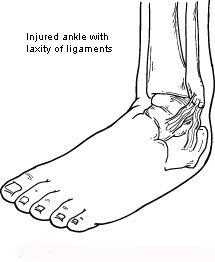
What is the best treatment for ligament laxity?
Ligamentous Laxity Treatment. Treating ligamentous laxity will depend on the extent of the loose joints, as well as the severity of any existing symptoms. Most serious cases involve strengthening the muscles, the use of pain relievers, and physiotherapy to use ligaments in a controlled manner.
How do you test for ligament laxity?
These include:
- Bending forward and placing your palms on the ground with your legs straight
- Bending your thumbs backwards
- Bending your little fingers backwards
Is being double jointed bad?
Hyperextending a limb may feel normal to you — and most of the time, if you’re so-called “double-jointed,” it’s not harmful to your body. But rarely, it can be a red flag for other health conditions. What does it mean to be double-jointed? In reality, there’s no such thing as being double-jointed. (Wait, what?)
What causes double jointedness?
These conditions include:
- Joint instability causing frequent sprains, tendinitis, or bursitis when doing activities that would not affect others
- Joint pain
- Early-onset osteoarthritis (as early as during teen years)
What causes ligamentous laxity?
While ligamentous laxity may be genetic and affect an individual from a very early age, it can also be the result of an injury. Injuries, especially those involving the joints, invariably damage ligaments either by stretching them abnormally or even tearing them.
How is ligamentous laxity treated?
How is it treated? Ligamentous laxity doesn't always require treatment, especially if it isn't causing you any pain. However, if it does cause pain, physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles surrounding your joints for added support. In severe cases, you may need surgery to repair the ligaments.
What does ligament laxity feel like?
Loose ligaments allow the joint to move beyond its normal range of motion2. The abnormal motion allowed by the strained ligament will produce painful sensations and make you aware of the problem. These sensations also include feelings of “numbness and tingling” and a phenomenon of referred pain.
How do you test for ligamentous laxity?
Asking the patient to touch his or her thumb to the ipsilateral wrist is an excellent way to judge general ligamentous laxity. Furthermore, instability of the shoulders and ease of putting the hand behind the back in “back scratch” position are other signs of instability and laxity.
What disease causes loose ligaments?
Joint hypermobility syndrome is a connective tissue disorder. Thick bands of tissue (ligaments) hold your joints together and keep them from moving too much or too far out of range. In people with joint hypermobility syndrome, those ligaments are loose or weak.
What deficiency causes weak ligaments?
Vitamin C: Tendons and ligaments also need vitamin C, a nutrient found in many vegetables and fruits, because both tissues contain large amounts of collagen. Vitamin C plays an essential role in new collagen production, and a Vitamin C deficiency can weaken your tendons and ligaments by preventing collagen synthesis.
Does ligament laxity show on MRI?
With healing, the ligament may remain thickened and show laxity. MRI changes are best demonstrated on axial or axial oblique images. Acutely the ligament may show partial or complete disruption, laxity, thickening or increased signal intensity (Figure 9a) [57].
How do you strengthen loose ligaments?
When exercising, use restraints to improve the strength of the ligaments and joints. Include several joint exercises such as squats, push-ups, pull-ups, and lunges with moderate resistance. For the best effect, complete them in sets up to 12 repetitions.
Is hypermobility a disability?
Is my hypermobility syndrome a disability? Some people are disabled by their hypermobility, other people are not. Symptoms can also change over time, so some people may go through periods of being disabled and periods of not being disabled by their condition. It all depends on how you personally are affected.
Do loose ligaments heal?
Grade 1 and 2 ligament injuries can heal without surgical intervention. Doctors will use a combination of bracing, physical therapy, heat therapy, and medication to help with healing. The ligament responds well to these methods with a high overall success rate.
Does hypermobility affect the brain?
Inferior parietal cortex can affect proprioceptive awareness and hypermobility is itself linked to dyspraxia. Our findings suggest that processes compromising function in neuro-developmental conditions may occur in individuals with hypermobility, putatively enhancing vulnerability to stress and anxiety.
What doctor do you see for hypermobility?
Treating joint hypermobility syndrome A GP may refer you to a physiotherapist, occupational therapist or podiatrist for specialist advice. You can also pay for these services privately. These physical therapies can help to: reduce pain and the risk of dislocations.
Do loose ligaments heal?
Grade 1 and 2 ligament injuries can heal without surgical intervention. Doctors will use a combination of bracing, physical therapy, heat therapy, and medication to help with healing. The ligament responds well to these methods with a high overall success rate.
How do you tighten your ligaments?
When exercising, use restraints to improve the strength of the ligaments and joints. Include several joint exercises such as squats, push-ups, pull-ups, and lunges with moderate resistance. For the best effect, complete them in sets up to 12 repetitions.
Does ligament laxity show on MRI?
With healing, the ligament may remain thickened and show laxity. MRI changes are best demonstrated on axial or axial oblique images. Acutely the ligament may show partial or complete disruption, laxity, thickening or increased signal intensity (Figure 9a) [57].
Can ligaments be strengthened?
Exercise training improves the repair strength of ligaments but does not result in normal values twelve weeks after the surgery. Exogenous administration of ICSH or testosterone results in higher repair strength whereas TSH, thyroxine, ACTH and growth hormone decreases this measure.
What is it called when your ligaments are too tight?
Most people have naturally tight ligaments. Ligamentous laxity occurs when your ligaments are too loose. You might also hear ligamentous laxity referred to as loose joints or joint laxity.
Where does ligamentous laxity occur?
Signs and symptoms of ligamentous laxity tend to occur in or around the affected joints. Possible symptoms near your joints include:
Why do athletes have loose ligaments?
among athletes, such as gymnasts, swimmers, or golfers, because they’re more prone to injuries like muscle strain. Having a job that requires a lot of repetitive movement can also increase your risk of an injury that might cause loose ligaments.
What is the Beighton score?
The Beighton score is a common screening tool for joint hypermobility. It involves completing a series of movements, such as pulling your fingers backward or bending over and placing your hands flat on the ground.
Can laxity be treated?
Ligamentous laxity doesn’t always require treatment, especially if it isn’t causing you any pain. However, if it does cause pain, physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles surrounding your joints for added support. In severe cases, you may need surgery to repair the ligaments.
Is ligamentous laxity more common in children than adults?
Some people are more likely to have loose joints, regardless of whether they have an underlying condition. For instance, ligamentous laxity is more common in children than adults. It also affects women more often than men.
Can a loose ligament cause laxity?
Injuries can also cause ligamentous laxity, especially muscle strains and repetitive motion injuries. However, people with loose ligaments also have a higher risk of injury, so it’s not always clear whether an injury is caused loose ligaments or vice versa.
Why are ligaments tight?
In most people, ligaments (which are the tissues that connect bones to each other) are naturally tight in such a way that the joints are restricted to 'normal' ranges of motion. This creates normal joint stability. If muscular control does not compensate for ligamentous laxity, joint instability may result.
What is referred to as trigger point?
Referred pain is created by ligamentous laxity around a joint, but is felt at some distance from the injury. (Pain will not only occur at the site of the injury and loose ligaments, but may also be referred to other parts of the body.) These painful points that refer pain elsewhere are called trigger points, and will be dealt with later. Abnormal joint movement also creates many “protective actions” by adjacent tissues. Muscles will contract in spasm in an attempt to pull the joint back to the correct location or stabilize it to protect it from further damage.
Why do people with ligamentous laxity have clumsy gaits?
In addition, people with ligamentous laxity often have clumsy or deliberate gaits, owing to the body having to overcompensate for the greater amount of energy required to offset the weakened ligaments. The feet may be spread apart at a wide angle, and the knees may flex backwards slightly after each stride.
What is the term for a loose ligament?
Ligamentous laxity. Ligamentous laxity, or ligament laxity, means loose ligaments. Ligamentous laxity is a cause of chronic body pain characterized by loose ligaments. When this condition affects joints in the entire body, it is called generalized joint hypermobility, which occurs in about ten percent of the population, and may be genetic.
What happens if muscular control does not compensate for ligamentous laxity?
If muscular control does not compensate for ligamentous laxity, joint instability may result. The trait is almost certainly hereditary, and is usually something the affected person would just be aware of, rather than a serious medical condition.
What is the pain associated with ligamentous laxity?
Arthralgia, or symptoms such as frequent sprained ankles, shoulder dislocations, knee effusions and back problems are common among individuals with ligamentous laxity. Afflicted individuals are also prone to bone dislocation, and those with a sedentary job often report back pain. In addition, people may experience referred pain, that is, pain in an area of the body away from the injured or otherwise affected site.
What is referred pain?
In addition, people may experience referred pain, that is, pain in an area of the body away from the injured or otherwise affected site. Individuals with extremely lax, or hypermobile joints, can be identified by their ability to bend their elbows, knees or hips past a position of neutrality.
Understanding Ligament Laxity
Ligament laxity is a type of medical condition that can cause loose joints. Ligaments are a type of tissue that connects bones together at the joint and help to provide your body with support and stability. A ligament can become damaged from a car accident and cause it to become loose, weak, or even torn.
Ligament Laxity and Whiplash
The neck is comprised of muscles, ligaments, and tendons that all help support and protect the spine. When all the muscles, ligaments, and tendons in your neck are functioning properly, they help keep your spine in healthy alignment so that the individual joints of the spine, known as vertebrae.
Diagnosing Whiplash vs. Ligament Laxity
When you visit a doctor after a car accident, they will want to know what symptoms you have been experiencing, when you first noticed them, and whether there has been an increase in severity over time. Your doctor will perform a physical examination of your neck and spine to assess how the car accident has affected you.
How Chiropractic Care Can Help
Chiropractors work with the entire musculoskeletal system and focus on how an injury impacts the healthy alignment and functioning of bones and joints. Chiropractic care involves therapeutic, non-invasive treatment for a wide variety of car accident injuries, including whiplash and ligament laxity.
What is Ligamentous Laxity?
Ligamentous Laxity or ligament laxity is nothing, but loose ligaments which lead to chronic body pains. If this condition affects all the joints of the body then this condition is known as generalized joint hypermobility. Individuals with Ligamentous Laxity are able to extend their joints easily and painlessly beyond the normal range of motion. Joint hypermobility occurs when the ligaments, which hold the joints together, are extremely loose. Weak muscles surrounding the joint also can contribute to joint hypermobility.
What is a Beighton score?
Beighton score is a tool, which is used for measuring loose ligaments or Ligamentous Laxity. Getting a score of 5 or more is a positive test; however, the patient may still have Ligamentous Laxity even if the test result is negative.
What causes vertebral instability?
Ligamentous Laxity in the back causes vertebral instability which is fixed by fusing the vertebrae with metal or bone.
What is the cause of degenerative joint conditions?
The poor limb positions which result from Ligamentous Laxity can contribute to degenera tive joint conditions .
What happens if you have ligamentous laxity in your spine?
Patients having Ligamentous Laxity in the spinal region can experience disc degeneration and osteoarthritis.
What causes laxity in the body?
Such ligamentous laxity is known as benign hypermobility syndrome. The only symptom of ligamentous laxity is hypermobile joints, the causes of which include: The structure and shape of the bone. The structure of the muscle, such as the strength ...
What is laxity in children?
Ligamentous Laxity is quite a common condition, particularly in children, as their connective tissues are not fully developed. As the child grows older, the laxity of the joints and the ability to hyperextend decreases. Ligamentous Laxity is also known as “loose joints,” “double-jointedness,” “hypermobility syndrome,” and “joint laxity.”.