
The disk diffusion test, or agar diffusion test, or Kirby–Bauer test (disc-diffusion antibiotic susceptibility test, disc-diffusion antibiotic sensitivity test, KB test), is a test of the antibiotic sensitivity of bacteria. It uses antibiotic discs to test the extent to which bacteria are affected by those antibiotics.
Full Answer
What is the Kirby Bauer disk diffusion test protocol?
Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol Protocol (PDF) The Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test determines the sensitivity or resistance of pathogenic bacteria to various antimicrobial compounds in order to assist physicians in selecting treatment options their patients.
What is a Kirby Bauer test used for?
Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test KIRBY-BAUER Kirby-Bauer testis widely used to determine the sensitivity or resistance of bacteria to various antimicrobial compounds, and it uses the Mueller Hinton agar. Mueller-Hinton agaris a non-selective, non-differential medium capable of growing a wide range of non-fastidious organisms.
What is disk diffusion in microbiology?
Disk Diffusion Method. The disk diffusion method (DDM) is classified as an agar diffusion method (ADM) because the plant extract to be tested diffuses from its reservoir through the agar medium seeded with the test microorganism. Generally, the reservoir is a filter paper disk, which is placed on top of an agar surface.
How do you test for pathogens using disk diffusion?
Disk diffusion by the Kirby-Bauer method is a standardized technique for testing rapidly growing pathogens.89 Briefly, a standardized inoculum (i.e., direct suspension of colonies to yield a standardized inoculum is acceptable) is swabbed onto the surface of MH agar (i.e., 150-mm plate diameter).
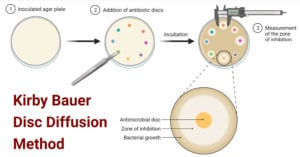
What is the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method and what is it used for?
The purpose of the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test is to determine the sensitivity or resistance of pathogenic aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria to various antimicrobial compounds in order to assist a physician in selecting treatment options for his or her patients.
How does Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion assay work?
0:324:37Testing an Antibiotic Using a Disk Diffusion Assay - Kirby Bauer MethodYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn this assay a filter paper disc is loaded with a specific amount of antibiotic. And placed on aMoreIn this assay a filter paper disc is loaded with a specific amount of antibiotic. And placed on a lot of bacteria. The antibiotic will diffuse out of the disc.
How is disk diffusion method done?
The method consists of placing paper disks saturated with antimicrobial agents on a lawn of bacteria seeded on the surface of an agar medium, incubating the plate overnight, and measuring the presence or absence of a zone of inhibition around the disks (Figure 1).
What is the advantage of the Kirby Bauer method?
Advantages. This test is used in determining the antibiotics of choice to treat an infection. It can be useful in monitoring antimicrobials and for the selection of proper antibacterial agents. It doesn't require special equipment to perform and can be interpreted by all medical personnel.
What are the factors that influence the Kirby-Bauer method?
The disc diffusion techniques most commonly used (the Kirby-Bauer and Stokes's tests) take account of important factors, including the inoculum density, the composition of the medium, the delay between application of the disc and incubation, the temperature ofincubation, etc., but the resulting zone of inhibition is ...
What is the purpose of the Kirby-Bauer method quizlet?
to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to select antiseptics and disinfectants.
What is disc diffusion test used for?
In diagnostic laboratories, the disk diffusion test is used to determine the susceptibility of clinical isolates of bacteria to different antibiotics. An effective antibiotic will produce a large zone of inhibition (disk C), while an ineffective antibiotic may not affect bacterial growth at all (disk A).
What is the disk diffusion test used for?
The Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test determines the sensitivity or resistance of pathogenic bacteria to various antimicrobial compounds in order to assist physicians in selecting treatment options their patients.
How is Kirby-Bauer test measured?
0:096:20Interpreting the Results of the Bauer Kirby Method of Antibiotic ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTo interpret the results of the Bauer biotic susceptibility testing we're going to be measuring theMoreTo interpret the results of the Bauer biotic susceptibility testing we're going to be measuring the diameter of zones of inhibition in millimeters using a metric ruler.
What are the limitations of the disc diffusion method?
However, the disk diffusion test has additional limitations that should be considered. Training and experience are required both for performing and reading the results. Further, the test is labor-intensive and has similar limitations to other culture-based tests.
Is the disk-diffusion technique measuring?
Is the disk-diffusion technique measuring bacteriostatic or bacterial activity? Explain. Measuring bacteriostatic because instead of killing the microorganisms they inhibit microbial growth.
What is the importance of measuring the zone of inhibition?
The size of the zone of inhibition is usually related to the level of antimicrobial activity present in the sample or product – a larger zone of inhibition usually means that the antimicrobial is more potent.
Is the disk-diffusion technique measuring?
Is the disk-diffusion technique measuring bacteriostatic or bacterial activity? Explain. Measuring bacteriostatic because instead of killing the microorganisms they inhibit microbial growth.
What is Stokes disc diffusion method?
The Stokes' method. allows each individual isolate to be compared with a. sensitive control of the same or similar species which is. subjected to the same technical conditions of medium, incubation time, atmosphere, temperature and disc con-
How antibiotic sensitivity test is done?
The test is done by taking a sample from the infected site. The most common types of tests are listed below. A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial.
How are agar plates inoculated for disk diffusion testing?
How are agar plates inoculated for disk diffusion testing of antiseptics and disinfectants? A swab is used to inoculate the entire surface of the plate, producing a lawn of growth.
What is the disk diffusion microbioassay?
A disk diffusion microbioassay with Bacillus subtilis (ATCC 6633) was used to evaluate the bactericidal effectiveness and the pharmacodynamic profile of moxifloxacin in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and to compare the bactericidal activity with that of ceftriaxone and meropenem therapy [172].
What is disk diffusion susceptibility test?
Disk-diffusion susceptibility testing is most frequently used to measure the antimicrobial resistance of isolates of N. gonorrhoeaefor patient management whereas determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) is more appropriate for surveillance programs. The methodology varies in different parts of the world and can be performed on both blood-containing media (Fig 2.45and 2.46). or on GC agar base supplemented with IsoVitaleX or an equivalent and to the use of either high- or low-dose discs.13
What is the primary method of MIC testing?
In most clinical laboratories, the disk dif fusion(DD) test, E-test strips, broth microdilution method (BMD) and the Vitek 2 system remain the routine susceptibility methods, among which the BMD is suggested as the primary method for polymyxins minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) testing. But the truth is that conventional methods have many drawbacks (Humphries, 2015). As aless toxin prodrug commonly used for therapy, the CMS yields erroneously high MICs in vitro so that it not be used for susceptibility testing (Landman et al., 2008). The poor and slow diffusion of polymyxins lead the results of DD test nonreliable, yielding small zones of inhibition (Lo-Ten-Foe et al., 2007). False susceptibility (32%) occurred with E-test, which MICs were significantly lower than those obtained by BMD for resistant isolates (Hindler and Humphries, 2013). Their amphiphilic nature make them adhere to the polystyrene surface of BMD microdilution plates, and lower concentrations of polymyxins showed higher absorption proportionally (Karvanen et al., 2013). Although the adsorption of colistin to polystyrene can be mitigated by the addition of a surfactant such as polysorbate 80 (P-80, namely toween-80), the use of P-80 is still questionable (Humphries, 2015). All above methods are laborious, manual preparation or expensive. The automatic systems allow rapid identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing and perform reliable results (Lo-Ten-Foe et al., 2007; Poirel et al., 2017). However, the Vitek 2 system displayed low sensitivity in the detection of polymyxins resistant Enterobacteriaceaeand care should be taken in the interpretation of the known heteroresistance subpopulations (Tan and Ng, 2007; Lo-Ten-Foe et al., 2007). It is time to ask for a suitable and standard method to detect resistant subpopulations. Additionally, polymyxins resistance would disappear after long-term storage at − 70°C (Hindler and Humphries, 2013), which calls for an easy, inexpensive and sensitive techniques to screen polymyxins resistance from fresh cultures or even clinical samples directly in routine laboratories. Colistin and polymyxin B breakpoints were interpreted according to the documents given by Clinical and Laboratory and Standards Institute (CLSI) or European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) in the past. Nowadays, the CLSI/EUCAST Joint Working Group recommended an update clinical breakpoints of Acinetobacterspp. and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as shown in Table 2(2016). However, there were insufficient data to establish clinical breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae, so the epidemiological cutoff values (ECVs) of Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Raoultella ornithinolyticawere set, as shown in Table 3. Among Enterobacteriaceae, the MIC of other genera and species distributions may be different. Meanwhile, neither PK-PD nor clinical data have been evaluated for polymyxins with any Enterobacteriaceae. So, the ECV interpretations are applied only for laboratorians, clinicians, and public health professionals to identify isolates that have colistin MICs above the wild-type (those with acquired and/or mutational resistance mechanisms to colistin, such as mcr-1). Recently, the Rapid Polymyxin NP test based on the detection of bacterial growth in the presence of a defined polymyxin concentration has been demonstrated with high specificity (99.3%) and sensitivity (95.4%) (Nordmann et al., 2016a). A Selective medium named “SuperPolymyxin”, which contains a colistin concentration (3.5 μg/mL), can detect any type of polymyxin resistant Gram-negative organism and prevent swarming of Proteusspp. The sensitivity and specificity of this medium can reach 100% (Nordmann et al., 2016b). In molecular level, a SYBR green-based real-time PCR assay that considered as a simple, specific, sensitive, and rapid method for detection of mcr-1-positive isolates was recently published (Bontron et al., 2016).
What is disk diffusion?
The disk diffusion method is among the most flexible susceptibility testing methods in terms of antimicrobial agents that can be tested. The method consists of placing paper disks saturated with antimicrobial agents on a lawn of bacteria seeded on the surface of an agar medium, incubating the plate overnight, and measuring the presence or absence of a zone of inhibition around the disks (Figure 1 ). Studies conducted at the University of Washington in the mid-1960s resulted in the technique often referred to as the ‘Kirby–Bauer method,’ which was published by Bauer and colleagues in 1966. This method standardized the variables of disk size, inoculum size, temperature, and time of incubation. Results are reported qualitatively as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant. The disk diffusion method described by Bauer and colleagues has been continually expanded and improved by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) in the United States. Several other international societies (e.g., the European Union Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST), and the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy) use similar techniques. Alternative disk-based methods, including the Roscoe NeoSensitabs and the Australian CDM method, are also used in some countries. Instruments that measure the zones of inhibition using cameras can speed the process of reading disk diffusion plates. These instruments can also transform the zone diameter readings into approximate MIC values.
What are the methods of susceptibility testing?
The main methods for susceptibility testing are broth dilution, agar dilution, and disk diffusion. In addition, several systems for automated AST are available. It is important to note that each method may have limitations for certain organism–drug combinations and that there may be minor differences between the results generated by the automated systems. For example, certain organism–drug combinations cannot be reliably tested on automated systems. Laboratories should ensure that they have implemented the recommended changes to their software if using automated instruments.
What is broth microdilution?
The broth microdilution assay is used commonly to determine MICs quantitatively.90MIC trays can be custom made in the laboratory or purchased commercially. Usually, five to eight concentrations of antibiotics representing therapeutically achievable ranges are tested against each organism, or one to three concentrations are used to determine activity at the breakpoint MIC. The latter allows only qualitative assessment of susceptibility; the exact MIC is unknown. Interpretation of these somewhat arbitrary standards must be made in the context of the organism, the likely site of infection, the density of the organism at the site, and the host's immunocompetence.
What is the reservoir of an agar?
Generally, the reservoir is a filter paper disk, which is placed on top of an agar surface. If tested plant extracts or isolated compounds are microbiologically active, an inhibition zone develops around the filter paper disk after incubation. The diameter of the inhibition zone properly describes the antimicrobial potency ...
What is Kirby-Bauer test?
Standard Kirby–Bauer testing: White disks containing antibiotics shown on an agar plate of bacteria. Circular zones of poor bacterial growth surround some disks, indicating susceptibility to the antibiotic.
What is disk diffusion test?
In diagnostic laboratories, the disk diffusion test is used to determine the susceptibility of clinical isolates of bacteria to different antibiotics. An effective antibiotic will produce a large zone of inhibition (disk C), while an ineffective antibiotic may not affect bacterial growth at all (disk A). Antibiotics to which a bacterial isolate is ...
What is a pure bacterial culture?
A pure bacterial culture is suspended in saline, its turbidity is standardized, and it is swabbed uniformly across an agar plate. An antibiotic- or extract-impregnated filter paper disk is then placed on the surface of the agar. The disk constituent (s) diffuse from the filter paper into the agar.
Where are antibiotic disks placed?
Disks containing increasing antibiotic concentrations are placed on a seeded bacterial lawn on the agar surface and plates are incubated. Zone sizes are measured from the edge of the disk to the end of the clear zone. Interpretation is more complicated in mixed susceptibility populations.
When was agar diffusion first used?
Agar diffusion was first used by Martinus Beijerinck in 1889 to study the effect of auxins on bacterial growth. However, the method has been developed, refined and standardized by many scientists and scientific organizations over the years including George F. Reddish, Norman Heatley, James G. Vincent, Alfred W. Bauer, William M.M. Kirby, John C.
What is the pH level of Kirby Bauer?
The media used in Kirby–Bauer testing must be Mueller-Hinton agar at only 4 mm deep, poured into either 100 mm or 150 mm Petri dishes. The pH level of the agar must be between 7.2 and 7.4. Bacteria l inoculum is prepared by diluting a broth culture to match a 0.5 McFarland turbidity standard, which is equivalent to approximately 150 million cells per mL.
What is KB test?
Not to be confused with the Kleihauer–Betke test, which is also often called a "KB test". Microbiology assay used in diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. It has been suggested that this article be merged into Antibiotic sensitivity testing. ( Discuss) Proposed since July 2020.
All Answers (5)
Kirby-Bauer antibiotic testing (also called KB testing or disk diffusion antibiotic sensitivity testing) uses antibiotic-containing wafers or disks to test whether particular bacteria are susceptible to specific antibiotics.
Similar questions and discussions
Is the disk diffusion technique still a valid technique for studies of antimicrobial susceptibility?
