
What causes cerumen impaction?
Nov 08, 2021 · Impacted earwax (cerumen) is a blockage of your ear canal by earwax. Earwax impaction can lead to conductive hearing loss and other issues, so it’s important to learn how to recognize the symptoms. Learn how earwax impaction happens and what treatments are available to quickly get rid of earwax blockage. We’ll also go over earwax impaction prevention …
What are the symptoms of cerumen impaction?
What is Impacted Cerumen? Our bodies naturally produce cerumen, or earwax, to keep the external ear canal free from detritus that might impact on our ability to hear. But sometimes this cleaning mechanism can go wrong and the wax itself becomes impacted.
How is cerumen impaction diagnosed?
Apr 10, 2022 · A cerumen impaction is an accumulation of cerumen that causes symptoms, such as hearing loss, fullness, otorrhoea, tinnitus, dizziness, or other symptoms, and/or prevents a required assessment of the ear canal, tympanic membrane, or audiovestibular system.
When is irrigation for Impacted cerumen contraindicated?
Apr 18, 2022 · Cerumen is the technical term for earwax, and a cerumen impaction refers to an earwax blockage. Over time, a gradually worsening impaction can cause an earache, mild hearing loss, or ringing noises in the ear called tinnitus. Earwax blockages can usually be cleared at home with simple techniques.
What is the cause of impacted cerumen?
What is the meaning of impacted cerumen?
What are the symptoms of impacted earwax?
- Earache.
- Feeling of fullness in the affected ear.
- Ringing or noises in the ear (tinnitus)
- Decreased hearing in the affected ear.
- Dizziness.
- Cough.
How is cerumen impaction diagnosed?
How do you remove cerumen impaction?
How do you remove impacted cerumen?
Is ear wax removal painful?
What is the best ear wax removal?
If you have a small amount of wax, over-the-counter ear cleaners work well. Look for drops that contain hydrogen peroxide or other kinds of peroxide. The peroxide does a good job of breaking up earwax.Nov 29, 2021
What color should ear wax be?
Who is at risk for cerumen impaction?
Will impacted ear wax fix itself?
How to diagnose cerumen impaction?
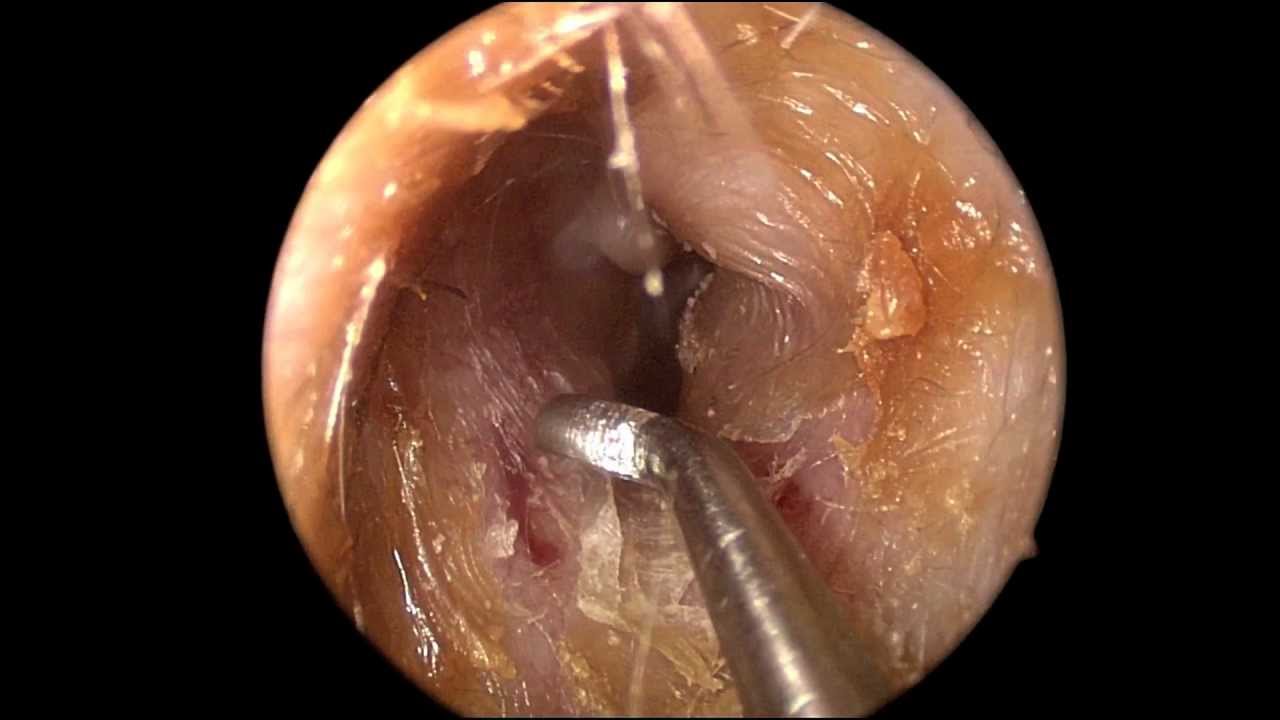
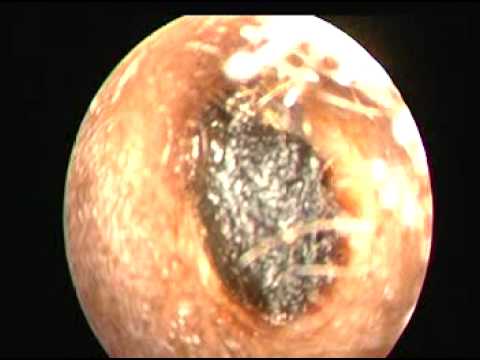
The diagnosis of cerumen impaction is made by direct visualization with an otoscope. Common symptoms include hearing loss, feeling of fullness in the ear, itching, otalgia, tinnitus, cough, and, rarely, a sensation of imbalance. 1, 7 Hearing loss from cerumen impaction can cause reversible cognitive impairment in older persons. 8 Some patients are unable to accurately convey symptoms, such as those with dementia or developmental delay; nonverbal patients with behavioral changes; and young children with fever, speech delay, or parental concerns. In these patients, cerumen should be removed when it limits examination. 3, 9, 10
Why do radiation patients have drier cerumen?
Patients with a history of head and neck radiation may have drier cerumen and require more careful debridement, because injury to the ear canal may evolve into osteoradionecrosis of the external auditory canal or temporal bone. 3 The presence of dermatologic conditions, such as eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and ectodermal dysplasia, can increase the frequency of impaction and the risk of otitis externa. 16 Anatomic challenges, such as narrowing of the ear canal, congenital or acquired stenosis, diffuse exostoses, and solitary osteomas (bony projections into the ear canal), can make irrigation or manual instrumentation difficult and can increase the risk of otitis externa. Microscope-assisted mechanical removal of cerumen is the preferred technique in patients with a perforated tympanic membrane or who have a patent tympanostomy tube.
What is earwax?
Cerumen, or earwax, is a combination of glandular secretions and desquamated epithelial cells that cleans, protects, and lubricates the external auditory canal. 1 Cerumen is typically expelled from the ear canal spontaneously via a self-cleaning mechanism that is assisted by jaw movement. 2 In some persons, however, this mechanism fails and cerumen becomes impacted. Cerumen impaction is defined as an accumulation of cerumen that causes symptoms or prevents assessment of the ear canal, tympanic membrane, or audiovestibular system; complete obstruction is not required. 3 Cerumen impaction is a common reason for consultation with primary care physicians and is present in about 10% of children, 5% of healthy adults, up to 57% of older persons in nursing homes, and one-third of patients with mental retardation. 1, 4 – 6 Cerumen-related procedures accounted for nearly $50 million in Medicare spending in 2012. 6
What is cerumenolytic agent?
Cerumenolytic agents are commonly used alone or in combination with irrigation or manual instrumentation to remove impacted cerumen. Topical preparations are available in three forms: water-based, oil-based, and non–water or oil-based ( Table 1). 19, 20 Based on low- to moderate-quality studies, a 2009 Cochrane review concluded that using ear drops is better than no treatment, but it is unknown whether any formulation is superior. 21 Although ear drops have the advantage of easy application and no risk of mechanical damage, some may cause ear canal irritation or contact dermatitis. Clinicians should ensure that the patient has no history of allergies to any of the components. Ear drops should be close to body temperature to avoid caloric effects (vertigo), and should not be used if there is a possibility that the tympanic membrane is not intact, if a patent tympanostomy tube is present, or if the ear canal is infected. 3
What is the best way to remove cerumen?
Manual removal of cerumen is the preferred technique in patients with abnormal ear canal anatomy, a history of ear surgery, systemic illnesses that increase the risk of infection, or a nonintact tympanic membrane. To minimize the risk of trauma, a cooperative patient and greater clinical skill than for other removal methods are required. 24 Manual removal is often quicker, involves the use of a metal or plastic loop or spoon, and allows direct visualization via a handheld otoscope or binocular microscope.
How many tympanic membranes are visualized without irrigation?
In one study, one-fifth of tympanic membranes were visualized without irrigation
Why should ear drops be close to body temperature?
Ear drops should be close to body temperature to avoid caloric effects (vertigo), and should not be used if there is a possibility that the tympanic membrane is not intact, if a patent tympanostomy tube is present, or if the ear canal is infected. 3. Enlarge Print. TABLE 1.
What are the symptoms of impacted cerumen?
These include a difficulty hearing, ringing in the ears, bad odors coming from the ear canal and dizziness. In addition, impacted cerumen is frequently accompanied by discharge coming out of the ear and a feeling of fullness in the ear canal.
How does ear wax move?
Secreted by the ear canal, earwax slowly moves towards the outside of the ear during chewing or speaking and then dries and flakes off when it reaches the outside world. However, this mechanism can fail.
Can hearing aids cause cerumen?
Impacted cerumen can lead to quality of life issues, especially for people who regularly use hearing aids. Because hearing aids are a risk factor for the condition, it’s worth paying a visit to your audiologist. At The Center for Audiology, our experts can help assist you in managing impacted cerumen and offer advice to prevent the condition from developing.
What is cerumen impaction?
A cerumen impaction is an accumulation of cerumen that causes symptoms, such as hearing loss, fullness, otorrhea, tinnitus, dizziness, or other symptoms, and/or prevents a required assessment of the ear canal, tympanic membrane, or audiovestibular system. [1]
What is the intervention for a cerumen impaction?
Intervention may include manual removal, irrigation, or use of cerumenolytic agents, or a combination of these modalities. After treatment, the clinician should re-examine the patient's ear and document the resolution of the cerumen impaction, and also inspect the previously occluded tympanic membrane.
What is cerumen in ear?
Summary. Cerumen is a naturally occurring substance that cleans, protects, and lubricates the external auditory canal. Impaction is diagnosed when an accumulation of cerumen results in symptoms, such as hearing loss, or when it prevents adequate assessment of the ear canal or tympanic membrane. Intervention may include manual removal, irrigation, ...
Who is at high risk for cerumen?
Young children, older patients, individuals with a cognitive impairment, and those in nursing homes are at high risk for cerumen impactions. Hearing-aid users are also at increased risk. These patients should be examined carefully for cerumen impaction during routine healthcare encounters.
How to remove cerumen impaction?
Most cases of cerumen impaction can be relieved with simple home remedies. Many people try to clean their ears with cotton swabs, though doctors generally advise against the practice as a swab can potentially damage the eardrum or push earwax further into the canal, thereby worsening the impaction. Instead, a person can take steps to soften the earwax and remove it with a soft cloth or tissue.
What is the purpose of the cerumen in the ear canal?
Glands in the ear canal produce cerumen to help trap dirt, bacteria, and other pathogens.
How to diagnose impacted cerumen?
The diagnosis of impacted cerumen is usually made by examining the ear canal and eardrum with an otoscope, an instrument with a light attached that allows the doctor to look into the canal.
How to tell if you have cerumen impaction?
Symptoms. The most important symptom of cerumen impaction is partial loss of hearing. Other symptoms are. Ear wax is removed by flushing the ear canal with warm fluid. itching, tinnitus (noise or ringing in the ears), a sensation of fullness in the ear, and pain.
What is the term for a condition in which earwax has become tightly packed in the outer ear
Impaction — A condition in which earwax has become tightly packed in the outer ear to the point that the external ear canal is blocked. Irrigation — The technique of removing cerumen from the ear canal by flushing it with water. Myringotomy — Surgical cutting of the ear drum to allow fluid to escape from the middle ear.
Why is my ear impacted by cerumen?
Causes. Cerumen is most likely to become impacted when it is pushed against the eardrum by cotton-tipped applicators, hair pins, or other objects that people put in their ears; and when it is trapped against the eardrum by a hearing aid. Less common causes of cerumen impaction include overproduction of earwax by the glands in the ear canal, ...
What are the symptoms of cerumen impaction?
The most important symptom of cerumen impaction is partial loss of hearing. Other symptoms are
What is impaction in earwax?
Impaction— A condition in which earwax has become tightly packed in the outer ear to the point that the external ear canal is blocked.
What is the term for earwax that accumulates in the inner part of the ear canal and blocks
Description. Cerumen impaction develops when earwax accumulates in the inner part of the ear canal and blocks the eardrum. It affects between 2%-6% of the general population in the United States. Impaction does not happen under normal circumstances because cerumen is produced by glands in the outer part of the ear canal;
What is cerumen impaction?
Cerumen is a naturally occurring, normally extruded product of the external auditory canal. It is usually asymptomatic, but when it becomes impacted it can cause complications such as hearing loss, pain, or dizziness. It also can interfere with examination of the tympanic membrane. Depending on available equipment, physician skill, and patient circumstances, treatment options for cerumen impaction include watchful waiting, manual removal, the use of ceruminolytic agents, and irrigation with or without ceruminolytic pretreatment. The overall quality of the evidence on treatment is limited. Referral to an otolaryngologist for further evaluation is indicated if treatment with a ceruminolytic agent followed by irrigation is ineffective, if manual removal is not possible, if the patient develops severe pain or has vertigo during irrigation, or if hearing loss is still present after cerumen has been removed. The use of cotton swabs and ear candles should be avoided.
How to diagnose cerumen impaction?
Cerumen impaction is diagnosed by direct visualization with an otoscope. Foreign bodies and a swollen canal from otitis externa can impair tympanic membrane visualization and should be ruled out before attempting cerumen removal. Impaction is a common cause of hearing impairment in older patients and in patients with mental retardation; therefore, it is reasonable to evaluate for cerumen impaction in patients with hearing problems. Similarly, it is appropriate to examine for cerumen impaction in older patients and in patients with mental retardation upon admission to a hospital or institution, as well as periodically thereafter. In one study, 35 percent of hospitalized patients older than 65 years had cerumen impaction and 75 percent of those had improved hearing after documented earwax removal. 5
Why is cerumen removed?
Because cerumen serves a protective function for the skin in the external auditory canal, removal has been associated with complications including otitis externa, pain, dizziness, syncope, tinnitus, tympanic membrane perforation, and even cardiac arrest.
What is the treatment for cerumen impaction?
Depending on available equipment, physician skill, and patient circumstances, treatment options for cerumen impaction include watchful waiting, manual removal, the use of ceruminolytic agents, and irrigation with or without ceruminolytic pretreatment. The overall quality of the evidence on treatment is limited.
How to remove cerumen?
Cerumen removal may be attempted by irrigation of the external auditory canal , with or without the use of ceruminolytics; by ceruminolytics alone; or by manual removal using a curette, forceps, or suction . Systematic reviews and one meta-analysis have evaluated these treatment options. 11 – 15 The body of evidence on treatment of cerumen impaction is limited, highlighting a need for well-designed, randomized trials to better inform clinical practice.
How long does it take for ceruminolytics to clear?
11 – 15 One small study comparing ceruminolytics with watchful waiting found that 5.3 percent of patients who were not treated had complete clearing of impacted cerumen and 26.3 percent had moderate clearing after five days. 16
What is the earwax?
Cerumen (i.e., earwax) is composed of secretions and sloughed epithelial cells and hair from the external auditory canal. It protects the skin in the canal and is naturally extruded. However, cerumen may accumulate and occlude the canal of one or both ears, causing discomfort, hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness, and chronic cough.
How to tell if you have impacted cerumen?
Common signs of impacted cerumen include a feeling of fullness in the ear, pain, ringing and dizziness. If the cerumen is not removed and continues to build up, it can cause more hearing loss. The wax builds up in front of the ear drum and greatly effects the sound coming into the ear.
What is the purpose of cerumen?
The cerumen acts as a stopping point for bacteria and fungus, causing them to get stuck in the sticky wax. These harmful substances then leave the body rather than penetrating further into the ear canal and causing damage. Anatomy of the Ear.
How to remove cerumen from ear?
The water bounces off of the ear drum and drains back out the ear. The force of the water loosens the impacted cerumen and drains it as the water is leaving the ear canal. A doctor may also use an ear curette or scoop to remove ear wax. This is only ever done by a trained doctor as the curette can damage the ear drum if inserted too far in the canal.
How to remove ear wax from ear drum?
To safely remove ear wax, doctors will often prescribe an over the counter wax softener. A few drops are placed in the ear, and the cerumen will loosen and drain on its own. This can also be done in a doctor's office, especially if they are trying to examine an ear and the wax is impeding the view of the ear drum.
Why is it important to have cerumen removed?
Sometimes wax will build up or be seen on the outer ear, and this is easily washed away. Impacted cerumen can result in hearing loss, which is why it is important to have it removed appropriately.
What is the medical term for ear wax?
Cerumen is the medical term for ear wax. It is made by the body in the outer ear canal as a way to protect and clean the ear. The yellowish waxy substance is a combination of lubricants and dry tissue from the body.
Why does the ear produce cerumen?
The ear produces cerumen to protect the ear canal from foreign bodies like bacteria, fungus and insects. Cerumen usually is drained by the natural movements of the ear, but sometimes it can build up. A build up of cerumen is called an impaction, and while not serious, can lead to hearing problems.
What is the purpose of cerumen?
Cerumen moisturizes the skin of the external auditory canal and protects it from infection, providing a barrier for insects and water. Cerumen is typically expelled from the ear canal spontaneously through natural jaw movement. However, in certain individuals, the self-cleaning mechanism fails, and cerumen can become impacted. [1][2] Cerumen impaction can occlude the canal or press against the tympanic membrane, potentially causing ear discomfort, conductive hearing loss, itching. Cerumen impaction occurs in up to 6% of the general population, affecting 10% of children and greater than 30% of the elderly and cognitively impaired. It is often seen in patients who routinely wear hearing aids or earplugs or patients with exostoses or anatomic abnormalities of the external ear canal. [1]
Why is it important to remove cerumen?
It is important to ensure other diagnoses are not falsely-attributed to the cerumen in patients being treated for cerumen impaction. The list of common presenting complaints is long and includes symptoms with many different causes such as otalgia, tinnitus, dizziness, hearing loss, aural fullness, ear itching, or foreign-body sensation. Once cerumen is removed, it is important to rule out diagnoses such as otitis media, otosclerosis, sensorineural hearing loss, temporomandibular joint syndrome, and upper respiratory tract infections, or other causes via further examination and testing if symptoms persist. [1]
How to remove cerumen from ear?
Commonly, warm water alone or a 50/50 mix of water and hydrogen peroxide is inserted into a syringe and discharged into the ear canal with a basin underneath. Another option is a standard oral jet irrigator, with or without a modified tip. Although these methods are inexpensive and generally safe, they can be potential causes of trauma, including perforation of the tympanic membrane. There are electronic irrigators available as well; however, there are no controlled trials to compare the different irrigation methods.
What is cerumenolytics?
Cerumenolytic agents are liquid solutions that help thin, soften, break up, and/or dissolve ear wax. These are typically water- or oil-based compounds, with water-based solutions being the most commonly used. Typical ingredients found in water-based cerumenolytics include hydrogen peroxide, acetic acid, docusate sodium, and sodium bicarbonate. Common ingredients in oil-based cerumenolytics include peanut, olive, and almond oil. Most drops are available over the counter. Typically, up to five drops are used per dose one to two times daily for three to seven days.
Can a cerumen be removed?
There are no absolute contraindications to cerumen removal. Physicians should exercise caution in patients with certain immunosuppressive illnesses (HIV, diabetes mellitus), chronic anticoagulation, or anatomical defects narrowing the canal as they may be prone to complications from manual removal. In patients with diabetes mellitus, a higher pH is typically present in the cerumen, making superimposed bacterial infections potentially common. Immunosuppressed patients (diabetes mellitus, HIV, other malignancy) are at higher risk of infection after even minor trauma, so meticulous atraumatic technique should be used in removal. Additionally, this population is at higher risk for malignant otitis externa, which can mimic cerumen impaction or aural polyp to the inexperienced examiner. Caution should be exercised in chronically anticoagulated patients as they are at a higher risk for hemorrhage or hematomas. Irrigation should not be utilized as a method for cerumen removal unless the tympanic membrane can be visualized first to rule out perforation. [6][7]
Is cerumen impingement asymptomatic?
Although the excessive accumulation of cerumen is typically asymptomatic, patients should be treated if they present with hearing loss, ear fullness, pruritus, dizziness, tinnitus, or otalgia. The inability to examine an ear due to cerumen impaction is another indication for cerumen removal.
Is it necessary to remove cerumen?
When discovered in the asymptomatic patient, it is not always necessary to treat. It is important to relate to patients that cerumen does not always need to be removed, as cerumen naturally has bacteriocidal, protective, and emollient properties. Observation should be offered as a management strategy if appropriate.
Management
Diagnosis
- The diagnosis of cerumen impaction is made by direct visualization with an otoscope. Common symptoms include hearing loss, feeling of fullness in the ear, itching, otalgia, tinnitus, cough, and, rarely, a sensation of imbalance.1,7 Hearing loss from cerumen impaction can cause reversible cognitive impairment in older persons.8 Some patients are una...
Contraindications
- Cerumen in the ear canal can compromise auditory or vestibular testing and should therefore be removed before these tests are performed. Cerumen does not affect temperature measurement with an ear thermometer.12 Patients with coagulopathies, hepatic failure, thrombocytopenia, or hemophilia and those taking antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications should be counseled abo…
Treatment
- Patients with a history of head and neck radiation may have drier cerumen and require more careful debridement, because injury to the ear canal may evolve into osteoradionecrosis of the external auditory canal or temporal bone.3 The presence of dermatologic conditions, such as eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and ectodermal dysplasia, can increase the frequency of impacti…
Use
- Cerumenolytic agents are commonly used alone or in combination with irrigation or manual instrumentation to remove impacted cerumen. Topical preparations are available in three forms: water-based, oil-based, and nonwater or oil-based (Table 1).19,20 Based on low- to moderate-quality studies, a 2009 Cochrane review concluded that using ear drops is better than no treatm…
Risks
- In a randomized trial of 237 adults with symptomatic cerumen impaction, those who received cerumenolytic drops and instructions for home irrigation with a bulb syringe had similar outcomes and satisfaction as those who received in-office irrigation by a primary care clinician.23 However, it is unclear if these results are generalizable to all patients with cerumen impaction, particularly …
Prevention
- The 2017 guideline on cerumen impaction by the American Academy of OtolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery Foundation, endorsed by the American Academy of Family Physicians, recommends that clinicians provide counseling on proper ear hygiene, especially to patients with cerumen impaction and those who are particularly susceptible, such as children, older adults, and patient…
Safety
- Although cleaning the outer ear is acceptable once cerumen is visible, patients should not insert foreign bodies into the ear canal, including cotton-tipped swabs and candles.3 Ear candling consists of lighting one end of a hollow candle and placing the other end in the ear canal. It is thought that the flame creates negative pressure, drawing wax and debris out of the ear. Howev…