Explore
The swings in blood pressure when you stand and sit as a result of orthostatic hypotension can be a risk factor for stroke due to the reduced blood supply to the brain. Cardiovascular diseases. Orthostatic hypotension can be a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and complications, such as chest pain, heart failure or heart rhythm problems.
How dangerous is orthostatic hypotension?
You may benefit from some of these simple changes in lifestyle: (7)
- Wear compression stockings. These can help keep blood from pooling in your legs, which forces it to be more available to the rest of your body. ...
- Exercise. Orthostatic hypotension can result from blood pooling in the limbs when you are inactive. ...
- Raise the head of your bed. ...
- Avoid hot tubs and long, hot showers. ...
- Avoid physical strain. ...
What are the ways to prevent orthostatic hypotension?
Treatment There is no cure for multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypotension. Treatment is aimed at controlling symptoms. Anti-Parkinson medication such as Sinemet may improve the general sense of well-being. Medications to elevate blood pressure while standing are often used, but may cause high blood pressure when lying down.
Is there a cure for orthostatic hypotension?
Orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension)
- Diagnosis. You begin by lying flat on a table. ...
- Treatment. Compression stockings, also called support stockings, compress your legs, promoting circulation. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
How to diagnose orthostatic hypotension?

What is the most common cause of orthostatic hypotension?
Loss of fluid within the blood vessels is the most common cause of symptoms linked to orthostatic hypotension. This could be due to dehydration brought about by diarrhea, vomiting, and the use of medication, such as diuretics or water pills.
How do you fix orthostatic hypotension?
These include:Wearing waist-high compression stockings. These may help improve blood flow and reduce the symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. ... Getting plenty of fluids. ... Avoiding alcohol. ... Increasing salt in the diet. ... Eating small meals. ... Exercising. ... Moving and stretching in certain ways. ... Getting up slowly.More items...•
What is orthostatic hypotension a symptom of?
The non-neurogenic form of orthostatic hypotension is often caused by environmental or health factors that impair the body's mechanisms to stabilize blood pressure upon standing. These factors include heart disease, low blood volume (hypovolemia), alcohol use, or advanced age.
What neurological conditions cause orthostatic hypotension?
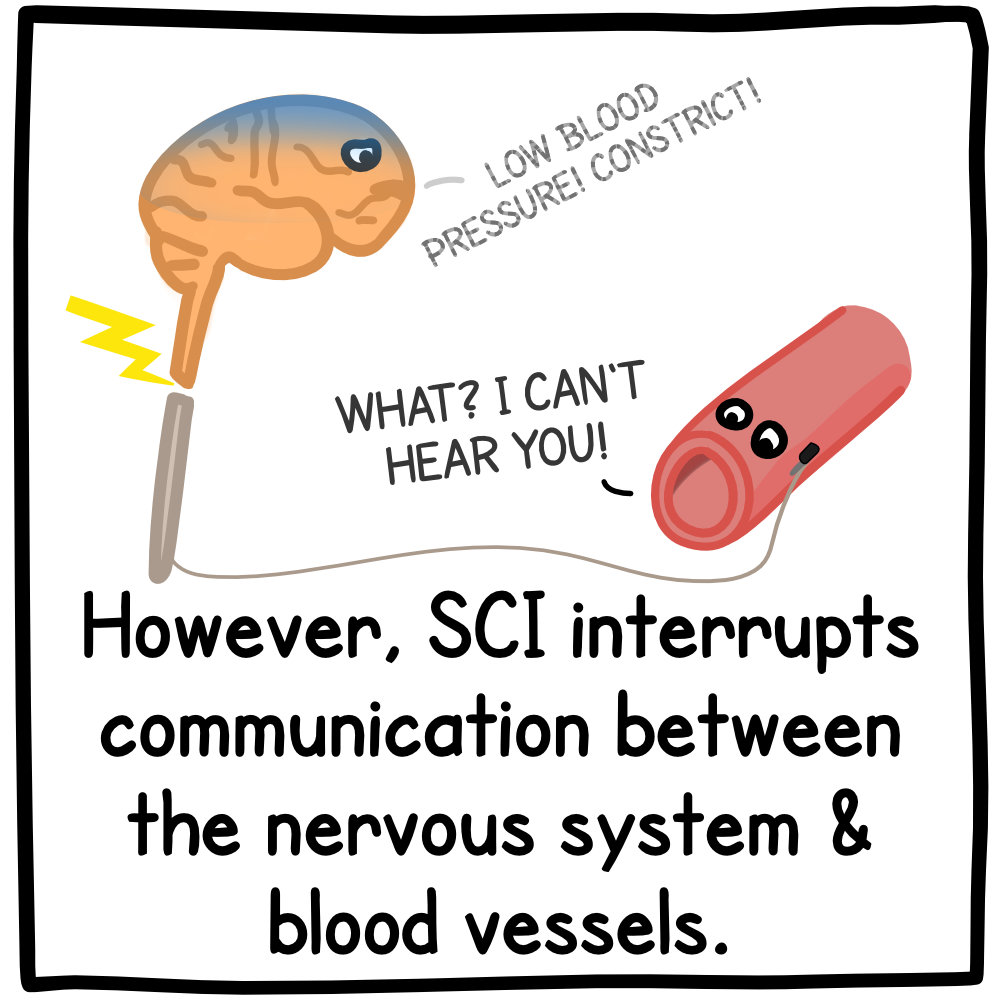
Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (nOH) results from impaired vasoconstriction due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system and is commonly associated with Parkinson disease (PD), multiple system atrophy (MSA), and pure autonomic failure.
Can orthostatic hypotension go away?
This condition has no cure, symptoms vary in different circumstances, treatment is nonspecific, and aggressive treatment can lead to marked supine hypertension.
Which client is at greatest risk for orthostatic hypotension?
Patients with cardiovascular diseases, such as aortic stenosis, pericarditis/myocarditis, or arrhythmias, are also at increased risk for orthostatic hypotension. It can also occur in younger and middle-aged patients, who, in the absence of volume depletion, usually have a chronic autonomic failure.
Can orthostatic hypotension cause brain damage?
Our study found that orthostatic hypotension, even asymptomatic orthostatic hypotension, was associated with an increased risk of dementia and accelerated progression from cognitive impairment to dementia.
What does orthostatic blood pressure indicate?
Orthostatic hypotension is a form of low blood pressure. It happens when the blood vessels do not constrict (tighten) as you stand up. It is usually a symptom of an underlying disorder rather than a disease in itself. The condition is also known as postural hypotension.
How do you test for orthostatic hypotension?
1 Have the patient lie down for 5 minutes. 2 Measure blood pressure and pulse rate. 3 Have the patient stand. 4 Repeat blood pressure and pulse rate measurements after standing 1 and 3 minutes.
Can a brain tumor cause orthostatic hypotension?
Abstract. Three patients with brainstem tumors had orthostatic hypotension as the major presenting manifestation. Two patients had primary tumors that involved the dorsal medulla, pons, and rostral spinal cord; one was a malignant astrocytoma and the other a hemangioblastoma.
What is the difference between POTs and orthostatic hypotension?
POTs is defined by a fast pulse on standing, and is not the same as orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure on standing), or syncope (passing out in any position). It also should be distinguished from other positional dizziness syndromes: Low CSF pressure syndrome -- typically there is headache on standing.
What is the best medicine for orthostatic hypotension?
The most commonly used agents are midodrine, droxidopa (Northera, Lundbeck), fludrocortisone and pyridostigmine (see Table below). Midodrine, an alpha-1 agonist, was the first medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of OH.
How do I stop getting dizzy when I stand up?
After sleeping, sitting for an extended period, or eating a full meal, take your time rising to a standing position. It may help to clench your leg muscles before standing to push the pooled blood into your system. Change your eating habits. If dizziness strikes after meals, try eating smaller but more frequent meals.
How do I take my blood pressure standing up?
1:453:11Lying and standing blood pressure - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTake the patient's blood pressure immediately. On. Sitting. Then wait for between 1 to 3 minutes andMoreTake the patient's blood pressure immediately. On. Sitting. Then wait for between 1 to 3 minutes and repeat blood pressure whilst they are still. Sitting.
What does orthostatic blood pressure indicate?
Orthostatic hypotension is a form of low blood pressure. It happens when the blood vessels do not constrict (tighten) as you stand up. It is usually a symptom of an underlying disorder rather than a disease in itself. The condition is also known as postural hypotension.
How do you know if you have orthostatic hypotension?
The most common symptoms of orthostatic hypotension are dizziness and lightheadedness upon standing up. The symptoms will usually go away when sitting or lying down.
What is the term for a sudden fall in blood pressure that occurs when you stand up quickly?
Orthostatic hypotension, also called postural hypotension, is a sudden fall in blood pressure that occurs when you stand up quickly. Hypotension is the term for low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of your blood against the walls of your arteries.
What causes a drop in blood volume?
dehydration. anemia, or low red blood cell count. a drop in blood volume, called hypovolemia, caused by certain drugs such as thiazide diuretics and loop diuretics. pregnancy. heart conditions, such as a heart attack or valve disease. diabetes, thyroid conditions, and other diseases of the endocrine system. Parkinson’s disease.
How to raise blood pressure in a dehydrated person?
Stand up slowly when getting out of a chair or bed. Perform isometric exercises before getting up to help raise your blood pressure. For example, squeeze a rubber ball or a towel with your hand.
Why do you wear compression stockings?
Wear compression stockings to help with circulation in your legs.
Can drugs cause orthostatic hypotension?
Many drugs can affect these normal reflexes and lead to orthostatic hypotension. These reflexes may also begin to weaken as you age. For this reason, orthostatic hypotension is more common in older adults. According to a 2011 study, about 20 percent of people older than 65 experience orthostatic hypotension. People with orthostatic hypotension may ...
Does orthostatic hypotension cure?
In most cases, treating the underlying condition will cure orthostatic hypotension. With treatment, people who experience orthostatic hypotension can reduce or eliminate symptoms.
What causes orthostatic hypotension?
Parkinson’s disease, pregnancy, and heart conditions such as irregular heart rhythms and valve disease are also known to cause symptoms connected to orthostatic hypotension.
Why is orthostatic hypotension common?
Orthostatic hypotension is common among people who are 65 or older because the body’s ability to react to drops in blood pressure can slow down as a person ages.
What is the term for a sudden drop in blood pressure caused by a change in posture?
Treatment and prevention. Orthostatic hypotension, also called postural hypotension, is defined as a sudden drop in blood pressure caused by a change in posture, such as when a person stands up quickly. When a person stands up after sitting or lying down, blood normally pools in the legs because of gravity.
Why is sudden drop in blood pressure a risk factor for stroke?
The sudden drops in blood pressure caused by orthostatic hypotension are a risk factor for strokes because of the reduced blood supply to the brain.
What is the cause of dizziness and blurred vision?
Dizziness, blurred vision, and feeling faint may be symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
Why do people wear compression stockings?
Compression stockings can promote circulation and help prevent fluid from pooling in the legs. Severe cases of orthostatic hypotension can be treated with drugs to raise blood pressure. Last medically reviewed on June 29, 2017. Blood / Hematology.
What is the blood pressure of a person measured in?
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and has two figures:
What is orthostatic hypotension?
Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing from a sitting or supine position. Clinically, this is diagnosed by a sustained reduction in systolic blood pressure of at least 20 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of 10 mmHg within three minutes of standing after being supine for five minutes or at a 60-degree angle on the tilt table. This sudden drop in blood pressure is usually secondary to failure of autonomic reflex, volume depletion, or adverse reaction to medication. Symptoms on presentation are commonly related to cerebral hypoperfusion, but patients can also be asymptomatic. There also is a high rate of morbidity and mortality related to this disease process due to frequent falls, which can lead to multiple hospital admissions. [1][2][3][4][5]
How long to stand for orthostatic blood pressure?
After five minutes of lying supine, the patient should be asked to stand quietly for two to five minutes, and vital signs should be taken again. If there is a 20 mmHg drop in systolic blood pressure or a 10 mmHg drop in diastolic blood pressure, one can make the diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. [6][7][8][9]
What happens when you stand up from a supine position?
This results in decreased venous return to the heart, and as a result, there is a decrease in cardiac output as defined by the Frank Starling Curve. The human body normally compensates with an increase in sympathetic tone and a decrease in vagal tone, known as the baroreceptor reflex. This increase in sympathetic outflow raises peripheral vascular resistance, which subsequently increases venous return and cardiac output, thereby limiting the fall in blood pressure. When patients lack this compensatory mechanism, they present with symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
Is orthostatic hypotension neurogenic?
Orthostatic hypotension can be caused by both neurogenic and non-neurogenic etiologies and can also be related to medication. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is characterized by autonomic instability secondary to neuropathic disease, neurodegenerative disease, or aging. Neuropathic diseases include diabetes, cholinergic receptor autoantibodies, and familial dysautonomia. Neurodegenerative diseases include Parkinson disease, multiple-system atrophy, and pure autonomic failure. Non-neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is most commonly due to volume depletion. One must also consider medication induced orthostatic hypotension particularly in the case of polypharmacy in the elderly.
Can orthostatic hypotension cause supine hypertension?
Approximately 50% of patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension suffer from supine hypertension. This association is due to side effects from anti-hypertensive medications as well as the common autonomic dysfunction seen in these patients due to comorbid conditions, such as diabetes mellitus. There is currently no approved anti-hypertensive medication that selectively targets the supine position. This complicates treatment because supine hypertension in patients with autonomic failure can result in end organ damage. The treatment approach for these patients is currently being studied and might be an outlet for individualized based medicine in the future.
How Long Drugs Stay in Saliva: Drug Detection Times
Saliva drug testing is a quick and easy way to test for the presence of drugs in a person's...
What You Should Know About Non-Surgical Nose Jobs
After staring at their image in a mirror, many people may desire their nose to look different, potentially through a...
Captivating Dental Promotional Strategies to Attract More Clients
Dental promotion is the process of marketing and advertising dental services to attract new patients. It is important to have...
Pathophysiology
When an adult rises to the standing position, 300 to 800 mL of blood pools in the lower extremities. 8, 9 Maintenance of blood pressure during position change is quite complex; many sensitive cardiac, vascular, neurologic, muscular, and neurohumoral responses must occur quickly.
Differential Diagnosis
Orthostatic hypotension can be classified as neurogenic, non-neurogenic, or iatrogenic (e.g., caused by medication). 12, 15 An algorithm to guide evaluation is given in Figure 1. Some of the etiologies of orthostatic hypotension are shown in Table 1. 11 – 13, 15 Clinical clues to help direct the evaluation are given in Tables 2 and 3. 1, 11, 15, 16
Treatment
The first steps in treatment of orthostatic hypotension are diagnosis and management of the underlying cause. A patient with symptomatic orthostatic hypotension who has a disease with no complete or specific cure may benefit from nonpharmacologic interventions.
Dizziness Symptoms
Dizziness is a feeling of being lightheaded or woozy. People often refer to dizziness as vertigo, unsteadiness, or lightheadedness. Some of the illnesses or conditions that cause dizziness include:
What is orthostatic hypotension?
When a person stands up from sitting or lying down, the body must work to adjust to that change in position. It is especially important for the body to push blood upward and supply the brain with oxygen. If the body fails to do this adequately, blood pressure falls, and a person may feel lightheaded or even pass out.
What are the symptoms of orthostatic hypotension?
When the brain does not get enough blood supply, it begins to shut down.
What are the risk factors for orthostatic hypotension?
Orthostatic hypotension most often occurs in the elderly. "Hardening of the arteries" or atherosclerosis that develops as we age makes it more difficult for blood vessels to adapt quickly when necessary. As well, many of the diseases that are associated with orthostatic hypotension are progressive, with symptoms worsening with age.
What causes orthostatic hypotension?
Orthostatic hypotension has many potential causes, some affecting only one part of the system that supplies blood to the brain, and others affecting two or three.
When should I call the doctor for orthostatic hypotension?
Feeling faint or lightheaded is not normal. While a rare episode that can be explained by circumstances, such as working or exercising in the heat, may be ignored, more frequent occurrences should be investigated.
How is orthostatic hypotension diagnosed?
The key to the diagnosis is a good history and physical examination. The health care practitioner will want to know the circumstances that are associated with the symptoms of lightheadedness or passing out, since the patient is unlikely to have taken their blood pressure and checked their pulse rate in the midst of the episode.
What are the causes of orthostatic hypotension?
the reasons for orthostatic hypotension, in this case, lie in the violation of the regulation of vascular tone at the highest level: the “orders” are given by the nervous system, which is not at all in good condition to command. Similar phenomena occur in diabetes and hypothyroidism.
Why is orthostatic hypotension possible?
This is possible due to hemodynamic disturbances in various pathologies, both cardiac and extracardiac origin (orthostasis is the vertical position of the body).
Can orthostatic hypotension cause dizziness?
Orthostatic hypotension may cause severe disability, and patients experience dizziness, dizziness, fainting, and other problems that can have a profound negative impact on daily life that requires standing or walking.
Why is my blood pressure low?
The causes of low blood pressure can range from dehydration to serious medical disorders. It's important to find out what's causing your low blood pressure so that it can be treated.
Why does blood pressure drop after standing for long periods?
It seems to occur because of a miscommunication between the heart and the brain.
What is the name of the drop in blood pressure caused by an infection?
When an infection in the body enters the bloodstream, it can lead to a life-threatening drop in blood pressure called septic shock. Severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). Common triggers of this severe and potentially life-threatening reaction include foods, certain medications, insect venoms and latex.
Why does blood pool in legs?
Gravity causes blood to pool in your legs when you stand. Ordinarily, your body compensates by increasing your heart rate and constricting blood vessels, there by ensuring that enough blood returns to your brain.
Why does blood pressure drop during pregnancy?
Pregnancy. Because the circulatory system expands rapidly during pregnancy, blood pressure is likely to drop. This is normal, and blood pressure usually returns to your pre-pregnancy level after you've given birth.
Why is it important to see a doctor for low blood pressure?
Still, it's important to see your doctor if you have signs or symptoms of low blood pressure because they can point to more-serious problems. It can be helpful to keep a record of your symptoms, when they occur and what you're doing at the time.
Can ACE inhibitors cause orthostatic hypotension?
A number of medications also can cause orthostatic hypotension, particularly drugs used to treat high blood pressure — diuretics, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors — as well as antidepressants and drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease and erectile dysfunction.
