
Creswell and Plano Clark (2011) define mixed-methods research as those studies that include at least one quantitative strand and one qualitative strand.
What are the pros and cons of mixed methods research?
- Triangulation – the confirmation of results by different methods.
- Complementarity – results from one method are used to enhance, elaborate or clarify results from another method.
- Initiation – where new insights are obtained which will stimulate new research questions.
- Development – results from one method shape another method.
What are examples of mixed method research?
What are the 5 theories of learning?
- Cognitive learning theory.
- Behaviorism learning theory.
- Constructivism learning theory.
- Humanism learning theory.
- Connectivism learning theory.
What is mix method in research?
- Collecting and analyzing both quantitative (closed-ended) and qualitative (open-ended) data.
- Using rigorous procedures in collecting and analyzing data appropriate to each method’s tradition, such as ensuring the appropriate sample size for quantitative and qualitative analysis.
- Integrating the data during data collection, analysis, or discussion.
What are the limitations of mixed methods research?
- Lack of clear purpose and substantive focus
- Appropriate use of quantified coding from qualitative data
- Appropriate use of generalization to match research methods (Bazely, p. 9)

What is mixed methods research by John Creswell?
Creswell and Plano Clark (2011) define mixed-methods research as those studies that include at least one quantitative strand and one qualitative strand.
What is the meaning of mixed methods in research?
A mixed methods study combines quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis in one study. Individually, these approaches can answer different questions, so combining them can provide you with more in-depth findings.
What is the meaning of mixed method?
"Mixed methods is a terms that is usually used to designate combining quantitative and qualitative research methods in the same research project. I prefer the term multimethod research to indicate that different sytles of research may be combined in the same research project.
What is a mixed method research PDF?
Mixed methods may be defined as 'research in which the investigator collects and. analyses data, integrates the findings and draws inferences using both qualitative. and quantitative approaches or methods in a single study'(Tashakkori and Creswell, 2007:4).
What is mixed method research according to authors?
In general, mixed methods research represents research that involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting quantitative and qualitative data in a single study or in a series of studies that investigate the same underlying phenomenon.
Why mixed method is used?
Mixed methods enables investigators conceptually and analytically to integrate qualitative research and qualitative data (e.g., semi-structured interviews, observations, focus groups) with traditional epidemiological and quantitative methods of research to facilitate translation.
What is mixed methods research scholarly articles?
MMR involves the application of a well-defined and pre-specified research design that articulates purposely and prospectively, qualitative and quantitative components to generate an integrated set of evidence addressing a single research question.
What is mixed method sampling?
Mixed Methods Sampling Strategies Two or more samples recruited from different levels of the population of interest.
How do you use mixed methods in research?
In mixed methods research, you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question. What is data collection? Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research.
When to use mixed methods research
Mixed methods research may be the right choice if your research process suggests that quantitative or qualitative data alone will not sufficiently answer your research question. There are several common reasons for using mixed methods research:
Mixed methods research designs
There are different types of mixed methods research designs. The differences between them relate to the aim of the research, the timing of the data collection, and the importance given to each data type.
Advantages of mixed methods research
Combining the two types of data means you benefit from both the detailed, contextualized insights of qualitative data and the generalizable, externally valid insights of quantitative data. The strengths of one type of data often mitigate the weaknesses of the other.
Disadvantages of mixed methods research
Mixed methods research is very labor-intensive. Collecting, analyzing, and synthesizing two types of data into one research product takes a lot of time and effort, and often involves interdisciplinary teams of researchers rather than individuals. For this reason, mixed methods research has the potential to cost much more than standalone studies.
Frequently asked questions
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Tegan George
Tegan is an American based in Amsterdam, with master's degrees in political science and education administration. While she is definitely a political scientist at heart, her experience working at universities led to a passion for making social science topics more approachable and exciting to students.
What is mixed methods research?
Mixed methods research is a research designwith a methodology and methods. As a methodology, it involves collecting,analyzing, and mixing qualitative and quantitative approaches at many phasesin the research process, from the initial philosophical assumptions to thedrawing of conclusions. As a method, it focuses on collecting, analyzing,and mixing quantitative and qualitative data in a single study or series of stud-ies. It is premised on the idea that the use of quantitative and qualitativeapproaches in combination provides a better understanding of researchproblems than either approach alone. This better understanding resultsbecause mixed methods offers strengths that offset the weaknesses of sepa-rately applied quantitative and qualitative research methods. It also encour-ages the collection of more comprehensive evidence for study problems,helps answers questions that quantitative or qualitative methods alone can-not answer, and reduces adversarial relationships among researchers andpromotes collaboration. Mixed methods encourages the use of multipleworldviews and is a practical and natural approach to research. Mixed meth-ods research is important today because of the complexity of problems thatneed to be addressed, the rise of interest in qualitative research, and thepractical need to gather multiple forms of data for diverse audiences. It hasevolved through four phases: a formative phase, the paradigm debate, theprocedural period, and the emerging recent interest exemplified in publicand federal funding, journals, disciplines, and special workshops.
Why do researchers need an introduction to mixed methods?
Because mixed methods is a new design, researchers need an introductionto the approach, guidance as to how to conduct the design, and informationabout the specific procedures involved. The purpose of this book is to pro-vide researchers with
What is the multimethod matrix?
They developed the mul-titrait, multimethod matrix, which was designed to attribute individual varia-tion in personality scale scores to the trait itself rather than to the methodused to measure it. Others combined both quantitative and qualitative datain this period (Sieber, 1973; Jick, 1979), and the question became whether itwas possible to combine both forms of data when they arose from differentperspectives (see Cook & Reichardt, 1979).
What are the four types of mixed methods?
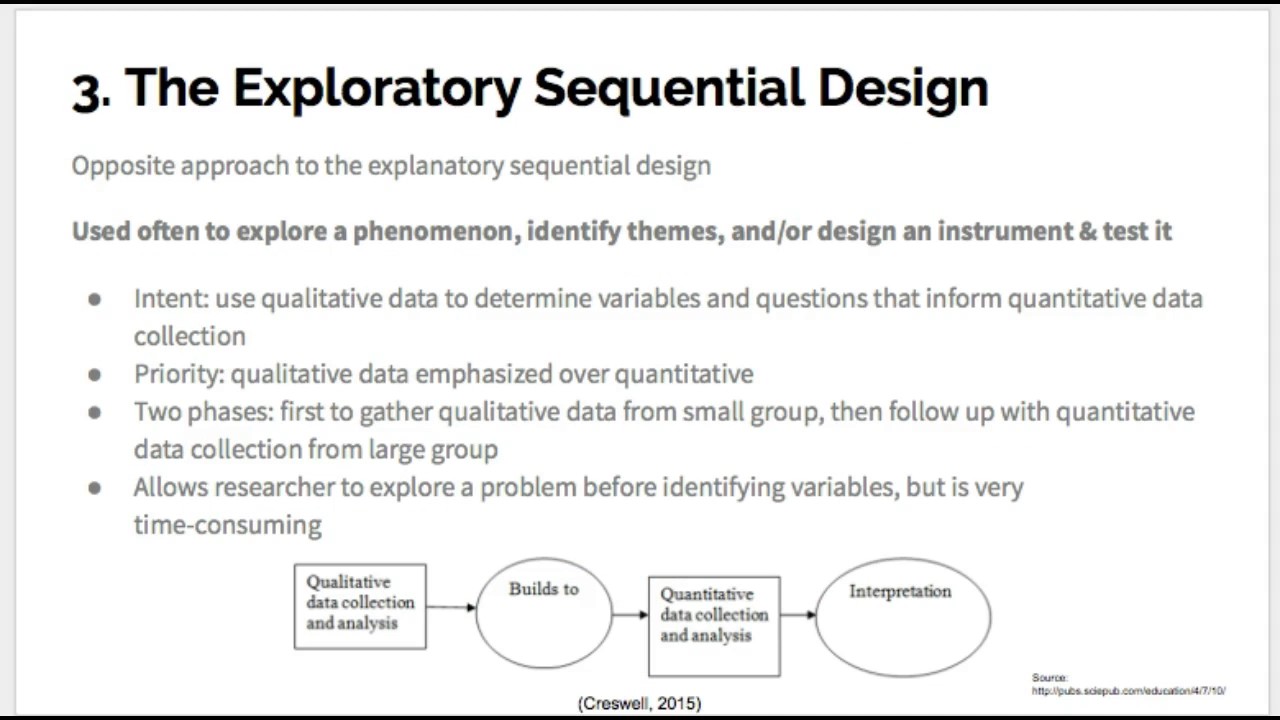
The four major types of mixed methods designs are the Triangulation Design,the Embedded Design, the Explanatory Design, and the Exploratory Design. The following sections provide an overview of each of these designs: theiruse, procedures, common variants, and challenges.
What is mixed method design?
The mixed methods sequential explanatory design consists of two distinctphases: quantitative followed by qualitative (Creswell, Plano Clark, et al.,2003). In this design, a researcher first collects and analyzes the quantita-tive (numeric) data. The qualitative (text) data are collected and analyzedsecond in the sequence and help explain, or elaborate on, the quantitativeresults obtained in the first phase. The second, qualitative, phase builds onthe first, quantitative, phase, and the two phases are connected in the inter-mediate stage in the study. The rationale for this approach is that the quan-titative data and their subsequent analysis provide a general understandingof the research problem. The qualitative data and their analysis refine andexplain those statistical results by exploring participants’ views in more depth(Rossman & Wilson, 1985; Tashakkori & Teddlie, 1998; Creswell, 2003).
What is research design?
Research designs are procedures for collecting, analyzing, interpreting,and reporting data in research studies. They represent different mod-els for doing research, and these models have distinct names andprocedures associated with them. Rigorous research designs are importantbecause they guide the methods decisions that researchers must make dur-ing their studies and set the logic by which they make interpretations at theend of studies. Once a researcher has selected a mixed methods approach fora study, the next step is to decide on the specific design that best addressesthe research problem. What designs are available, and how do researchersdecide which one is appropriate for their studies? Mixed methods researchersneed to be acquainted with the major types of mixed methods designs andthe common variants among these designs. Important considerations whenchoosing designs are knowing the intent, the procedures, and the strengthsand challenges associated with each design. Researchers also need to befamiliar with the timing, weighting, and mixing decisions that are made ineach of the different mixed methods designs.
When to Use Mixed Methods Research
- Mixed methods research may be the right choice if your research processsuggests that quantitative or qualitative data alone will not sufficiently answer your research question. There are several common reasons for using mixed methods research: 1. Generalizability: Qualitative research usually has a smaller sample size, and thus is not generalizable. In mixed methods res…
Mixed Methods Research Designs
- There are different types of mixed methods research designs. The differences between them relate to the aim of the research, the timing of the data collection, and the importance given to each data type. As you design your mixed methods study, also keep in mind: 1. Your research approach (inductive vs deductive) 2. Your research questions 3. What kind of data is already ava…
Advantages of Mixed Methods Research
- “Best of both worlds” analysis
Combining the two types of data means you benefit from both the detailed, contextualized insights of qualitative data and the generalizable, externally valid insights of quantitative data. The strengths of one type of data often mitigate the weaknesses of the other. For example, solely qu… - Method flexibility
Mixed methods are less tied to disciplines and established research paradigms. They offer more flexibility in designing your research, allowing you to combine aspects of different types of studies to distill the most informative results. Mixed methods research can also combine theory generat…
Disadvantages of Mixed Methods Research
- Workload
Mixed methods research is very labor-intensive. Collecting, analyzing, and synthesizing two types of data into one research product takes a lot of time and effort, and often involves interdisciplinary teams of researchers rather than individuals. For this reason, mixed methods re… - Differing or conflicting results
If your analysis yields conflicting results, it can be very challenging to know how to interpret them in a mixed methods study. If the quantitative and qualitative results do not agree or you are concerned you may have confounding variables, it can be unclear how to proceed. Due to the fa…