
What is HNP medical term?
They can include:
- Chronic pain
- Pain traveling the length of a nerve
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Tingling
- Loss of reflexes
When to treat the sacroiliac joint vs. lumbar spine?
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Facet and Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Goals of Radiofrequency Ablation. Reduce neck or back pain for longer periods of time, typically for more than 6 months. ...
- Types of Radiofrequency Ablation. ...
- When Radiofrequency Ablation Is Considered. ...
- When Radiofrequency Ablation May Not be Performed. ...
- Radiofrequency Ablation Success Rates. ...
What does HNP mean?
HNP, or a herniated nucleus pulposus, is the more medically oriented term for what most people refer to as a herniated disc or slipped disc. You are certainly not alone in your diagnosis, as a herniated disc is one of the most common spine conditions among adults and there are a variety of treatment options available.
What are the symptoms of the lumbar spine?
Symptoms generated from nerve compression in the lumbar spine basically include pain, numbness, paresthesias (pins and needles sensation) and possibly motor weakness. Each nerve demonstrates slightly different symptoms in terms of specific areas of the leg that are involved. Weakness of a muscle group can lead to an abnormal walking ability ...
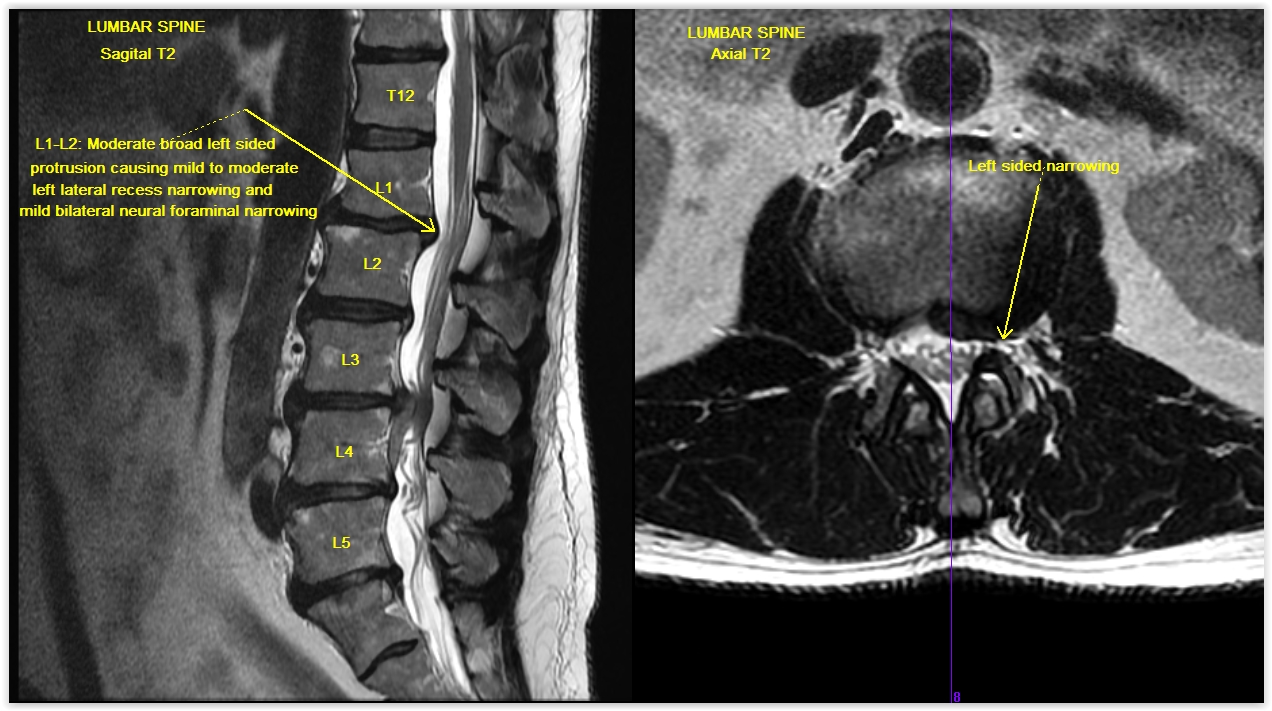
Is herniated nucleus pulposus serious?
While a herniated nucleus pulposus is asymptomatic, a protruding nucleus can compress nearby nerves or the spinal cord, sometimes leading to serious nerve damage and should be treated immediately.
What causes HNP?
Most people can't pinpoint the cause of their herniated disk. Sometimes, using the back muscles instead of the leg and thigh muscles to lift heavy objects can lead to a herniated disk, as can twisting and turning while lifting. Rarely, a traumatic event such as a fall or a blow to the back is the cause.
What does HNP mean on an MRI?
Abstract. The acute lumbar herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP) can often be diagnosed on good quality MRI or CT examination.
Is herniated nucleus pulposus the same as a herniated disc?
Bulging and Herniated Discs Explained "A bulging disc is like letting air out of a car tire. The disc sags and looks like it is bulging outward. With a herniated disc, the outer covering of the disc has a hole or tear. This causes the nucleus pulposus (jelly-like center of the disc) to leak into the spinal canal."
How long does herniated nucleus pulposus take to heal?
Self care: In most cases, the pain from a herniated disc will get better within a couple days and completely resolve in 4 to 6 weeks. Restricting your activity, ice/heat therapy, and taking over the counter medications will help your recovery.
Can herniated nucleus pulposus be fixed?
Usually, a herniated nucleus pulposus only becomes apparent when the displaced disc material interrupts the spine's structural integrity or begins to compress nearby nerves, ligaments and tissues. A disc with a herniated nucleus pulposus can almost always be managed or fully repaired through proper treatment.
What does HNP mean in medical terms?
Overview. Herniated nucleus pulposus is a condition in which part or all of the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk, resulting in back pain and nerve root irritation.
Which of the following symptoms would occur with a herniated nucleus pulposus?
Symptoms and Signs of Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Herniated disks often cause no symptoms, or they may cause symptoms and signs in the distribution of affected nerve roots. Pain usually develops suddenly, and back pain is typically relieved by bed rest.
What is diagnosis HNP?
What is a Herniated Disc? Herniation of the nucleus pulposus (HNP) occurs when the nucleus pulposus (gel-like substance) breaks through the anulus fibrosus (tire-like structure) of an intervertebral disc (spinal shock absorber).
Is herniated nucleus pulposus a permanent disability?
A herniated disc injury may result in a designation of permanent disability and make you eligible for disability benefits from workers' compensation if: The herniation compromises a nerve root or the bundle of nerves that lead out from the spinal cord.
Does nucleus pulposus grow back?
To regenerate nucleus pulposus tissue, the cells must produce an appropriate proteoglycan-rich matrix, as this is essential for the functioning of the intervertebral disc.
Can herniated nucleus pulposus causes pain?
Nucleus pulposus herniation is the most common cause of radicular pain in the lumbar spine and the second most common cause in the cervical spine after degenerative spondylosis; however, other conditions in the differential diagnosis should be considered such as: Conjoined nerve root.
HNP symptoms
Believe it or not, even if you aren’t experiencing back pain or other symptoms, it’s still entirely possible that you have one or more herniated discs at various levels of your spine at this very moment. That’s because by itself, HNP does not necessarily produce any negative side effects.
Treatment options
After asking your physician, “What is HNP?” your next question will undoubtedly be, “How do I treat it?” The good news is that most people can find relief from their pain and other symptoms through a series of conservative, non-surgical treatments.
Minimally Invasive Alternatives
Some individuals simply don’t experience pain relief through conservative methods, however, and instead turn to a last resort — elective surgery. If you haven’t been able to reduce your pain from HNP after weeks or months of conservative treatment, contact USA Spine Care today to learn more about our advanced, minimally invasive procedures.
HNP symptoms
Interestingly, HNP does not in itself result in any symptoms beyond localized disc pain. Only when the nucleus pulposus compresses a nearby nerve or the spinal cord do the more serious symptoms arise.
Treating HNP
If your doctor has determined that a herniated disc is compressing a nerve and causing your symptoms, he or she will likely recommend a treatment program consisting of one or more nonsurgical treatments. For many people, such treatments are often very effective in managing the pain and other symptoms associated with HNP.
Minimally invasive alternatives for HNP
Some patients, however, simply aren’t able to ease their HNP symptoms through conservative methods, and instead turn to elective surgery as a last resort. If this describes your situation, contact Laser Spine Institute today to learn more about our available treatments.
What is a herniated nucleus pulposus?
This is known as herniated nucleus pulposus. A herniated nucleus pulposus is a deteriorating spine condition which can also be referred to as a ruptured disc, slipped disc, or herniated disc. It is common given the normal breakdown of the body. These discs are tasked with absorbing every impact, whether harsh or light every, ...
What is the spine?
The spine is a complex structure that supports the body and houses the central nervous system. It consists of a chain of vertebrae, each separated by intervertebral discs that act as cushions between them. These cushions can become worn from overuse as you get older. Injury, or possibly even disease can advance degenerative spine conditions, ...
What is the best treatment for a herniated nucleus pulposus?
Surgically, this means a discectomy, foraminotomy, or laminectomy are most useful in the treatment of herniated nucleus pulposus. All of these surgeries can be performed by a skilled orthopedic surgeon in an outpatient setting. These three procedures are safer and more effective alternative to open back surgery.
Why is herniated nucleus pulposus so hard to diagnose?
Herniated nucleus pulposus is tough to diagnose at times because it does not always cause localized pain. In some cases it isn’t until the nerves are compressed that the symptoms begin to show. Once a nerve has become pinched, it’s only a matter of time until symptoms grow more severe.
What is a spine surgeon?
A Spine Surgeon can diagnose your condition and discuss conservative and interventional treatment options. Depending on the site of discomfort and the longevity of your symptoms, your options for effective treatment will vary.
Where does pain originate from in the spinal cord?
It is important to note that painful symptoms are largely absent the disc material comes into contact with the nerves at their roots in the spinal cord. This is where the discomfort and pain originates — a pinched nerve.
Does orthopedic surgery help with herniated nucleus pulposus?
Orthopedic surgery has helped thousands of Americans find relief for their persistent pain and numbness. Individuals who seek long-term relief for herniated nucleus pulposus need not look any further than an orthopedic surgeon.
How many stages of HNP?
The progression to an actual HNP varies from slow to sudden onset of symptoms. There are four stages: (1) disc protrusion (2) prolapsed disc (3) disc extrusion (4) sequestered disc. Stages 1 and 2 are referred to as incomplete, where 3 and 4 are complete herniations. Pain resulting from herniation may be combined with a radiculopathy, ...
What is the term for the herniation of the nucleus pulposus?
Herniation of the nucleus pulposus (HNP) occurs when the nucleus pulposus (gel-like substance) breaks through the anulus fibrosus (tire-like structure) of an intervertebral disc (spinal shock absorber).
What does it mean when your hip is flexed?
The patient lies down, the knee is extended, and the hip is flexed. If pain is aggravated or produced, it is an indication the lower lumbosacral nerve roots are inflamed. Other neurological tests are performed to determine loss of sensation and/or motor function.
Is Dr Dawson's article on herniated discs accurate?
Dawson's article on herniated disc is quite informative, and it has been written in such a way for a lay person to understand the content. The description on the extent of herniation is quite accurate and MRI is quite helpful in determining the type and location of herniated disc.
What is the term for the degeneration of the spine?
Spinal Spondylosis: Also called spinal osteoarthritis, spondylosis is a generic term that describes spinal degeneration, typically brought on by the natural aging process. The wear and tear of the spinal discs, muscles, tendons, ligaments or cartilage can cause inflammation, joint friction, or painful, stiff and weak back muscles.
Why is the spine important?
Quite literally the pillar of strength, and the backbone of your body, your spine is an important measure of your overall health. From age-triggered osteoarthritis or poor posture, to impact sports injuries or obesity, there are various reasons why you may develop spinal injuries or other degenerative conditions.
How to treat stenosis?
Most often, you will find relief for stenosis, spondylosis or HNP through conservative, non-surgical methods such as: 1 Complete bed rest or drastic reduction in strenuous physical activities 2 Over-the-counter pain relief medication, or anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen 3 Prescription medication with higher doses, if over-the-counter options do not work 4 Joint injections that temporarily numb the pain 5 Epidural or corticosteroid steroid injections that arrest and reduce the inflammation around a compressed nerve root 6 Physical therapy or chiropractic care for healing soft tissues and strengthening the muscles that support the spine
How to treat stenosis and spondylosis?
Most often, you will find relief for stenosis, spondylosis or HNP through conservative, non-surgical methods such as: Complete bed rest or drastic reduction in strenuous physical activities. Over-the-counter pain relief medication, or anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
What is the best treatment for a compressed nerve root?
Epidural or corticosteroid steroid injections that arrest and reduce the inflammation around a compressed nerve root. Physical therapy or chiropractic care for healing soft tissues and strengthening the muscles that support the spine.
Can spondylosis affect your back?
This can significantly impact or impair your bodily movements. Depending on the location of the affected area, the spondylosis may be lumbar (lower back), thoracic (upper or mid back), cervical (neck) or multilevel.
