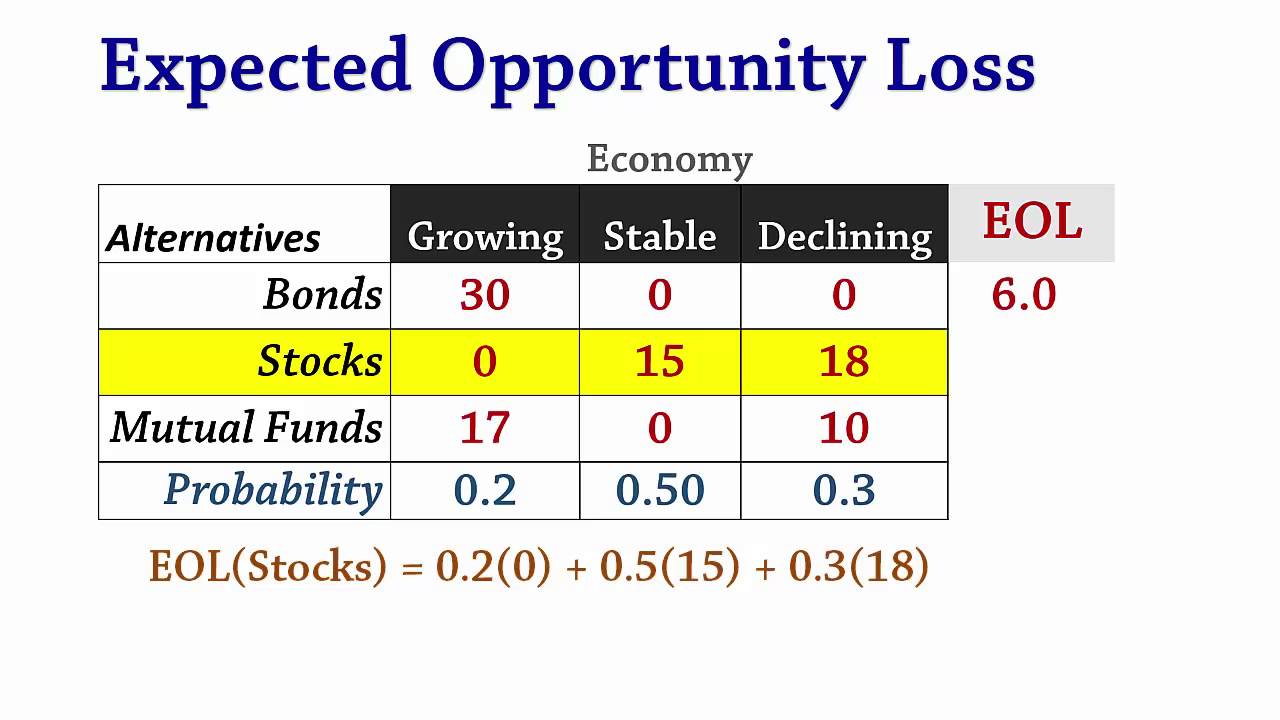
What is expected opportunity loss in decision making?
The Expected Opportunity Loss (EOL) Criterion, is a technique used to make decisions under uncertainty, under the assumption that the probabilities of each state of nature is known. The decision made and the final state of nature (which the decision maker does not know beforehand) determines the payoff. Click to see full answer.
What is opportunity loss table?
Opportunity Loss Table: The opportunity Loss is defined as the difference between highest possible profit for a state of nature and the actual profit obtained for the particular action taken. In short opportunity loss is the loss incurred due to failure of not adopting the best possible course of action or strategy.
How do you calculate the probability of opportunity loss?
Referring to the Opportunity Loss table that you calculated above, multiply each of the predicted losses times the probability of that loss occurring. For example, the top row represents the low demand market, which has a probability of 0.4.
What is the theoretical loss of each choice?
This makes sense because they are comparisons of each choice against itself, so there is no theoretical loss. However, compare the other values and you will see the amount of money that, based on your prediction data, you would lose under each scenario.

What do you mean by opportunity loss table in context of decision theory?
Opportunity Loss Table : The opportunity Loss is defined as the difference between highest possible profit for a state of nature and the actual profit obtained for the particular action taken. In short opportunity loss is the loss incurred due to failure of not adopting the best possible course of action or strategy.
How do you find opportunity loss?
To calculate the expected opportunity loss, simply subtract the actual payoff amount from the optimal payoff amount.
What is opportunity loss or regret?
Regret (also called opportunity loss) is defined as the difference between the actual payoff and the payoff that would have been obtained if a different course of action had been chosen. This is also called difference regret.
What is opportunity loss in quantitative techniques?
The value or potential gains that an investor forgoes by choosing a specific type of asset or strategy. In other words, it is the value of a lost chance that would have brought about some amount of profits had the investor stuck to a corresponding course of action.
What is opportunity loss?
The value of a lost chance or a potential profit that was not realized because a course of action was taken that did not permit the investor to obtain that profit.
How do you prepare an opportunity loss table?
0:142:59Decision Analysis 2b: Expected Opportunity Loss (EOL) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe will be using this payoff table where payoffs are profits and the probabilities of the states ofMoreWe will be using this payoff table where payoffs are profits and the probabilities of the states of nature are point two point five and point three respectively. To begin we obtain a regret or an
What is regret in decision theory?
What Is Regret Theory? Regret theory states that people anticipate regret if they make the wrong choice, and they consider this anticipation when making decisions. Fear of regret can play a significant role in dissuading someone from taking action or motivating a person to take action.
What is expected opportunity loss criterion?
The Expected Opportunity Loss (EOL) Criterion, is a technique used to make decisions under uncertainty, under the assumption that the probabilities of each state of nature is known.
What is Laplace in decision making?
EQUALLY LIKELY (LAPLACE) : This criterion uses all the payoffs for each alternative . this is also called laplace, decision criterion. This criteria finds the average payoff for each alternative and select the alternative with highest average.
What is EMV and EOL?
Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Criterion. Expected Opportunity Loss (EOL) Criterion. Expected Profit with Perfect Information (EPPI) and Expected Value of Perfect. Information (EVPI)
What is opportunity cost give example?
A student spends three hours and $20 at the movies the night before an exam. The opportunity cost is time spent studying and that money to spend on something else. A farmer chooses to plant wheat; the opportunity cost is planting a different crop, or an alternate use of the resources (land and farm equipment).
What is opportunity gain?
Opportunity Gain is an index that measures the increase of economic complexity that a product will give a region, meaning, the contribution of a given product to the complexity of the region economy.
What is opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost is the forgone benefit that would have been derived by an option not chosen. To properly evaluate opportunity costs, the costs and benefits of every option available must be considered and weighed against the others. Considering the value of opportunity costs can guide individuals and organizations to more profitable ...
Why are opportunity costs important?
Because by definition they are unseen, opportunity costs can be easily overlooked if one is not careful. Understanding the potential missed opportunities foregone by choosing one investment over another allows for better decision-making.
What is the difference between opportunity cost and sunk cost?
The difference between an opportunity cost and a sunk cost is the difference between money already spent in the past and potential returns not earned in the future on an investment because the capital was invested elsewhere. Buying 1,000 shares of company A at $10 a share, for instance, represents a sunk cost of $10,000. This is the amount of money paid out to make an investment, and getting that money back requires liquidating stock at or above the purchase price. But the opportunity cost instead asks where could have that $10,000 been put to use in a better way.
How to determine the potential profitability of an investment?
When assessing the potential profitability of various investments, businesses look for the option that is likely to yield the greatest return. Often, they can determine this by looking at the expected rate of return for an investment vehicle. However, businesses must also consider the opportunity cost of each option.
Do financial reports show opportunity costs?
While financial reports do not show opportunity costs, business owners often use the concept to make educated decisions when they have multiple options before them. Bottlenecks, for instance, are often a result of opportunity costs.
Is clipping coupons an opportunity cost?
Even clipping coupons versus going to the supermarket empty-handed is an example of an opportunity cost unless the time used to clip coupons is better spent working in a more profitable venture than the savings promised by the coupons. Opportunity costs are everywhere and occur with every decision made, big or small.