Material Cost Variance gives an idea of how much more or less cost has been incurred when compared with the standard cost. Thus, Variance Analysis is an important tool to keep a tab on the deviations from the standard set by a company. The cost of raw materials changes all the time in the business world.
How do you calculate total material variance?
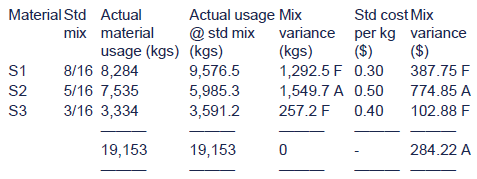
Material Mix Variance will be calculated as follows: Step 1: Calculate the total consumption of raw materials. Total Raw Materials Consumption (100 + 150 + 250) = 500 tons. Step 2: Calculate the Standard Mix. Step 3: Calculate the Variance.
What is the formula for material variance?
What is the formula for material price variance?
- Direct materials. This is called the material yield variance, and is calculated as: (Actual unit usage - Standard unit usage) x Standard cost per unit.
- Direct labor. This is called the labor efficiency variance, and is technically related more to material usage than to efficiency.
- Overhead.
How do you calculate direct materials price variance?
How do you calculate direct materials price variance? To compute the direct materials price variance, take the difference between the standard price (SP) and the actual price (AP), and then multiply that result by the actual quantity (AQ): Direct materials price variance = (SP – AP) x AQ.
What is the standard variance formula?
Variance is given by the formula σ 2 = ∑ (x – M) 2/n; The standard deviation is a metric that expresses how dispersed the observations in a dataset are. Standard Deviation is given by the formula σ = √∑ (x – M) 2/n; The spread of data from its mean point is measured by both variance and standard deviation.

What do you mean by material variance?
Material Variance Related to Materials This is the difference between the actual cost incurred for direct materials and the expected (or standard) cost of those materials. It is useful for determining the ability of a business to incur materials costs close to the levels at which it had planned to incur them.
What is the importance of material variance analysis?
Variance analysis is used to assess the price and quantity of materials, labour and overhead costs. These numbers are reported to management. While it's not necessary to focus on every variance, it becomes a signalling mechanism when a variance is salient.
What is material variance example?
Materials mix variance is that portion of the materials quantity variance which is due to the difference between the actual composition of a mixture and the standard mixture. Example: A product is made from two raw materials, material A and material B. One unit of finished product requires 10 kg of material.
What is meant by variance analysis?
Definition: Variance analysis is the study of deviations of actual behaviour versus forecasted or planned behaviour in budgeting or management accounting. This is essentially concerned with how the difference of actual and planned behaviours indicates how business performance is being impacted.
What are the types of variance analysis?
Variance analysis can be applied to both revenues and expenses. When actual results are better than planned, variance is referred to as 'favourable'....There are four main forms of variance:Sales variance.Direct material variance.Direct labour variance.Overhead variance.
What are the advantages of material variance?
The material usage variance gives all the information management needs to make decisions. Like if the actual quantity used is higher than the estimated quantity, there may be chances that the wastage of raw material is higher than expected. Management can easily compare their planning with the actual work done.
Who is responsible for material variance?
The production department, and specifically the production manager is therefore held responsible for the material usage variance.
What are the reasons for material variance?
If there is a material quantity variance, one or more of the following is usually the cause:Low quality of raw materials.Incorrect specification of materials.Raw materials obsolescence.Damage in transit to the company.Damage while being moved or stored within the company.Damage during the production process.More items...•
What do you mean by variance?
The term variance refers to a statistical measurement of the spread between numbers in a data set. More specifically, variance measures how far each number in the set is from the mean (average), and thus from every other number in the set. Variance is often depicted by this symbol: σ2.
What is an example of variance analysis?
Variance analysis is the comparison of predicted and actual outcomes. For example, a company may predict a set amount of sales for the next year and compare its predicted amount to the actual amount of sales revenue it receives.
How do you perform a variance analysis?
Below are the five basic steps to performing variance analysis.Step 1: Gather Data. Before beginning it is best to gather and aggregate all relevant data in one centralized location. ... Step 2: Calculate Variances. ... Step 3: Analyze Variances. ... Step 4: Compile Management Reports. ... Step 5: Adjust Forecasts.
What is the correct test of material variance?
The difference between the actual quantity and the standard quantity, multiplied by the standard price is the material usage variance.
What is the importance of variance?
Statisticians use variance to see how individual numbers relate to each other within a data set, rather than using broader mathematical techniques such as arranging numbers into quartiles. The advantage of variance is that it treats all deviations from the mean as the same regardless of their direction.
What is the importance of variance and standard deviation?
Standard deviation measures how far apart numbers are in a data set. Variance, on the other hand, gives an actual value to how much the numbers in a data set vary from the mean. Standard deviation is the square root of the variance and is expressed in the same units as the data set.
What is the significance of variance?
The variance is a measure of variability. It is calculated by taking the average of squared deviations from the mean. Variance tells you the degree of spread in your data set. The more spread the data, the larger the variance is in relation to the mean.
What are the importance of direct materials?
Advantages of Direct Materials Direct materials are a key variable cost that fluctuates with production volume. As such, they provide an accurate representation of a company's variable costs. Direct materials are directly linked to the production process and can be easily traced to specific products or services.
What is variance analysis?
Variance analysis can be summarized as an analysis of the difference between planned and actual numbers. The sum of all variances gives a picture of the overall over-performance or under-performance for a particular reporting period. .
What is variance in accounting?
Variances are computed for both the price and quantity of materials, labor, and variable overhead, and are reported to management. However, not all variances are important. Management should only pay attention to those that are unusual or particularly significant. Often, by analyzing these variances, companies are able to use ...
What is the role of standard in variance analysis?
The Role of Standards in Variance Analysis. In cost accounting, a standard is a benchmark or a “norm” used in measuring performance. In many organizations, standards are set for both the cost and quantity of materials, labor, and overhead needed to produce goods or provide services.
What is financial accounting theory?
Financial Accounting Theory Financial Accounting TheoryFinancial Accounting Theory explains the why behind accounting - the reasons why transactions are reported in certain ways. This guide will
What is the difference between cost and quantity standards?
Quantity standards indicate how much labor (i.e., in hours) or materials (i.e., in kilograms) should be used in manufacturing a unit of a product. In contrast, cost standards indicate what the actual cost of the labor hour or material should be. Standards, in essence, are estimated prices or quantities that a company will incur.
Why should management pay attention to variances?
Often, by analyzing these variances, companies are able to use the information to identify a problem so that it can be fixed or simply to improve overall company performance.
What is normalization in financial statements?
Financial Statement Normalization NormalizationFinancial statements normalization involves adjusting non-recurring expenses or revenues in financial statements or metrics so that they only reflect the usual transactions of a company. Financial statements often contain expenses that do not constitute a company's normal business operations
What are the factors that determine material variance?
Material variances include two factors: (1) the quantity of materials that should have been used to produce one unit of output and (2) the prices that should have been paid in acquiring this quantity of materials.
What is total material cost variance?
Hence, the total material cost variance may result from the difference between the standard and actual quantities of materials used, the difference between the standard and actual prices paid for materials, or from a combination of the two.
What is variance analysis?
Variance analysis refers to the comparison of predicted and actual outcomes. For example, a company may predict a set amount of sales for the next year and compare their predicted amount to the actual amount of sales revenue they received. Variance measurements might occur monthly, quarterly or yearly, depending on individual business preferences.
Key terms for variance analysis
Here are some helpful key terms to help you gain a better understanding of variance analysis:
Types of variance analysis
The type of variance analysis you perform depends on the information you are examining. Here are steps and formulas for calculating three different variance analyses:
Examples of variance analysis
Feminine Fashionista, a clothing company, is interested in calculating its overall material variance. It has an actual quantity of 30,000 pieces of fabric at a standard price of $0.65 per fabric and a standard quantity of 25,000 pieces of fabric at an actual price of $0.50 per fabric.
What is material price variance?
Material Price Variance is the difference between the standard price and the actual price for the actual quantity of materials used for production. The cause for material price variance can be many including changes in prices, poor purchasing procedures, deficiencies in price negotiation, etc.
How to find material cost variance?
This means Material Cost Variance = Material Price Variance + Material Usage Variance. We can confirm and cross check this equation with the help of our example.
Why is variance favorable?
The variance is favorable because the actual price is less than the standard price. In cases where the actual price is more than the standard price, the result is (A) which means adverse. Let us now understand the meaning of Material Usage Variance.
What is the difference between the standard cost of direct materials specified for production and the actual cost of direct materials used in production?
The difference between the standard cost of direct materials specified for production and the actual cost of direct materials used in production is known as Direct Material Cost Variance. Material Cost Variance gives an idea of how much more or less cost has been incurred when compared with the standard cost. Thus, Variance Analysis is an important tool to keep a tab on the deviations from the standard set by a company.
What is the Variance Analysis?
Variance analysis refers to identifying and examining the difference between the standard numbers expected by the business to achieve and the actual numbers achieved by them , which helps the company analyze favourable or unfavourable outcomes.
How does variance analysis help minimize risk?
Thus Variance analysis helps to minimize the Risk by comparing the actual performance to Standards.
What is the reason for sales variation?
Further Sales Variance is due to either change in sales price or Change in Sales Volume
What are the four types of variance analysis?
Here we look at the calculation and examples of the top 4 types of variance analysis, including material variance, sales variance, labor variance, and variable overheads. You may also take a look at the following articles:-
Why is it important to know the cause of variance analysis?
It is very important to know the cause of variance analysis so that one can approach for corrective measure
Is production cost dependent on purchasing cost?
Both purchasing and production costs are dependent on each other, so we have to look into not only the purchasing cost but also the Production Cost to know the total variance as well.
How to calculate material yield variance?
Material yield variance. Subtract the total standard quantity of materials that are supposed to be used from the actual level of use and multiply the remainder by the standard price per unit.
What is Variance Analysis?
Variance analysis is the quantitative investigation of the difference between actual and planned behavior. This analysis is used to maintain control over a business through the investigation of areas in which performance was unexpectedly poor. For example, if you budget for sales to be $10,000 and actual sales are $8,000, variance analysis yields a difference of $2,000. Variance analysis is especially effective when you review the amount of a variance on a trend line, so that sudden changes in the variance level from month to month are more readily apparent. Variance analysis also involves the investigation of these differences, so that the outcome is a statement of the difference from expectations, and an interpretation of why the variance occurred. To continue with the example, a complete analysis of the sales variance would be:
What is variance source information?
Variance source information. Many of the reasons for variances are not located in the accounting records, so the accounting staff has to sort through such information as bills of material, labor routings, and overtime records to determine the causes of problems. The extra work is only cost-effective when management can actively correct problems based on this information.
How to calculate variable overhead efficiency variance?
Variable overhead efficiency variance. Subtract the budgeted units of activity on which the variable overhead is charged from the actual units of activity, multiplied by the standard variable overhead cost per unit.
Why is variance analysis important?
Variance analysis is especially effective when you review the amount of a variance on a trend line, so that sudden changes in the variance level from month to month are more readily apparent. Variance analysis also involves the investigation of these differences, so that the outcome is a statement of the difference from expectations, ...
What is purchase price variance?
Purchase price variance. The actual price paid for materials used in the production process, minus the standard cost, multiplied by the number of units used.
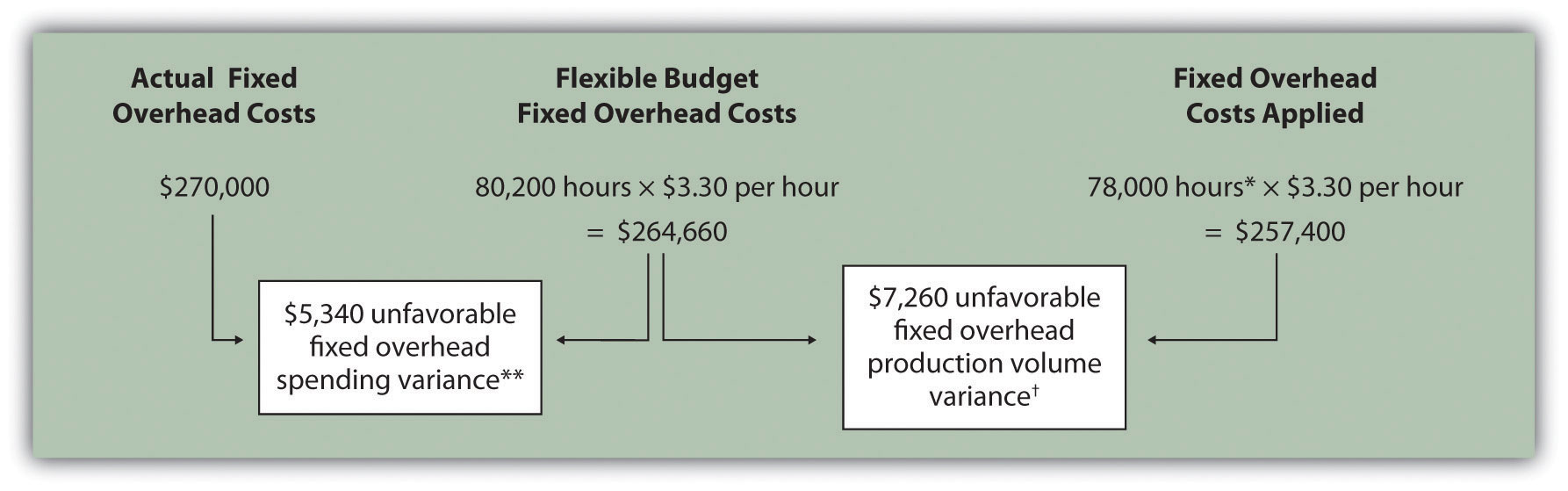
What is fixed overhead variance?
Fixed overhead spending variance. The total amount by which fixed overhead costs exceed their total standard cost for the reporting period.
How to calculate direct materials price variance?
To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500). This difference comes to a $13,500 favorable variance, meaning that the company saves $13,500 by buying direct materials for $9.90 rather than the original standard price of $10.35.
Why is it important to know the price variance when purchasing raw materials?
It is usually better to compute the variance when materials are purchased because that is when the purchasing manager, who has responsibility for this variance, has completed his or her work. In addition, recognizing the price variance when materials are purchased allows the company to carry its raw materials in the inventory accounts at standard cost, which greatly simplifies bookkeeping. The material price variance calculation tells managers how much money was spent or saved, but it doesn’t tell them why the variance happened. One common reason for unfavorable price variances is a price change from the vendor. Companies typically try to lock in a standard price per unit for raw materials, but sometimes suppliers raise prices due to inflation, a shortage or increasing business costs.
How to do activity based variance analysis?
The first step in activity-based variance analysis is to assign all overhead costs to a level of activity. To reach this standard rate, the annual overhead cost is divided by the cost center’s practical capacity. Practical capacity is used so that idle capacity may be found and put to better use.
What is the difference between the standard and actual cost per unit of direct materials purchased?
Purchase price variance. This is the difference between the standard and actual cost per unit of the direct materials purchased, multiplied by the standard number of units expected to be used in the production process. This variance is the responsibility of the purchasing department.
What is purchase price variance?
The purchase price variance is the difference between the standard costs for the material and landed cost elements and the corresponding actual costs from the matched, posted, and extracted vouchers.
What is PPV variance?
The term “purchase price variance, ” or PPV variance, is used to show the difference between the estimated and actual costs in accounting.
Where to record capitalizable variances?
When complete, capitalizable variances should be recorded in a “standard-to-actual” reserve within inventory on the balance sheet with the remainder being appropriately expensed through the income statement. This reserve has the effect of adjusting the company’s inventory balances to “actual,” which is appropriate under GAAP. On a net basis, the purchase price variance is really the difference between standard cost of the material and the actual invoice price of the material. The materials price variance can be computed either when materials are purchased or when they are placed into production.