
What does predominantly parabasal cells mean?
Parabasal cells are immature squamous cells seen on the cervix in the absence of oestrogen. They are often seen in post menopausal or post natal women or in those who are taking a progesterone only pill. It is not a cytological abnormality. What are parabasal cells? Parabasal cells are the smallest epithelial cells seen on a typical vaginal smear.
Is Pap smear a primary prevention?
Secondary prevention often occurs in the form of screenings. For example, a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is a form of secondary prevention aimed to diagnose cervical cancer in its subclinical state before progression. Tertiary Prevention: Tertiary prevention targets both the clinical and outcome stages of a disease.
Should you do a Pap smear?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that all women between the ages of 21 and 65 should get regular Pap smears tests. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) do not recommend Pap smears for people under the age of 21.
What STD can cause abnormal Pap smear?
One of the most common abnormal Pap smear causes is the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
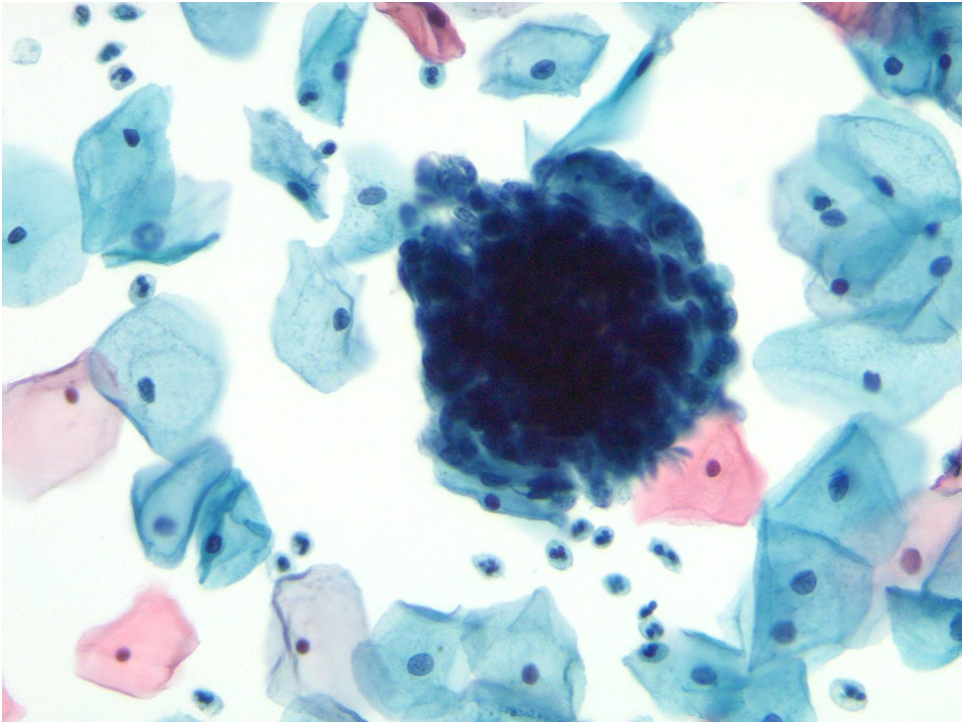
What does atrophic pattern mean in Pap smear?
Sometimes after menopause or when breast feeding there are 'atrophic changes' in the cervix, caused by decreased hormone levels. If your Pap smear result is 'atrophic' you may be given some local oestrogen treatment (for example, oestrogen cream) and asked to have the Pap smear repeated in three months.
Should I worry about atypical squamous cells?
Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US)—ASC-US means that changes in the cervical cells have been found. The changes are almost always a sign of an HPV infection. The changes may also be a result of infection or inflammation. ASC-US is the most common abnormal Pap test result.
Are squamous cells normal in Pap smear?
A normal Pap smear shows healthy squamous cells (flat cells that look like fish scales) from the surface of the cervix. There are no signs of infection and no abnormal cells. Even if your Pap results are healthy, you should be tested regularly.
What is normal endocervical cells?
Normal endocervical cells usually means columnar cells which morphology may be secretory or less frequently ciliated. Columnar endocervical cells are generally larger than endometrial cells.
What causes atypical squamous cells Pap smear?
Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance is the most common abnormal finding in a Pap test. It may be a sign of infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) or other types of infection, such as a yeast infection.
Can atypical squamous cells go away?
They usually go away on their own and do not require treatment. CIN 2 changes are moderate and are typically treated by removing the abnormal cells. However, CIN 2 can sometimes go away on its own. Some women, after consulting with their health care provider, may decide to have a colposcopy with biopsy every 6 months.
What causes parabasal cells?
Parabasals are an uncommon finding on Pap smears of women with estrogen production or replacement hormone. These cells are often seen in patients who lack estrogen, including those who are premenstrual, post partum, taking estrogen-restricting hormones, or postmenopausal.
Can squamous cells be benign?
Squamous cell lesions of the urinary bladder are generally rare, and they may be benign or malignant [4–7].
Are squamous epithelial cells cancerous?
The cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a malignant skin tumor that arises from epithelial keratinocytes and shows some degree of maturation towards keratin formation. After the basal cell carcinoma, it is the second most common form of skin cancer.
Should endocervical cells be present in Pap smear?
Guidelines do not mention the presence or absence of endocervical cells. Guidelines are summarized in the Pap test learning module as follows: “The presence of squamous metaplastic cells and/or dysplastic cells and/or endocervical cells is generally regarded as evidence of adequate sampling of the transformation zone.
Are endocervical cells cancerous?
Cell types This is called the endocervix. The skin-like cells of the ectocervix can become cancerous, leading to a squamous cell cervical cancer. This is the most common type of cervical cancer. The glandular cells of the endocervix can also become cancerous, leading to an adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
How do I read my Pap smear results?
A Pap test result can be normal, unclear, or abnormal.Normal. A normal (or “negative”) result means that no cell changes were found on your cervix. ... Unclear (ASC-US) It is common for test results to come back unclear. ... Abnormal. An abnormal result means that cell changes were found on your cervix. ... Negative. ... Positive.
What does atypical squamous cells present mean?
Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) ASC-US means that changes in the cervical cells have been found. The changes are almost always a sign of an HPV infection. ASC-US is the most common abnormal Pap test result.
Are atypical squamous cells cancerous?
A finding of abnormal cells in a Pap test. It means there are abnormal squamous cells in the tissue that lines the outer part of the cervix. Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude a high-grade lesion may be a sign of a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL), which may become cervical cancer if untreated.
Should I be worried about ASCUS?
If abnormal cells persist or the condition worsens, referral to specialist clinic for colposcopy will be required. Since the progression from severe deterioration of cervical cells to cancer generally takes about 5 to 10 years, the condition does not pose any immediate threat, please do not worry excessively.
Does HPV ASCUS go away?
CONCLUSION: How to treat an ASCUS (Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance) Pap test has been a major source of anxiety for patients and physicians. Most mild cervical abnormalities go away without treatment.
My pap smear (atrophic) shows predominantly parabasal cells with scattered superficial squamous cells. no dyskaryosis is seen . what does this mean ?
Not cancer: Needs to be repeated when the cycle of cells in the cervix has shed in 3-4 months and will probably be normal.
Pap showed atrophic pattern, what does this mean?
Low estrogen: Atrophic patterns on pap smears are usually associated with decreased estrogen levels. Low estrogen levels are found in women that are either going i... Read More
If my left testicle atrophied from infection a decent amount, is it possible that the leydig cells are still left in it and only the sertoli died?
Here are some ...: The pattern of tissue changes after bacterial orchitis may widely vary among individual and reflecting bacterial virulence and host immune defense abi... Read More
What is a parabasal on a Pap smear?
Parabasals are an uncommon finding on Pap smears of women with estrogen production or replacement hormone. These cells are often seen in patients who lack estrogen, including those who are premenstrual, post partum, taking estrogen-restricting hormones, or postmenopausal.
When do endometrial cells appear on a Pap test?
In cycling women, endometrial cells are expected to be seen on Pap tests from the first day bleeding starts through the twelfth day. After day twelve, the presence of endometrial cells may be considered a significant finding.
Where are intermediate squamous cells located?
The polygonal-shaped intermediate squamous cell size ranges 1,256-1,618 µm. The cell is found in the stratum spongiosum (midzone) layer of the squamous epithelium. The intermediate cell’s cytoplasm is thin, transparent, and typically stains basophilic. The centrally placed nucleus is 35 µm. The nucleus is vesicular with fine evenly dispersed granular chromatin. Intermediate squames are seen in abundance when progesterone is at high levels. This occurs during the luteal and early follicular phases of the menstrual cycle, and the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
Why do we do a Pap smear?
Why it's done. A Pap smear is used to screen for cervical cancer. The Pap smear is usually done in conjunction with a pelvic exam. In women older than age 30, the Pap test may be combined with a test for human papillomavirus (HPV) — a common sexually transmitted infection that can cause cervical cancer.
What does it mean when a Pap smear is positive?
If abnormal or unusual cells were discovered during your Pap smear, you're said to have a positive result. A positive result doesn't mean you have cervical cancer. What a positive result means depends on the type of cells discovered in your test.
How to do a Pap test?
Pap test. Pap test. In a Pap test, your doctor uses a vaginal speculum to hold your vaginal walls apart and to see the cervix. Next, a sample of cells from your cervix is collected using a small cone-shaped brush and a tiny plastic spatula (1 and 2). Your doctor then rinses the brush and spatula in a liquid-filled vial ...
What are the risk factors for a Pap smear?
These risk factors include: A diagnosis of cervical cancer or a Pap smear that showed precancerous cells. Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES) before birth. HIV infection.
How long should I wait before a Pap smear?
Avoid intercourse, douching, or using any vaginal medicines or spermicidal foams, creams or jellies for two days before having a Pap smear, as these may wash away or obscure abnormal cells. Try not to schedule a Pap smear during your menstrual period. It's best to avoid this time of your cycle, if possible.
What happens if you have only normal cervical cells?
If only normal cervical cells were discovered during your Pap smear, you're said to have a negative result. You won't need any further treatment or testing until you're due for your next Pap smear and pelvic exam.
When should I stop a Pap test after a hysterectomy?
Older age. Doctors generally agree that women can consider stopping routine Pap testing at age 65 if their previous tests for cervical cancer have been negative.
What does transformation zone mean in pap?
Transformation zone component present. Another phrase that means your pap sampled cells both on the surface of your cervix and inside the canal.
What does "endocervical cells present" mean?
Endocervical cells present. This phrase means that cells from the inside of your cervical canal were sampled at the time of the pap test, which is something your doctor tries to do. Sometimes it’s hard to reach these cells, which may lead to the phrase…. Endocervical cells absent.
How long does it take for a gyno to repeat an HPV test?
Could be an infection, could be the start of a true abnormality. Your gyno will either repeat the test in 6-12 months, or order an HPV test. If the HPV test was done at the same time and was negative, you’re in the clear.
Is a pap test reported in medical speak?
Most medical testing — from blood tests to radiology exams to your pap tests — are still reported out in medical-speak that seems very far from English. Let me decode the mysterious language, and what it means for you.
Can you sample cells during a pap?
This means that the sampling of cells during your pap didn’t include those inside-the-canal cells. If you’ve never had an abnormal pap in the past, it’s fine for an occasional pap to not sample these cells. But if your pap was performed to follow-up an abnormal test, your doctor may want you to return to the office for a repeat pap.
What is a Pap test?
Definition / general. Normal and nonneoplastic findings in cervical components of Pap test for routine screening for cervical cancer. Preparations: conventional and liquid based (ThinPrep and SurePath)
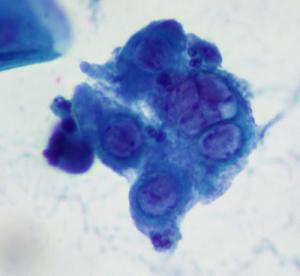
Where do cytotrophoblasts come from?
Cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast: Cytotrophoblastic cells: Derived from the placenta in late pregnancy and postpartum. Typically single cells, occasionally in small clusters. May resembling small squamous metaplastic or endometrial cells, as well as high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion cells.
Overview
Why It's Done
- A Pap smear is used to screen for cervical cancer. The Pap smear is usually done in conjunction with a pelvic exam. In women older than age 30, the Pap test may be combined with a test for human papillomavirus (HPV) — a common sexually transmitted infection that can cause cervical cancer. In some cases, the HPV test may be done instead of a Pap smear.
Risks
- A Pap smear is a safe way to screen for cervical cancer. However, a Pap smear isn't foolproof. It's possible to receive false-negative results — meaning that the test indicates no abnormality, even though you do have abnormal cells. A false-negative result doesn't mean that a mistake was made. Factors that can cause a false-negative result include: 1. An inadequate collection of cell…
How You Prepare
- To ensure that your Pap smear is most effective, follow these tips prior to your test: 1. Avoid intercourse, douching, or using any vaginal medicines or spermicidal foams, creams or jellies for two days before having a Pap smear, as these may wash away or obscure abnormal cells. 2. Try not to schedule a Pap smear during your menstrual period. It's best to avoid this time of your cyc…
What You Can Expect
- During the Pap smear
A Pap smear is performed in your doctor's office and takes only a few minutes. You may be asked to undress completely or only from the waist down. You'll lie down on your back on an exam table with your knees bent. Your heels rest in supports called stirrups. Your doctor will gently insert a… - After the Pap smear
After your Pap smear, you can go about your day without restrictions. Depending on the type of Pap testing you're undergoing, your doctor transfers the cell sample collected from your cervix into a container holding a special liquid to preserve the sample (liquid-based Pap test) or onto a …