exhalation of this increased carbon dioxide load. Advertisement.
What is the dead space of the lungs?
Consider the "Dead Space". Your lungs are made up of tissues that can exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen, and also of tissues that cannot. The air included in a tidal volume measurement interacts with both of these parts — so it follows that not all of the air in the tidal volume is exchanging carbon dioxide for oxygen.
Why does tidal volume increase?
Tidal volume is the volume of air you breathe in a single breath. Exercise causes an increase in tidal volume because your requirements for oxygen go up. This increase is mediated in different ways depending on when it occurs during your exercise. An increase in tidal volume is necessary to effectively meet your body's increased oxygen requirements, as an increase in your rate of respiration alone is not sufficient.
How to move air into lungs during exercise?
In order to move more air into your lungs during exercise, you have two options: increase the rate at which you're breathing, or increase your tidal volume.
What chemicals increase lung capacity?
The chemicals involved in this increase include oxygen, carbon dioxide, lactic acid, arachadonic acid and bradykinin, and the receptors involved are located on many organs throughout your body. Read more: How to Improve Lung Capacity for Running. Advertisement.
What is the function of the lungs?
Your lungs' job is to meet your body's demand for oxygen, which is required for the cells in your body to produce enough energy to function. Your lungs do this by bringing in fresh air with every breath; this amount is measured in part by the tidal volume. During exercise, your body's production of carbon dioxide goes up.
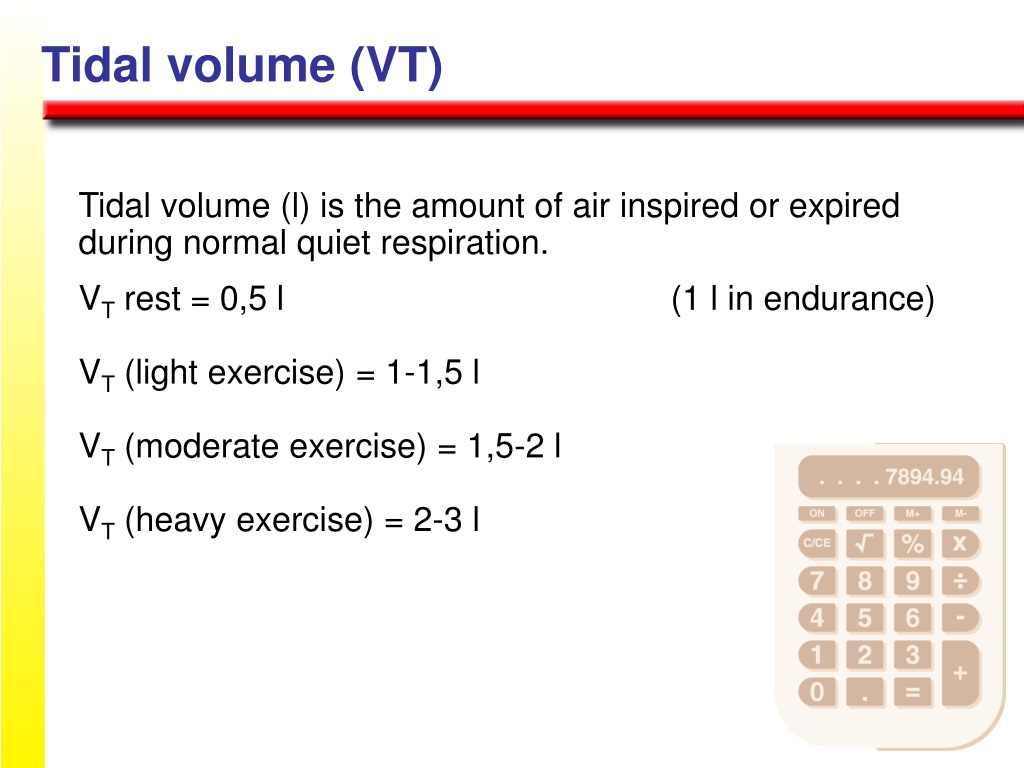
How much tidal volume is normal?
What is Tidal Volume. According to Duke University, in a normal male adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 ml of air per breath. For women, the amount is 20 to 25 percent less than that. However, changes in air requirements, such as those that occur during exercise, and changes in your lungs' ability to expand and contract, ...
Mechanical Ventilation- Increase the Rate or the Tidal Volume
Let’s assume that the patient is being ventilated with assist control ventilation.
Guidelines for the management of tracheal intubation in critically ill adults
Having read the guidelines I made these infographics. They are FREE. Just let me know your email address and they will be sent to you.
What is volume of ELF?
Volume of ELF (mL) = total amount urea in BALF (mg)/concentration of urea in plasma (mg/mL) (I)
How much V T should I use for ventilation?
Mechanical ventilation in patients without lung disease is commonly provided by using a V T around 10 ml/Kg predicted body weight and a low PEEP [ 16 ]. Few studies addressed the effects of mechanical ventilation using a high V T strategy on pulmonary inflammatory response in patients without lung disease, mostly during major surgery [ 11, 12, 16 – 18 ]. In addition, data in non acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS) ICU patients comes from retrospective analysis [ 9, 19 ]. Our study distinguishes our study from others as we have shown that protective ventilation in near normal lung patients in an ICU scenario is also beneficial by preventing additional injury.
How is urea used in BAL?
The technique of BAL is based on the concept that aliquots of sterile normal saline solution infused through the bronchoscope mix with epithelial lining fluid (ELF). The use of urea to quantify the amount of ELF recovered by BAL is based on the knowledge that urea is freely diffusible through most body compartments, including the lungs. Urea concentration was measured in BAL fluid and blood and ELF volume calculated according to the formula described below [ 15 ]. In this context, if the concentration of urea in plasma is known and the quantity of urea in a lavage sample is measured, the volume of recovery ELF can be calculated as:
How much saline is used in bronchoscopy?
BAL was performed by instillating 100 ml sterile isotonic saline (five aliquots of 20 ml) in segments of the right lower lobe and sequentially suctioned; 30% to 50% of this aliquot was recovered. The first aliquot was discharged. During bronchoscopy FIO 2 was kept at 100%. Lavage fluids were filtered through sterile gauze filters, collected on ice, and immediately centrifuged at 1,500 g for 10 minutes. Supernatant aliquots were kept frozen at -40°C for subsequent analysis.
What is the effect of mechanical ventilation with lower V T?
Mechanical ventilation with lower V T in patients without lung disease resulted in attenuation of pulmonary production of inflammatory mediators.
How long are patients on mechanical ventilation?
Patients were on mechanical ventilation for a maximum of 12 hours at the time of initiating one of the two randomized MV strategies, including the surgical period. On ICU admission, the following standard ventilation protocol was applied: patients were continuously sedated (benzodiazepines and/or opioids), remained supine and were ventilated with intermittent positive pressure ventilation, assist/control mode on a Siemens Elema 900C Servo ventilator (Solna, Sweden). V T, respiratory rate, and fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO 2) were adjusted to maintain arterial oxygen saturation >90%, PaCO 2 of 35 to 45 mmHg and pH >7.25. PEEP was kept at 5 cmH 2 O. The inspiratory:expiratory (I:E) ratio was 1:2. All ventilator circuits were equipped with a heat-moisture exchanger.
Why did all patients receive sedation and analgesia?
All patients received sedation and analgesia to keep them comfortable while on mechanical ventilation. Patients were not left on ventilation for the study and one patient was extubated and excluded from the analysis before protocol initiation.