What is inflammation Slideshare? Introduction • Inflammation is defined as the local response of living mammalian tissues to injury due to any agent.injury due to any agent. • Body defense reaction – eliminate or limit the spread of injurious agent facebook.com/trigemclasses. Cause of Inflammation 1. Click to see full answer.
Full Answer
What is the inflammation?
Inflammation is an essential part of your body's healing process. It occurs when inflammatory cells travel to the place of an injury or foreign body like bacteria. If inflammatory cells stay too long, it may lead to chronic inflammation.
What is inflammation and its type?
There are two types of inflammation, acute and chronic. You can think of acute inflammation as the “good” kind because it helps us heal, while chronic inflammation is the “bad” kind because of its association with chronic disease.
What are 4 types of inflammation?
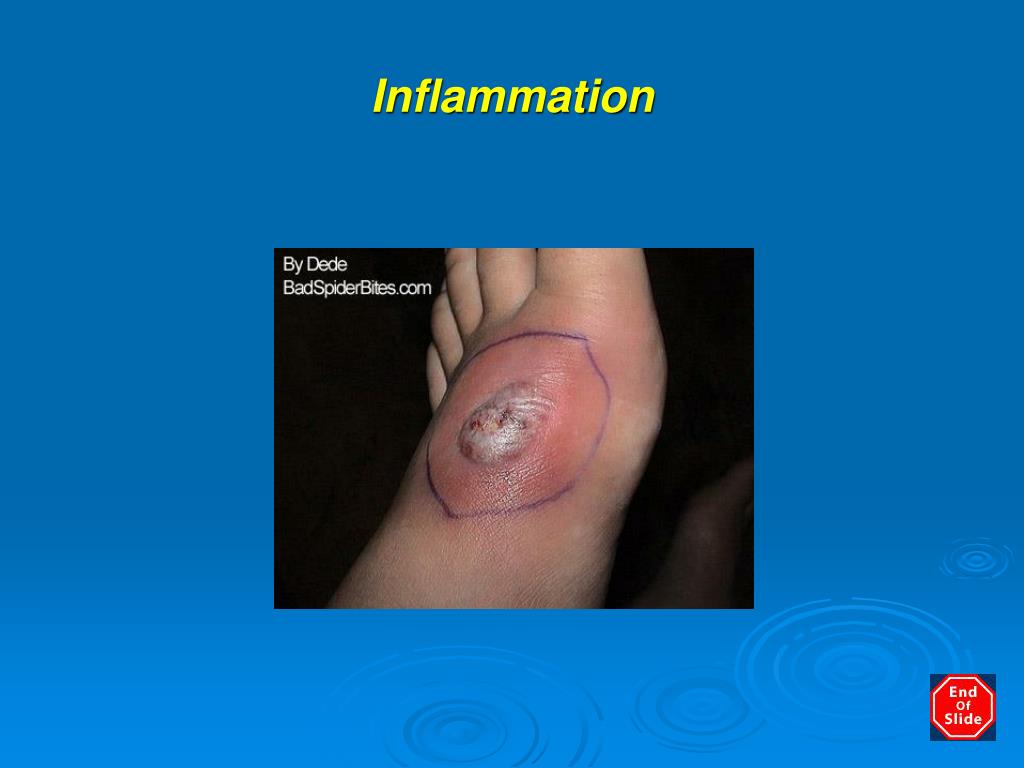
The four cardinal signs of inflammation are redness (Latin rubor), heat (calor), swelling (tumor), and pain (dolor). Redness is caused by the dilation of small blood vessels in the area of injury.
What is inflammation and its steps?
Inflammation is the immune system's response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, toxic compounds, or irradiation [1], and acts by removing injurious stimuli and initiating the healing process [2]. Inflammation is therefore a defense mechanism that is vital to health [3].
What are the 3 main causes of inflammation?
Causes of an inflammationPathogens (germs) like bacteria, viruses or fungi.External injuries like scrapes or damage through foreign objects (for example a thorn in your finger)Effects of chemicals or radiation.
What are the 3 stages of inflammation?
The Three Stages of InflammationWritten by Christina Eng – Physiotherapist, Clinical Pilates Instructor.Phase 1: Inflammatory Response. Healing of acute injuries begins with the acute vascular inflammatory response. ... Phase 2: Repair and Regeneration. ... Phase 3: Remodelling and Maturation.
What are the 2 types of inflammation?
There are two main types of inflammation: acute and chronic.
What are the five stages of inflammation?
Clinically, acute inflammation is characterized by 5 cardinal signs: rubor (redness), calor (increased heat), tumor (swelling), dolor (pain), and functio laesa (loss of function) (Figure 3-1).
What are the characteristics of inflammation?
The affected area turns red, it gets hot, it swells up, and it hurts. These are the four major characteristics of inflammation described by Celsus almost 2,000 years ago, which is known as The Pillars of Inflammation: rubor (redness), calor (warmth) tumor (swelling), and dolor (pain) (Figure 1).
What are the 6 steps in inflammation?
Appointments & EnquiriesAcute -swelling stage.Sub-acute – regenerative stage.Chronic – scar tissue maturation and remodelling stage.
What is the first step of inflammation?
The beginning of the inflammatory phase is characterized by the release of proinflammatory molecules by the platelets, forming the hemostasis clot and damaged host cells.
What is mechanism of inflammation?
MECHANISMS OF INFLAMMATION. Inflammation consists of a tightly regulated cascade of immunological, physiological, and behavioral processes that are orchestrated by soluble immune signaling molecules called cytokines. The first step of the inflammatory cascade involves recognition of infection or damage (Figure 1b).
What is inflammation in biology?
Inflammation Definition Inflammation is a complex reaction to injurious agents such as microbes and damaged, usually necrotic, cells that consists of vascular responses, migration and activation of leukocytes and systemic reactions. (Robins and Cotran; 7th ed.) 5.
What is the purpose of inflammation?
Overview. 2. Introduction Inflammation is a protective response intended to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury as well as necrotic cells and tissues resulting from the original insult. It sets into motion the events that eventually heal and reconstitute the sites of injury. 3.
What is the immediate response to injury?
Inflammation Inflammation is divided into two basic patterns: Acute Inflammation : It is the immediate and early response to injury, designed to deliver leukocytes to the site of injury.
Inflammation
1. INFLAMMATION Enflammare Set a fire Presented by Anusha Vaddi MDS Narayana dental college
Editor's Notes
Dynamic process occuring in vascularised vaible tissues……..medico legal distinction between antemortem and postmortem tissues can be made by presence of infl …………