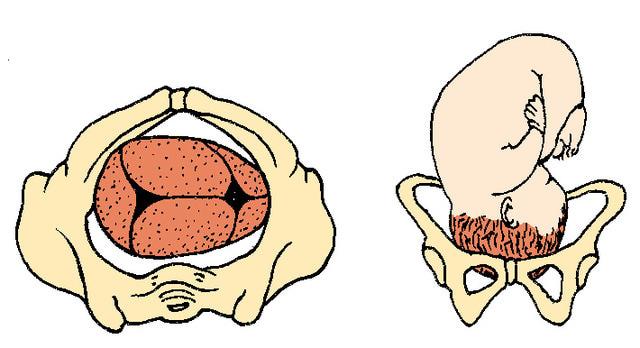
What is a breech presentation?
How to diagnose breech presentation?
What are the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation?
What are the clinical conditions associated with breech presentation?
What is the recurrence rate after a breech delivery?
What is the gestational age for breech?
Who is responsible for breech delivery?
See 4 more
About this website
Is breech presentation good for normal delivery?
How does a breech baby affect delivery? If your baby presents in a breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy, your birthing plan will likely change. It's usually unsafe for a breech baby to be born vaginally due to risks of injury. In most cases, a planned C-section is the safest way to deliver your baby.
What is breech lie in pregnancy?
Bottom first or feet first (breech baby) If your baby is lying bottom or feet first, they are in the breech position. If they're still breech at around 36 weeks' gestation, the obstetrician and midwife will discuss your options for a safe delivery.
Is breech presentation a high risk pregnancy?
In moderate to late preterm delivery, breech presentation is a high-risk state and some obstetric risk factors are yet visible in early preterm delivery.
What are the four types of breech presentation?
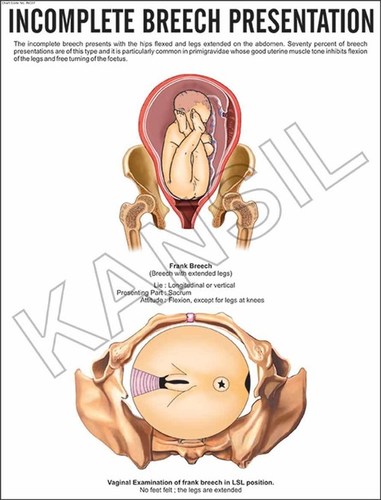
There are three types of breech presentation: complete, incomplete, and frank. Complete breech is when both of the baby's knees are bent and his feet and bottom are closest to the birth canal. Incomplete breech is when one of the baby's knees is bent and his foot and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Are breech babies boy or girl?
In breech presentations a little more girls are born than boys, among head presentations there is a slight excess of boys. Among the factors favoring pelvic presentation birth weight has, according to present investigations, a decisive influence on the different sex relationship in the two presentations.
How should you sleep with a breech baby?
Khosa suggests sleeping on your side with a pillow between your knees and ankles. “The more room your baby has, the easier it will be for them to find their way to a vertex position,” she says.
Is breech baby normal?
Occasionally fetuses with certain birth defects will not turn into the head-down position before birth. However, most fetuses in a breech presentation are otherwise normal.
How do you treat a breech presentation?
Treatment options include external cephalic version to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth or a planned cesarean section, the optimal gestation being 37 and 39 weeks, respectively. Planned cesarean section is considered the safest form of delivery for infants with a persisting breech presentation at term.
Do breech babies have problems?
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong? Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Which presentation is good for normal delivery?
Ideally for labor, the baby is positioned head-down, facing your back, with the chin tucked to its chest and the back of the head ready to enter the pelvis. This is called cephalic presentation. Most babies settle into this position with the 32nd and 36th week of pregnancy.
Do breech babies go full term?
About 3 to 4 percent of babies still hang out head-up by the time they're full-term. But just because your baby is bottom-down in the weeks before your due date doesn't mean she'll remain breech when it comes time for delivery. Some babies don't let on what end will ultimately be up until just before birth.
Can breech babies turn?
It is fairly common for a baby to be in a breech position before 35 to 36 weeks gestation, but most gradually turn to the head-down position before the last month.
Do breech babies have problems?
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong? Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
What are the signs of a breech baby?
How can you tell if your baby is in a breech position? As your due date nears, your doctor or midwife will determine your baby's position by feeling the outside of your abdomen and uterus. If your baby is breech, her firm, round head will be toward the top of your uterus and her softer, less round bottom will be lower.
Will a breech baby turn?
The ideal position for birth is head-first. Most babies that are breech will naturally turn by about 36 to 37 weeks so that their head is facing downwards in preparation for birth, but sometimes this does not happen. Around three to four babies in every 100 remain breech.
How can I turn my breech baby naturally?
Techniques you could try to turn your breech baby naturally: Adopting a knee-to-chest position. Kneel on a mat on the floor, with your bottom in the air, and your head and shoulders on the floor. The aim is to tip your baby back up and out of your pelvis, to give him more room to turn around.
Breech presentation - Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment - BMJ
Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head. Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency caesarean section and placenta praevia; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and perinatal mortality.
Breech Presentation Article - StatPearls
Hinnenberg P,Toijonen A,Gissler M,Heinonen S,Macharey G, Outcome of small for gestational age-fetuses in breech presentation at term according to mode of delivery: a nationwide, population-based record linkage study.
Breech Presentation | ECV | Summary | Geeky Medics
Clinical features. Before 36 weeks, breech presentation is not significant, as the fetus is likely to revert to a cephalic presentation.The mother will often be asymptomatic with the diagnosis being incidental.. The incidence of breech presentation is approximately 20% at 28 weeks gestation, 16% at 32 weeks gestation and 3-4% at term.Therefore, breech presentation is more common in preterm labour.
Breech Presentation: Overview, Vaginal Breech Delivery ... - Medscape
Footling breech presentation. Once the feet have delivered, one may be tempted to pull on the feet. However, a singleton gestation should not be pulled by the feet because this action may precipitate head entrapment in an incompletely dilated cervix or may precipitate nuchal arms.
What is longitudinal lie?
longitudinal lie a situation in which the long axis of the fetus is parallel to that of the mother; in presentation, either the head or breech presents first. oblique lie a situation in which the long axis of the fetal body crosses that of the maternal body at an angle close to 45 degrees; in presentation, the shoulder usually presents first, ...
What is a transverse lie?
transverse lie a situation in which the long axis of the fetus is transverse to that of the mother; see illustration.
What is a breech presentation?
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section.
When to intervene in oblique lie?
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Where is the footling breech pointed?
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
What does it mean when a baby is in a complete breech?
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
What is the best position for a vaginal delivery?
Head down, facing down (anterior position) A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery. This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) ...
How to tell if a baby is facing your spine?
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis. Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior ...
What is the purpose of a baby's knees bent in an incomplete breech?
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.
What is breech presentation in late pregnancy?
Breech presentation of the fetus in late pregnancy may result in prolonged or obstructed labour with resulting risks to both woman and fetus. Interventions to correct breech presentation (to cephalic) before labour and birth are important for the woman’s and the baby’s health. The aim of this review is to determine the most effective way of managing a breech presentation in late pregnancy.
What appendix is the study not included in this review?
Studies not included in this review with reasons for their exclusions are provided in appendix K.
What policy did Nice use to record declarations of interest?
Declarations of interest were recorded according to NICE’s conflicts of interest policy.
What is a breech presentation?
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
How to diagnose breech presentation?
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
What are the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation?
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6][7]
What are the clinical conditions associated with breech presentation?
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4][5]These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
What is the recurrence rate after a breech delivery?
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10% , and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
What is the gestational age for breech?
One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
Who is responsible for breech delivery?
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12][13][14]
