dental pulp the richly vascularized and innervated connective tissue inside the pulp cavity of a tooth. digital pulp a cushion of soft tissue on the palmar or plantar surface of the distal phalanx of a finger or toe.
What damages a tooth's pulp in the first place?
Some of the common causes of damage to tooth's pulp include physical trauma to the tooth, a deep cavity that extends close to the dental pulp, a cracked tooth, preparations for dental crown placement, repeated invasive dental procedures and bruxism or teeth clenching can cause the blood vessels in the pulp to get inflamed.
Which is better pulp or no pulp?
The pulp is little orange particles in orange juice (but it's not like skin or anything, it's perfectly edible and imo makes the drink better) while no pulp filters it all out, just leaving the juice. Basically, orange juice with pulp is more natural while orange juice without pulp is more processed.
What are the functions of the pulp of the tooth?
What is the Pulp of the Tooth?
- Composition of the tooth. The enamel is a thin, hard (hardest substance in our body) outer layer. ...
- Composition of the Pulp. The pulp itself is composed of connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels. ...
- Functions of the Pulp. Formation of new dentin via the odontoblasts. ...
- Diseases of the Pulp. ...
- Prevention of Pulp Disease. ...
What do I do if my tooth pulp is exposed?
What You Should Do
- Gather the broken pieces and place them in a clean, dry container for transport to the dentist.
- Rinse the remaining tooth with warm water to remove dirt and debris.
- If an injury broke the tooth, place a cold compress on the area to help prevent swelling.
- Call your dentist to arrange an appointment. ...

What does the pulp cavity contain?
Our pulp cavities are critical. They contain the nerves and blood supply that keep our teeth alive. Each cavity includes two parts: the pulp chamber and the root canals. The pulp chamber is the upper section of the cavity contained within the crown of the tooth.
What is found in the pulp of teeth mainly?
Cells found in the dental pulp include fibroblasts (the principal cell), odontoblasts, defence cells like histiocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, mast cells, and plasma cells.
What types of cells does pulp contain?
Histology of Dental Pulp Dental pulp is a loose connective tissue with an appearance similar to mucoid CT. It contains the components common to all connective tissues: Cells: fibroblasts and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells (Lab Image 1 ) as well as other cell types (macrophages, lymphocytes, etc.)
What are the cells of dental pulp?
Dental pulp is a specialized tissue consists of several cell types including DPSCs, odontoblasts, endothelial cells, immune cells, and neurons. It also contains growth factors (GFs) and the ECM (Monteiro and Yelick, 2019).
Where is the dentin found?
Primary dentin, the most prominent dentin in the tooth, lies between the enamel and the pulp chamber (near dentinoenamel junction). The outer layer closest to enamel is known as mantle dentin.
Why is pulp called pulp?
Cocker's original preference was to name the band after the film Pulp starring Michael Caine, though it was decided that this was too short. Instead, the two took inspiration from a copy of the Financial Times which listed the Arabicas coffee bean in its commodity index.
What is plexus Raschkow?
a plexus of myelinated nerve fibers located between the core of the pulp of the tooth and the cell-rich zone; axons of Raschkow plexus lose their myeline sheath (but not their Schwann cells) as they penetrate the cell-rich and cell-free zones to make synaptic contact with the odontoblast cell body in the pulp or ...
Where is the enamel?
Tooth enamel is the thin outer covering of a tooth. It covers the crown of the tooth, which is the part you can see outside of the gums. Although it is the outer layer, enamel is see-through. Dentin, the hard tissue beneath the enamel, is what gives teeth their color.
What is the pulp of a tooth?
Your tooth pulp is the innermost layer of your tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. Your tooth pulp is protected by layers of dentin and enamel. However, tooth decay or injuries to your tooth can expose your pulp and make it susceptible to infection. If you notice any signs of tooth decay or have symptoms such as pain, sensitivity, ...
Where is the pulp located in a tooth?
Your tooth pulp is found in the hollow center of your tooth. This hollowed out area is divided into two parts: your pulp chamber and your root canal. Your pulp chamber is the hollowed-out space in the body or crown of your tooth, and your root canal is the section that extends down the root.
What is the condition that causes hard lumps of calcium to form in your teeth?
Dental pulp calcification is a condition that causes hard lumps of calcium to form in your pulp. These hard lumps are also known as dental pulp stones. Pulp stones can develop in one or all of your teeth, according to a 2016 research review.
What is the function of the nerves in the pulp of a tooth?
Nerves in your dental pulp help protect your tooth by allowing you to sense damage to your tooth as well as changes in temperature or pressure. Your tooth pulp is the only part of your tooth that contains blood vessels and nerves. If your pulp becomes severely damaged, your tooth will lose its blood and nerve supply.
How to prevent tooth pulp necrosis?
This includes: brushing your teeth twice a day for a minimum of 2 minutes each time with a soft-bristled brush.
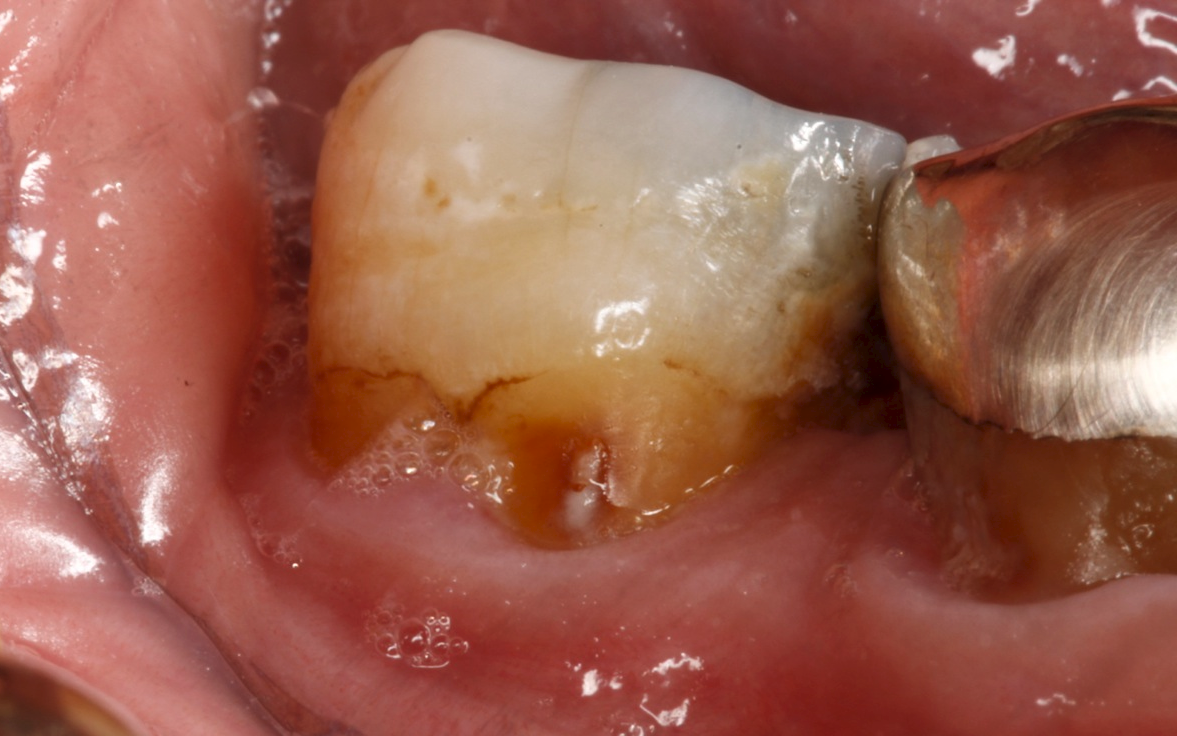
Why is my tooth pulp exposed?
Your tooth pulp is protected by the harder outer layers. But if your tooth is damaged or if you have tooth decay , the pulp can become exposed. Exposed pulp is susceptible to an infection and requires prompt treatment from a dental professional.
What is the function of tooth pulp?
The main functions of your tooth pulp are to create dentin. Trusted Source. and to provide your tooth with nutrition. Your tooth pulp also helps keep your dentin layer healthy by providing it with moisture and essential nutrients like albumin and fibrinogen.
What are the two parts of a pulp cavity?
Pulp cavities contain two main parts: the pulp chamber and the root canals. The pulp chamber is the upper section of the cavity contained within the crown of the tooth. The root canals are the lower section of the cavity found within the tooth roots. According to a review published in the Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, the number of roots may vary from a tooth on the upper jaw (also known as a maxillary tooth) to a tooth on the lower jaw (also known as a mandibular tooth). The number of root chambers in the pulp cavity may vary from tooth to tooth, as well.
How to prevent cavities in the pulp of the tooth?
Remember to brush your teeth twice a day and floss once per day. A good oral hygiene routine helps remove food particles and plaque from the teeth, which helps prevent cavities.It's also important to protect your teeth from trauma that could injure the pulp cavity. If you play sports, wear an appropriate sports mouth guard. If you clench your teeth and your dentist has recommended a bruxism mouth guard, remember to wear it at night.In addition, see your dentist regularly for check-ups. At these visits, your teeth will be thoroughly cleaned to remove plaque and tartar. The dentist can also thoroughly examine your teeth for problems like cavities that could affect the pulp cavity if left untreated.Pulp cavities are an important part of the teeth's structure. To protect the pulp cavities, follow a good oral hygiene routine, protect the teeth from trauma and see a dentist regularly.
How do you know if you have a tooth abscess?
Symptoms of a tooth abscess may include a severe toothache, facial swelling or a fever. If you have signs of a tooth abscess, see your dentist immediately.Cavi ties and dental trauma aren't the only situations that can affect the pulp cavities. The blood vessels within the pulp can become inflamed due to stressors like repeated dental procedures or clenching and grinding the teeth, a condition known as bruxism. A dentist can evaluate the affected teeth and recommend an appropriate treatment. In some cases, the pulp inflammation goes away once the source of irritation is gone. In other cases, the pulp has been damaged beyond repair and needs to be removed.
What are the optical properties of teeth?
Color is always considered the most crucial property. Besides color, opacity and translucence; fluorescence; opalescence; and metamerism, etc. also play important roles in the optical characteristics of teeth. All these optical properties are attributed to the special compositions or construction of natural teeth, when exposed to light and as seen by the human eye.
What is fluorescence in teeth?
Fluorescence is the emission of luminous energy by a material when a beam of light is shone on it. 17 Natural teeth are fluorescent. By absorbing ultraviolet light (365 nm), blue or white visible light is emitted. Particularly in the blue region (450 nm) of the spectrum, fluorescence becomes polychromatic with great intensity. It gives natural teeth a blue and white appearance under fluorescent light, which is complementary to the yellow color observed under visible light. Fluorescence of natural teeth originates from the fluorescent substances contained in dental tissues. Dickson et al. first reported that dentin was more fluorescent than enamel. 26 When ultraviolet radiation (365 nm) hits dentin, fluorescent light with a 440±10 nm wavelength is emitted, the intensity of which is four times that emitted by enamel under the same conditions. The main fluorescent substances in dentin and enamel are dentinal tubules and enamel lamellae and tufts, respectively. The positive correlation between the intensity of fluorescence and the degree of mineralization of the tissue has been confirmed. 27 Increases in fluorescence intensity are also caused by structural arrangements such as those found in the Hunter-Schreger bands of enamel. Opinions on the effect of fluorescence on tooth color are controversial. 28 Some researchers consider that the fluorescent light emitted by both dentin and enamel could increase the lightness and whiteness of natural teeth without obvious changes in translucency, while others believe that the influence of fluorescence on tooth color is too small to be detected under daily lighting conditions.
How to tell if a tooth is in a fire?
Heat-related colour changes in roots are distinct. It is even possible to determine how deeply a tooth sat in its socket during the fire; that part of the root that was protected will be black to dark blue or grey, whereas the exposed root will be grey or white. If a root falls out of its socket onto the ground, then the groundside is darker in colour than the more heat-exposed side, which becomes calcined. Because roots are protected for at least some of the burning period, individual roots are frequently multi-coloured.
Do cheek teeth have multiple roots?
This is due, in part, to the fact that cheek teeth have multiple roots, giving them a greater likelihood of being found simply because of their great frequency. However, there may be another variable that helps to keep roots around long enough to be recovered virtually intact: unlike enamel crowns, roots are always imbedded in alveoli, even after the tooth has erupted, which means they are constantly protected. As noted, anterior teeth are single-rooted and are susceptible to falling out once the soft tissues have either decayed or burned away. The molars, by virtue of being multi-rooted, are firmly placed in their alveoli and rarely fall out until the roots themselves fracture. Usually the exception to this rule is the third molar because its roots often fuse and create what is essentially a large, single cone-like root.
What is the pulp of a tooth made of?
The pulp is the part in the center of a tooth made up of living connective tissue and cells called odontoblasts. The pulp is a part of the dentin–pulp complex (endodontium).
What are the cells in the pulp of the tooth?
Cells found in the dental pulp include fibroblasts (the principal cell), odontoblasts, defence cells like histiocytes, macrophage, granulocytes, mast cells and plasma cells. The nerve plexus of Raschkow is located central to the cell-rich zone.
Why is pulp considered pulp?
The pulp has a background similar to that of dentin, because both are derived from the dental papilla of the tooth germ. During odontogenesis, when the dentin forms around the dental papilla, the innermost tissue is considered pulp.
What is the Pulpal core?
Pulpal core, which is in the center of the pulp chamber with many cells and an extensive vascular supply; except for its location, it is very similar to the cell-rich zone. Cell rich zone; which contains fibroblasts and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells.
Which plexus is separated from the odontoblasts?
They branch to form the subodontoblastic nerve plexus of Raschkow which is separated from the odontoblasts by a cell-free zone of Weil, therefore this plexus lies between the cell free and cell rich zones of the pulp. Legend: 1 - Odontoblast layer; 2 - Cell-free zone of Weil; 3 - Cell-rich zone; 4 - Pulp core.
Why do teeth have pulp necrosis?
It is often subsequent to chronic pulpitis. Teeth with pulp necrosis will need to undergo root canal treatment or extraction to prevent further spread of infection which may lead to an abscess.
Where are accessory canals located?
Accessory canals are pathways from the radicular pulp, extending laterally through the dentin to the periodontal tissue seen especially in the apical third of the root. Accessory canals are also called lateral canals because they are usually located on the lateral surface of the roots of the teeth.
What is the pulp cavity?
1. Pulp cavity - The pulp cavity is the entire central space in the dentin of a tooth, both root and crown, which contains the pulp tissue in a vital tooth. The outline of the pulp cavity generally corresponds to the external contour of the tooth, especially in newly erupted teeth.
What is the section of the pulp cavity that is located in the anatomical root of the tooth?
It is normally larger in diameter than any portions of the pulp cavity found in roots. 3. Pulp canal (s) - The section of the pulp cavity which is located basically in the anatomical root of the tooth, or in other words, that portion which is apical to the pulp chamber. Another term which is appropriate is root canal.
Which direction do x-rays take teeth?
As was previously mentioned, normal periapical radiographs (x-rays) of the teeth are taken in a faciolingual direction, thus outlining the pulp cavity in a mesiodistal section. However, the pulpal contours from this aspect are less variable than are those from a proximal aspect.
Which root is larger, the mesial or distal?
The chamber is widest near the pulp horn level, but constricts only slightly to the chamber floor, which is apical to the cervical line. The mesial root is larger than the distal, and it is the only one visible in this section. The mesial root normally has two root canals, named MB and ML canals.
How many pulp horns are there in a tooth?
Pulp chamber - Normally, there are two pulp horns which correspond in size to the cusps of this tooth. There is a large and pointed buccal horn, and a small, sometimes rounded, lingual horn. However, it is not unusual for the lingual horn to be entirely missing, in which case the outline is like that of the canine.
Which section of the dog has a longer pulp canal?
Mesiodistal Section - This section is nearly identical to the mandibular canine, although the canine has a longer root, and hence a longer pulp canal. 4. Cervical Cross Section - Both root and root canal in this view are normally ovoid, and wider buccolingually. 5.
What is the apical foramen?
Apical foramen (pi.-foramina) - The constricted opening (s), at, or near the root apex, through which the main nutrient and nervous supply to the pulp enter and exit. The apical foramen is thus the apical limit of the pulp cavity. 6.
What is the pulp of a tooth?
So if you’re wondering, what is the pulp of the tooth, now you know! Finally, covering the root of the tooth is cementum , which connects a tooth to the jawbones. In other words, you can think of the pulp chamber as the heart of the tooth, as blood flow through the area keeps the pulp and nerve healthy. According to StatPearls, the pulp has four ...
What is pulpitis in dental?
A common complication associated with the pulp chamber is called pulpitis. Pulpitis, according to the Merck Manual, is the inflammation of the dental pulp. This can be due to cavities progressing into the dentin, trauma affecting the lymphatic and blood supply to the tooth pulp, and multiple invasive dental procedures that can damage the tooth. In some cases, early stages of pulpitis can be reversible and treated with a filling; more severe cases may require a root canal or tooth extraction. Your dental professional may also prescribe antibiotics if the area becomes infected.
What is the function of the enamel on a tooth?
According to the American Dental Association, the hard enamel on the tooth’s surface helps break down food to support digestion and protect the tooth during use. Below, the softer dentin helps absorb pressure from eating and acts as a support for the enamel. In the middle of the tooth below the dentin is the pulp chamber—which houses nerves ...
How to tell if tooth pulp is necrotic?
A sign that the pulp is becoming necrotic is pain when coming into contact with heat; a sign that the pulp is entirely necrotic is when the tooth does not respond to heat or cold but becomes sensitive to pressure. Your dental professional will treat it according to the severity and cause in any instance of oral infection.
How to keep your pulp chamber healthy?
First, try your best to curb your sweet tooth. The acid from the sugary snacks breaks down your tooth enamel. If you do indulge in a sweet treat, swish with water afterward. Then, make sure that you follow good oral care habits. Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste to add strength to your enamel, and clean between your teeth with floss, water flossers, or another interdental cleaning device to avoid bacteria-causing plaque that can lead to cavities.
What is the function of pulp?
According to StatPearls, the pulp has four main functions: formation of the dentin, nutrition of the dentin, innervation of the tooth, and defense of the tooth. The most important role is the formation and nutrition of the dentin, as the dentin protects the tooth from decay and cavities. The pulp mediates this role by producing hard dentin tissue.
Where is the pulp chamber?
Located beneath the dentin layer (which is the hard tissue right below your enamel) is the pulp chamber, which is the space where your dental pulp lives. Pulp is the soft tissue at the center of your teeth housing connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels.
What is the pulp of a tooth?
Inside the dentin lies the pulp — a soft, non-calcified tissue consisting of blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. When decay reaches the pulp, it can cause severe pain and require a root canal or tooth extraction to treat. In certain situations, the healthy pulp can become exposed from decay or trauma.
When to use pulp cap?
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) recommends using a direct pulp cap only on a primary tooth when exposure results from mechanical trauma. If exposure results from decay removal, indirect pulp capping, or a pulpotomy — the partial removal of pulp — is performed instead.
How to prevent tooth decay from root canal?
Though pulp capping can help prevent the more invasive and costly root canal, you want to do whatever you can to avoid tooth decay. Start with creating and following a good dental care routine: Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush.
How to remove decay from dentin?
This procedure involves: Removing decay. The dental professional will drill the cavity and remove any decayed tooth material. They will then thoroughly clean the site . Adding sedative material. Once all the decay is removed, the dental professional will use a sedative material to protect the pulp from bacteria until the dentin can repair itself. ...
Why do you need a permanent filling?
Finally, a permanent filling is placed to strengthen the tooth and allow the patient to chew and bite normally. Typically, your dental professional will recommend indirect pulp capping when you experience no pain, but decay has penetrated the dentin so deeply that removal will expose the pulp.
How long does it take for a dental professional to remove a temporary filling?
Evaluating the progress. Six to eight months later, the dental professional will remove the temporary filling to evaluate the healing. In many cases, the previously decayed dentin has regenerated, and any residual decay is removed. Providing permanent restoration.
What is sedative filling?
Sedative, or temporary, fillings are commonly used in extensive restoration procedures that require multiple sessions or during pulp capping. The name "sedative filling" comes from its ability to soothe a tooth nerve aggravated by decay.
What is the pulp chamber in a tooth?
There is a pulp chamber inside of each of your teeth. The chamber holds blood vessels and nerves that are inside small pieces of flesh. This flesh, or pulp, is protected by the enamel of the tooth. When your tooth is damaged by decay or injury, the pulp can get infected and eventually die off.
What causes pulpitis?
Pulp necrosis is the end-stage of pulpitis, which can be caused by: 1 Cavities that are untreated and progress deep into the tooth. 2 Trauma to the tooth interfering with the tooth's blood supply. 3 Multiple invasive treatments on a tooth.
What is pulp necrosis?
Medically Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on April 12, 2021. Pulp necrosis is an irreversible condition that occurs when the soft pulp inside of a tooth dies. This is the last stage of a disease called pulpitis. There is a pulp chamber inside of each of your teeth. The chamber holds blood vessels and nerves that are inside small pieces of flesh.
What is the end stage of pulpitis?
Pulp necrosis is the end-stage of pulpitis, which can be caused by: Cavities that are untreated and progress deep into the tooth. Trauma to the tooth interfering with the tooth's blood supply. Multiple invasive treatments on a tooth.
How to prevent pulpitis?
Good dental hygiene, including brushing and flossing, is the key to preventing pulpitis and pulp necrosis. Regular flossing and brushing prevent decay from forming. It's also important that you eat a healthy diet since your teeth need vitamins and minerals to stay healthy.
What is the order of progression of pulp necrosis?
The usual order of progression for pulp necrosis is: A cavity or dental injury occurs. Bacteria enter the pulp through an opening in the tooth. The healthy pulp tries to fight off the bacteria. The infection causes swelling, which causes pain. The tooth nerve is deprived of oxygen and nutrition.
How to remove necrotic pulp?
The necrotic pulp has to be removed. This can be completed in one of two ways. Root canal. In this procedure, the dentist removes the damaged and infected pulp. Then the pulp chamber is cleaned and treated so that no bacteria can grow. That empty space is filled in and the tooth is covered with a crown. Extraction.
Overview
Pulp diagnoses
In a healthy tooth,
Reversible pulpitis is a mild to moderate inflammation caused by any momentary irritation or stimulant whereby no pain is felt upon the stimulants' removal. The pulp swells when the protective layers of enamel and dentine are compromised. Unlike irreversible pulpitis, the pulp gives a regular response to sensibility tests and inflammation resolves with management of the …
Anatomy
The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor t…
Development
The pulp has a background similar to that of dentin because both are derived from the dental papilla of the tooth germ. During odontogenesis, when the dentin forms around the dental papilla, the innermost tissue is considered pulp.
There are 4 main stages of tooth development:
1. Bud stage
Internal structure
The central region of the coronal and radicular pulp contains large nerve trunks and blood vessels.
This area is lined peripherally by a specialized odontogenic area which has four layers (from innermost to outermost):
1. Pulpal core, which is in the center of the pulp chamber, with many cells and an extensive vascular supply; except for its location, it is very similar to the cell-rich zone.
Functions
The primary function of the dental pulp is to form dentin (by the odontoblasts).
Other functions include:
• Nutritive: the pulp keeps the organic components of the surrounding mineralized tissue supplied with moisture and nutrients;
• Protective/Sensory: extremes in temperature, pressure, or trauma to the dentin or pulp are perceived as pain;
Pulp testing
The health of the dental pulp can be a variety of diagnostic aids which test either the blood supply to a tooth (Vitality Test) or the sensory response of the nerves within the root canal to specific stimuli (Sensitivity Test). Although less accurate, sensitivity tests, such as Electric Pulp Tests or Thermal Tests, are more routinely used in clinical practice than vitality testing, which requires specialized equipment.
See also
• Dental pulp stem cells
• Dental pulp test