What is Losch's model of location?
Lösch's Model: The Location Theory Origin and Meaning of the Model - The original central place theory was developed by German geographer Walter Christaller in 1933. - Christaller's theory was modified in 1954 by German economist August Losch, as he believed it too rigid.
Why did Losch modify Christaller's central place theory?
In 1954, German economist August Losch modified Christaller's central place theory because he believed it was too rigid. He thought that Christaller's model led to patterns where the distribution of goods and the accumulation of profits were based entirely on location.
What is Losch's model of profitability?
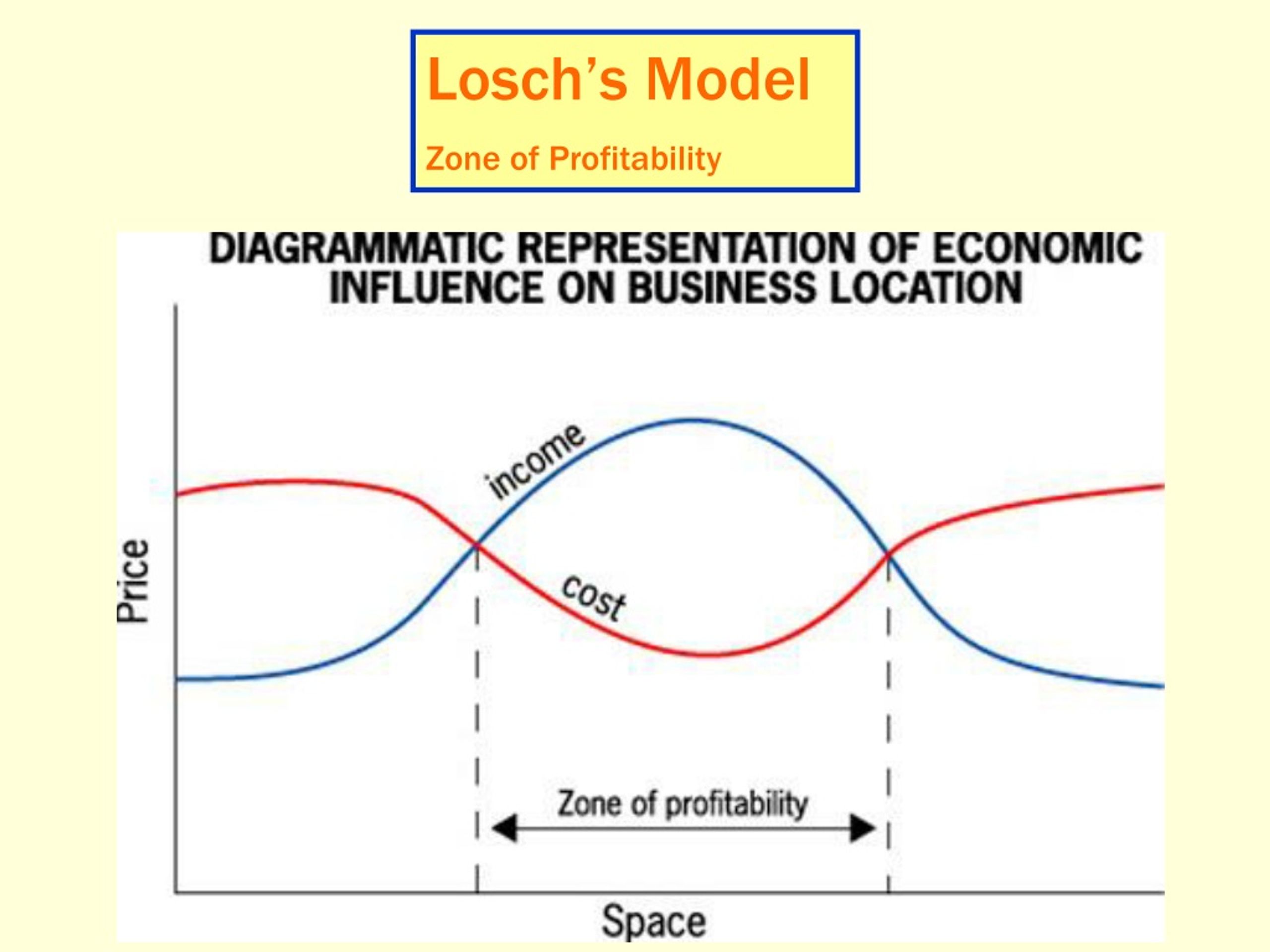
Losch's Model. zone of profitability; firms will identify a zone of profitability (not just a point) where income will outpace costs. ex: A place w/ low labor costs, easy travel, and resources.
What is the purpose of the Losch modification to the economy?
- Losch's modification instead focused on creating an ideal environment for consumers and maximizing consumer welfare, in that the need to travel to receive goods was minimized and profits were held level, rather than being inflated to earn extra.

What is Christaller theory?
Christaller's theory assumes that central places are distributed over a uniform plane of constant population density and purchasing power.
Why did August Losch modify Christaller's central place theory?
In 1954, German economist August Losch modified Christaller's central place theory because he believed it was too rigid. He thought that Christaller's model led to patterns where the distribution of goods and the accumulation of profits were based entirely on location.
What is the main aim of central place theory?
Central Place Theory sought to explain the economic relationships of cities with smaller settlements. It also seeks to explain why cities are located where they are geographically and how they serve the surrounding smaller settlements with speciality goods and services.
What is an example of central place theory?
Fens of East Anglia The land in the Fens is fertile and hence supports a large number of settlements, most of which have sprung up in accordance with the tenets of the Central Place Theory, which is to say, a honeycomb like layout of large market towns surrounded by smaller towns in a triangular or hexagonal pattern.
What is the Christaller's central place theory?
Walter Christaller developed his "Central Place Theory" in the 1930s. This theory is based on his idea that settlements only existed to function as "central places" to provide services for the surrounding area. This theory is part of the study of urbanization, taking into account the importance of supply and demand.
Is Christaller's theory still applicable in our world today?
The central-place system of Christaller is applicable partially even to this day in countries of the developing world including India, China and areas where primary occupations predominate. The theory, it is again emphasized, is normative in character.
What are the four elements of central place theory?
Christaller's theory states that this hierarchy comprises seven levels which he describes with four main parameters: the number of centers, their sphere of influence, the population affected and the number of goods and services offered.
Who first proposed central place theory?
The intellectual roots of central place theory can be found in the works of rural sociologists and geographers in the early 1900s, but the main contributions to the development of the theory were made in the 1930s and 1940s by two German scholars, Walter Christaller and August Lösch.
What are the advantages of central place theory?
What are the advantages of central place theory? The theory does a reasonably good job of describing the spatial pattern of urbanization. No other economic theory explains why there is a hierarchy of urban centers.
What are the 3 parts of the central place theory?
All areas have: an unbounded isotropic (all flat), homogeneous, limitless surface (abstract space) an evenly distributed population. all settlements are equidistant and exist in a triangular lattice pattern.
What are the five assumptions of central place theory?
Christaller began his theory development with a set of assumptions: first, the surface of the ideal region would be flat and have no physical barriers; second, soil fertility would be the same everywhere; third, population and purchasing power would be evenly distributed; next, the region would have a uniform ...
What are the characteristics of a central place?
Central places tend to have a more or less uniform, dispersed distribution over any area with homogeneous physical and economic characteristics, and are basically centers performing commercial functions.
Who modified the Christaller model of central place?
geographer August LöschStarting in the 1930s, German geographer August Lösch began to build upon and modify Christaller's model. He did this, in part, because he noticed that the variation in K is very important in shaping the organizations of centers and the numbers of centers at each level in a hierarchy.
What assumptions are in Christaller's central place theory?
Christaller began his theory development with a set of assumptions: first, the surface of the ideal region would be flat and have no physical barriers; second, soil fertility would be the same everywhere; third, population and purchasing power would be evenly distributed; next, the region would have a uniform ...
Who developed the central place theory?
Water ChristallerThe first explicit statement of central place theory was made by German geographer Water Christaller and refined by German economist August Lösch. Although there are important differences between the models of Christaller and Lösch, they share a number of commonalities in terms of reasoning and underlying assumptions.
What is the name of the principal associated with K 3 as per Christaller's central place theory?
Christaller noted three different arrangements of central places according to the following principles: 1. The marketing principle (K=3 system); 2. The transportation principle (K=4 system); 3.
What are the modifications introduced by Losch?
In the critical evaluation, the modifications introduced by Losch reflect the major discrepancies of Christaller e. g. the fixed variability of ‘K’, supply-based model instead of demand-based, complex nesting pattern, space geometry, gross generalization of Goods & Services into 3 principles
Who modified Christaller's model?
Christaller’s model has been modified by an economist & geographer with a view to render this model practical & applicable to the real world.
Why are such models desirable?
Such models are highly desirable since they provide scientific temperament and structure to the subject matter
Is Landscape Understudy isolated?
The region is isolated i.e. Landscape understudy is isolated & has no connection with the rest of the world
Origin of the Theory
The theory was first developed by the German geographer Walter Christaller in 1933 after he began to recognize the economic relationships between cities and their hinterlands (areas farther away).
Christaller's Assumptions
To focus on the economic aspects of his theory, Christaller had to create a set of assumptions. He decided that the countryside in the areas he was studying would be flat, so no barriers would exist to impede people's movement across it. In addition, two assumptions were made about human behavior:
Geometry and Ordering
The central place is located at the vertexes (points) of equilateral triangles. Central places serve the evenly distributed consumers who are closest to the central place. As the vertexes connect, they form a series of hexagons—the traditional shape of many central place models.
Central Place Theory Today
Though Losch's central place theory looks at the ideal environment for the consumer, both his and Christaller's ideas are essential to studying the location of retail in urban areas today. Often, small hamlets in rural areas do act as the central place for various small settlements because they are where people travel to buy their everyday goods.