Neutrophilic leukocytosis is an abnormally high number of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that help the body fight infections and heal injuries. Neutrophils may increase in response to a number of conditions or disorders, including
What is leukocytosis and what does it indicate?
Leukocytosis, or high white blood cell count, can indicate a range of conditions, including infections, inflammation, injury and immune system disorders. A complete blood count (CBC) is usually performed to check for leukocytosis. Treating the underlying condition usually reduces your white blood cell count. What is leukocytosis?
What is leukocytosis and what causes it?
Leukocytosis, a common laboratory finding, is most often due to relatively benign conditions (infections or inflammatory processes). Much less common but more serious causes include primary bone marrow disorders. The normal reaction of bone marrow to infection or inflammation leads to an increase in the number of white blood cells ...
What causes low WBC and low neutrophils?
what is the cause of low neutrophil and wbc count? Dr. Christian Schultheis answered 24 years experience Hematology and Oncology Many things: Medications, infections, bone marrow problems. The most common is medications. Sometimes in 6-12% of the population, the WBC is low. Other reasons ... Read More 1 doctor agrees Send thanks to the doctor
What are the causes of increased lymphocytes in leukocytosis?
The most common cause of lymphocytic leukocytosis is infection with a virus. Other causes include: Two blood cancers, lymphoma and lymphocytic leukemia, are associated with high numbers of lymphocytes in the bloodstream. Neutrophils, like lymphocytes, protect against bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungal growth.

What causes neutrophilic leukocytosis?
Neutrophilic leukocytosis is one of the most frequent abnormalities found in any population of sick patients and is most often caused by infections, hypoxic tissue damage, trauma, inflammatory diseases, malignancy, or trauma.
How is neutrophilic leukocytosis treated?
This condition is a medical emergency and requires hospitalization so fluids can be given by vein and drugs to reduce the white blood cell count (hydroxyurea and chemotherapy drugs) can be given. Sometimes, a type of blood-filtering treatment (leukapheresis.
What does it mean when neutrophils and leukocytes are high?
Neutrophilia leukocytosis is caused by a high number of neutrophils (the most plentiful type of white blood cell, which helps resolve infections and heal damaged tissues). Lymphocytosis refers to high levels of lymphocytes (white blood cells that protect your lymphatic system).
What kind of infection causes high neutrophils?
Most bacterial infections cause a high neutrophil count but not all of them do. Viral infections don't generally cause neutrophilia but they may in the early stage of infection. Some fungal and parasitic infections can cause neutrophilia as well. Inflammation.
Is leukocytosis a leukemia?
Excessive numbers of white blood cells are most often due to the response of normal bone marrow to infection or inflammation. In some instances, leukocytosis is a sign of more serious primary bone marrow disease (leukemias or myeloproliferative disorders).
Should I worry about high neutrophils?
Outlook. If your neutrophil counts are high, it can mean you have an infection or are under a lot of stress. It can also be a symptom of more serious conditions. Neutropenia, or a low neutrophil count, can last for a few weeks or it can be chronic.
Can stress cause high neutrophils?
With reactive neutrophilia, there is an increase in the number of neutrophils in response to infections or stress. Anxiety can cause neutrophilia, as stress hormones in your body cause a greater than normal number of these cells to be released from the bone marrow.
What is an alarming WBC count?
How many white blood cells (WBCs) someone has varies, but the normal range is usually between 4,000 and 11,000 per microliter of blood. A blood test that shows a WBC count of less than 4,000 per microliter (some labs say less than 4,500) could mean your body may not be able to fight infection the way it should.
How high are neutrophils in leukemia?
55 percent increase in neutrophils. 38 percent increase in monocytes. 36 percent reduction in lymphocytes. no change to eosinophils and basophils.
What is the most common cause of neutrophilia?
Acute bacterial infections, such as pneumococcal, staphylococcal, or leptospiral infections, are the most frequent causes of infection-induced neutrophilia. Certain viral infections, such as herpes complex, varicella, and EBV infections, may also cause neutrophilia.
What cancers cause neutrophilia?
Neutrophils can also influence the migration potential of cancer cells. In several types of cancer it has been shown that neutrophils promote metastasis. These tumors include skin squamous cell carcinoma [135], melanoma [136], adenocarcinomas [137], HNSCC [83], and breast cancer [138].
What happens if neutrophil count is high?
Neutrophilia: Neutrophilia, also known as neutrophilic leukocytosis, occurs when your neutrophil count is too high, which is often the result of a bacterial infection. To combat the infection, immature neutrophils leave your bone marrow too soon and enter into your bloodstream.
How do you treat high neutrophils naturally?
To help reduce the risk of high or low neutrophil levels, people may want to try the following tips: Try not to over-exercise or exercise beyond comfort levels. Reduce stress levels and treat chronic or severe stress.
How high are neutrophils in leukemia?
55 percent increase in neutrophils. 38 percent increase in monocytes. 36 percent reduction in lymphocytes. no change to eosinophils and basophils.
What cancers are associated with high neutrophils?
Neutrophils can also influence the migration potential of cancer cells. In several types of cancer it has been shown that neutrophils promote metastasis. These tumors include skin squamous cell carcinoma [135], melanoma [136], adenocarcinomas [137], HNSCC [83], and breast cancer [138].
What are the common causes of neutrophilia?
Acute bacterial infections, such as pneumococcal, staphylococcal, or leptospiral infections, are the most frequent causes of infection-induced neutrophilia. Certain viral infections, such as herpes complex, varicella, and EBV infections, may also cause neutrophilia.
What is the diagnosis of neutrophilic leukocytosis?
Diagnosis of Neutrophilic Leukocytosis. Doctors often do a blood test called a complete blood count. This test may be done for many different symptoms, including signs of infection (such as fever, cough, or abdominal pain), or signs of chronic illness (such as weight loss or fatigue).
What is a neutrophil?
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that help the body fight infections and heal injuries. Neutrophils may increase in response to a number of conditions or disorders, including.
Why do neutrophils increase?
Infections by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites may all increase the number of neutrophils in the blood. The number of neutrophils may rise in people who have an injury, such as a hip fracture or burn. Inflammatory disorders, including autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause an increase in the number and activity ...
What does it mean when you have a neutrophil in your blood?
Immature neutrophils in the blood may indicate the presence of a disorder in the bone marrow, such as leukemia. When immature neutrophils are found in the blood, doctors usually take a sample of bone marrow ( bone marrow examination ).
What happens if you have too much neutrophils?
Very rarely, in people with leukemia, extremely high levels of immature neutrophils (more than 100,000 cells per microliter of blood [100 × 10 9 per liter]) can cause the blood to become too thick and cause breathing problems, stroke, and death. This condition is a medical emergency and requires hospitalization so fluids can be given by vein and drugs to reduce the white blood cell count ( hydroxyurea and chemotherapy drugs) can be given. Sometimes, a type of blood-filtering treatment ( leukapheresis) is used to remove the white blood cells from the blood.
What is the treatment for white blood cell count?
Sometimes, a type of blood-filtering treatment ( leukapheresis ) is used to remove the white blood cells from the blood.
What is CLL in medical terms?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a generally slow-growing blood disorder. In CLL, lymphocytes (small white blood cells found mostly in the lymph system) become cancerous. Gradually, these cancerous cells replace normal cells. More than three-quarters of people with CLL belong to one age group.
What is the name of the abnormally high number of neutrophils in the blood?
Neutrophilic leukocytosis is an abnormally high number of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood.
Why do neutrophils increase?
In many instances, the increased number of neutrophils is a necessary reaction by the body, as it tries to heal or ward off an invading microorganism or foreign substance. Infections by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites may all increase the number of neutrophils in the blood.
What is the condition where the bone marrow produces red blood cells that are large and abnormal?
Deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folate (folic acid) cause a condition called megaloblastic anemia. In patients with megaloblastic anemia the bone marrow produces red blood cells that are large and abnormal (megaloblasts). Which of the following is NOT a cause of Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency?
What is the best way to test for immature neutrophils?
When immature neutrophils are found in the blood, doctors usually take a sample of bone marrow ( bone marrow examination ).
Can leukemia cause death?
Very rarely, in people with leukemia , extremely high levels of immature neutrophils (more than 100,000 cells per microliter of blood [100 × 10 9 per liter]) can cause the blood to become too thick and cause breathing problems, stroke, and death. This condition is a medical emergency and requires hospitalization so fluids can be given by vein and drugs to reduce the white blood cell count ( hydroxyurea and chemotherapy drugs) can be given. Sometimes, a type of blood-filtering treatment ( leukapheresis ) is used to remove the white blood cells from the blood.
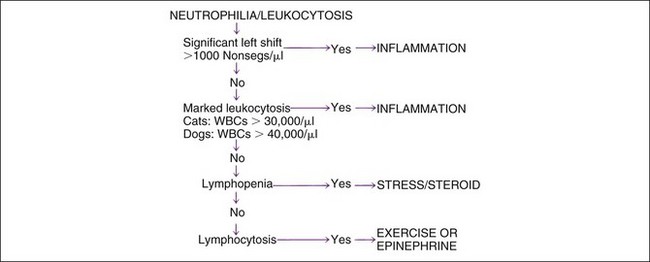
What is neutrophilic leukocytosis?
A neutrophilic leukocytosis is seen in a variety of illnesses and conditions and is widely regarded an indicator of infection or inflammation. Intoxication by intraperitoneal injection or oral gavage equally potentiates postburn organ damage and inflammation.
What causes leukocytosis in the body?
Counts almost as high occur in leukemoid (leukemia-like) reactions caused by infection and non-infectious inflammation. Drugs can also cause leukocytosis. Cortisone-like drugs (prednisone), lithium, and NSAIDs are the most common offenders. Non-specific stresses also cause white blood cells to increase in the blood.
What type of leukocytosis is leftshift?
Hematologic results revealed neutrophilic leukocytosis with leftshift and toxic neutrophils.
What is the term for a transient increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood?
leukocytosis. [ loo″ko-si-to´sis] a transient increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood, due to various causes. basophilic leukocytosis basophilia (def. 1). eosinophilic leukocytosis eosinophilia (def. 1). mononuclear leukocytosis mononucleosis. neutrophilic leukocytosis neutrophilia. pathologic leukocytosis that due to some morbid ...
Why do leukocytes increase?
The increased number of leukocytes can occur abnormally as a result of an infection, cancer , or drug intake; however, leukocytosis can occur normally after eating a large meal or experiencing stress.
What is a condition characterized by an elevated number of white cells in the blood?
Leukocytosis is a condition characterized by an elevated number of white cells in the blood.
Why does neutrophilia increase?
Tissue damage from other causes raises the white count for similar reasons. Burns, infarction (cutting off the blood supply to a region of the body so that it dies), crush injuries, inflammatory diseases , poisonings , and severe diseases, like kidney failure and diabetic ketoacidosis, all cause neutrophilia.
What causes leukocytosis?
Causes of leukocytosis. Causes of leukocytosis can be classified by type of WBC. Causes of neutrophilia: infections. anything that causes long-term inflammation, including injuries and arthritis. reaction to some drug such as steroids, lithium, and some inhalers.
What is the most common type of leukocytosis?
Neutrophilia. This common type of leukocytosis is caused by an increase in neutrophils, which account for 40–60 percent of the white blood cells in your body.
How many WBCs are needed for leukocytosis?
How leukocytosis is diagnosed. Normally you have between 4,000 and 11,000 WBCs per microliter of blood if you aren’t pregnant. Anything higher is considered leukocytosis. WBC counts between 50,000 and 100,000 per microliter usually mean a very severe infection or cancer somewhere in the body.
Why is my WBC so high?
However, it can be caused by serious diseases such as leukemia and other cancers, so it’s important that your doctor diagnosis the cause of an increased WBC when it’s found. Leukocytosis associated with pregnancy or in response to exercise is normal and nothing to worry about. Last medically reviewed on July 18, 2018.
What percentage of white blood cells are monocytes?
Monocytosis. This form of leukocytosis is characterized by high levels of monocytes, which comprise about 2 – 8 percent of your white blood cells.
What happens when you have high white blood cells?
When you have very high levels of white blood cells in your body, they can cause your blood to become very thick, which can impair blood flow.
Why do white blood cells increase?
These are the cells in your blood that help your body fight infections and some diseases. When the number of white cells in your blood is higher than normal, it’s called leukocytosis. This usually happens because you’re sick, but sometimes it’s just a sign that your body is stressed.
What happens to the neutrophils during infection?
During established infection, the neutrophil count remains elevated, with equal numbers in the marginal and the circulating pool. During the recovery phase, the flow of cells from the marrow decreases, with a resultant decrease in the number of neutrophils. 1
Why do neutrophils increase?
The most common cause of an increased number of neutrophils is the normal response of the body to an infection. In many instances, the increased number of neutrophils is a necessary reaction by the body, as it tries to heal or ward off an invading microorganism or foreign substance. Infections by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites may all increase the number of neutrophils in the blood. 2
What is a higher than normal number of neutrophils?
Neutrophilia refers to a higher than normal number of neutrophils. Neutrophilia may result from a shift of cells from the marginal to the circulating pool (shift neutrophilia) without an increase in the total blood granulocyte pool (TBGP) or from a true increase in TBGP size (true neutrophilia). 1
What bacteria infections can cause pharynx congestion and enlarged tonsils that lead to neutrophilic leukocytosis?
Strept throat is one: Any throat infection, commonly viruses, but strept. throat is one of the bacteria commonly involved.
What is the name of the drug that causes a rise in white blood cell count?
A corticosteroid...: ...called "fluticasone" is one of the ingredients of Advair. Corticosteroids are well known for causing temporary rises in white blood cell counts (le... Read More
Can neutrophilic rhinosinusitis be preventable?
Probably: The diagnosis that you have provided suggests that you have had a biopsy. Neutrophiles are the first line of defense in what is called innate immunit... Read More
