
Where is Penicillium naturally found?
Penicillium is a genus of microscopic filamentous fungi, common in the environment. They can be found in the air, soil, in plants and vegetables. They are cosmopolitan in distribution. In nature, they fulfill the role of decomposers of organic matter. Many species can become pathogens of fruits, vegetables and cereals.
Are basidiospores harmful to humans?
If inhaled in significant amounts, Basidiospores can lead to serious health issues. Most issues are associated with the respiratory tract. Basidiospores have been reported in cases of allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis, allergic fungal rhinosinusitis and fungus associated chronic cough [5].
What is Penicillium used for?
Penicillium is used to created some cheeses. Penicillium is a large genus of fungi that are in the air, in soil and frequently on bread and produce. Different species of these fungi produce many types of secondary metabolites, ranging from the antibacterial drug penicillin to the antifungal drug griseofulvin, along with many compounds that are toxic to humans and animals.
Is Penicillium a saprophyte?
The Penicillium fungus can easily be found or grown on citrus and other fruits and on foodstuff. It generally grows in association with Aspergillus, but since it is a weak saprophyte it is dominated by Aspergillus. Cell wall of fungal cellulose. A definite cell wall present. Mycelium septate.
What is Penicillium spp mold?
What Is Penicillium Mold? This family of molds was first identified in 1809 in a book by German naturalist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. Most of the estimated 300 or more species produce blue, green or yellow spores, and are one of the most common causes of fruit and vegetable spoilage.
Is Penicillium harmful or beneficial?
Is Penicillium harmful or beneficial? Penicillium is one of the most common fungi. It is both beneficial as well as harmful. Some of the species are used for the production of antibiotics, cheese, organic acids and enzymes.
Is Penicillium mold harmful?
Penicillium digitatum, P. expansum and P. chrysogenum are some of the other less common pathogenic fungi belonging to the genus Penicillium. Although they are not frequently mentioned in relation to penicilliosis, these fungal species cause infections in human that could be fatal.
What disease is caused by Penicillium sp?
Superficial infection (keratitis and otomycosis) is commonly caused by Penicillium spp. Allergic pulmonary disease, often occupational (such as various cheeseworkers' diseases), is also common. Optimal therapy for invasive infection is not established, but surgery may be advisable if possible.
How does Penicillium enter the body?
Most fungi enter the body 1) through hair follicles, 2) through the nasal passages, 3) through abrasions and injuries, and 4) through the alimentary canal. The types of tissue reactions induced in man by these organisms are ex- tremely variable.
What foods contain Penicillium?
PENICILLIUM | Penicillium/Penicillia in Food Production Penicillium species, especially Penicillium roqueforti, Penicillium camemberti, and Penicillium nalgiovense, are used in the production of blue cheeses, white cheeses, and mold-fermented meat sausages.
What kills Penicillium mold?
Vinegar with about 4 percent acetic acid can kill Penicillium chrysogenum but not Aspergillus fumigatus mold. A 2015 study found that vinegar with about 4 percent acetic acid was capable of treating common household molds including Penicillium chrysogenum but not Aspergillus fumigatus.
Is Penicillium common in homes?
Mold can also grow in dust, paints, wallpaper, insulation, drywall, carpet, fabric, and upholstery. The most common indoor molds are Cladosporium, Penicillium, and Aspergillus.
How do you treat Penicillium fungus?
Patients with Penicillium species infections have been treated successfully with itraconazole [8], amphotericin B [3, 9], or fluconazole [3]. However, some patients with conditions caused by Penicillium species have died despite treatment with ketoconazole [2], amphotericin B [2], or itraconazole [10].
Where is Penicillium spp found?
Penicillium are very commonly found in soil, on decaying vegetation and compost or on wood, dried foodstuffs, spices, dry cereals, fresh fruit and vegetables {808, 3095}they are also found growing on building materials in water-damaged environments {413} as well as in indoor air and house dust.
What are the symptoms of Penicillium?
SymptomsFever.General discomfort.Weight loss.Cough.Swollen lymph nodes.Difficulty breathing.Swelling of the liver and spleen.Diarrhea.More items...
What is penicillin fungus?
Penicillium griseofulvum was found to be a new penicillin producer and to have a penicillin gene cluster similar to that of Penicillium chrysogenum. No other species among the studied fungi were found to produce penicillin or to possess the penicillin biosynthetic genes, except P.
What are the benefits of Penicillium?
Penicillium is an important genus of phylum ascomycota, found in the natural environment as well as in food and drug production. Some members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule used as an antibiotic that kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body.
How can Penicillium chrysogenum be beneficial?
The filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum is well-known by its ability to synthesize β-lactam antibiotics as well as other secondary metabolites.
Can Penicillium cause human infection?
Penicillium marneffei is an emerging pathogenic fungus that can cause a fatal systemic mycosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). P. marneffei infection is endemic in tropical Asia, especially Thailand, northeastern India, China, Hong Kong, Vietnam, and Taiwan (25, 33, 61, 125, 151, 185).
How is Penicillium protective?
Penicillium also protects plants from diseases preventively by inducing the defense systems of plants and developing systemic acquired resistance in plants.
What is the color of penicillium?
Some species have a blue color, commonly growing on old bread and giving it a blue fuzzy texture. Some Penicillium species affect the fruits and bulbs of plants, including P. expansum, apples and pears; P. digitatum, citrus fruits; and P. allii, garlic.
Who first described penicillium?
The genus was first described in the scientific literature by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in his 1809 work Observationes in ordines plantarum naturales; he wrote, "Penicillium. Thallus e floccis caespitosis septatis simplicibus aut ramosis fertilibus erectis apice penicillatis", where penicillatis referred to "pencil-like" (referring to a Camel's hair pencil brush. Link included three species— P. candidum, P. expansum, and P. glaucum —all of which produced a brush-like conidiophore (asexual spore-producing structure). The common apple rot fungus P. expansum was later selected as the type species.
What is Penicillium nalgiovense used for?
Penicillium nalgiovense is used in soft mold-ripened cheeses, such as Na lžovy ( ellischau) cheese, and to improve the taste of sausages and hams, and to prevent colonization by other molds and bacteria.
What is the name of the bacteria that makes brie?
Penicillium candidum, which is used in making Brie and Camembert. It has been reduced to synonymy with Penicillium camemberti. Penicillium chrysogenum (previously known as Penicillium notatum ), which produces the antibiotic penicillin. Penicillium claviforme.
What are the four subgenera of penicillium?
Pitt divided Penicillium into four subgenera based on conidiophore morphology and branching pattern: Aspergilloides, Biverticillium, Furcatum, and Penicillium. Species included in subgenus Biverticillium were later merged into Talaromyces .
What are the two macromolecules produced by Penicillium and Aspergillus?
In addition to their importance in the food industry, species of Penicillium and Aspergillus serve in the production of a number of biotechnologically produced enzymes and other macromolecules, such as gluconic, citric, and tartaric acids, as well as several pectinases, lipase, amylases, cellulases, and proteases.
What are the fungi that live in soil?
Species of Penicillium are ubiquitous soil fungi preferring cool and moderate climates, commonly present wherever organic material is available. Saprophytic species of Penicillium and Aspergillus are among the best-known representatives of the Eurotiales and live mainly on organic biodegradable substances. Commonly known in America as molds, they are among the main causes of food spoilage, especially species of subgenus Penicillium. Many species produce highly toxic mycotoxins. The ability of these Penicillium species to grow on seeds and other stored foods depends on their propensity to thrive in low humidity and to colonize rapidly by aerial dispersion while the seeds are sufficiently moist. Some species have a blue color, commonly growing on old bread and giving it a blue fuzzy texture.
What is the name of the strain of Penicillium spp. isolated from grapes used for the production?
Torelli, E. et al, 2006. Ochratoxin A-producing strains of Penicillium spp. isolated from grapes used for the production of ‘‘passito’’ wines. International Journal of Food Microbiology 106 (2006) 307 – 312
What are the physiological traits of a mold?
Physiological Traits: Saprophyte, nutrients out of dead & decayed substances. Penicillium mold inhibits bacterial biofilm formation in part by producing penicillic acid and patulin. Dry spores are easily spread through the air as well as carried by water. Toxin and allergenic compounds producer.
Is penicillium a carcinogen?
OTA: The International Agency for Research on Cancer classified OTA in group 2B as a possible human carcinogen.
Is a penicillum a filamentous fungus?
Penicillum spp. are filamentous fungi. They have branched conidiospores. Conidia are round and unicellular. Penicillium reproduces asexually. Species are classified based on the way conidia are produced. In some species, conidia are born on phialidies.
Where is Penicillium found?
Penicillium spp. are widespread and are found in soil, decaying vegetation, and the air. Showing again how it is distinct from other species in this genus, Penicillium marneffei is endemic specifically in Southeast Asia where it infects bamboo rats which serve as epidemiological markers and reservoirs for human infections.
What are the different types of penicillium?
The most common ones include Penicillium chrysogenum, Penicillium citrinum, Penicillium janthinellum, Penicillium marneffei, and Penicillium purpurogenum. Identification to species level is based on macroscopic morphology and microscopic features [ 531 ].
What temperature does Penicillium marneffei produce?
Penicillium marneffei is thermally dimorphic and produces filamentous, flat, radially sulcate colonies at 25°C. These colonies are bluish-gray-green at center and white at the periphery. The red, rapidly diffusing, soluble pigment observed from the reverse is very typical. At 37°C, Penicillium marneffei colonies are cream to slightly pink in color and glabrous to convoluted in texture [ 531, 1295, 2144, 2202 ].
How does Penicillium differ from Paecilomyces?
Penicillium differs from Paecilomyces by having flask-shaped phialides and globose to subglobose conidia; from Gliocladium by having chains of conidia; and from Scopulariopsis by forming phialides. Penicillium marneffei differs as well by its thermally dimorphic nature.
How is Penicillium marneffei induced to produce the arthroconidial state?
Penicillium marneffei is easily induced to produce the arthroconidial yeast-like state by subculturing the organism to an enriched medium like BHI and incubating at 35°C, in which after a week, yeast-like structures dividing by fission and hyphae with arthroconidia are formed [ 531, 1295, 2144, 2202 ].
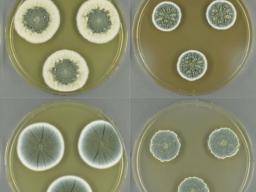
What color are penicillium colonies?
The colonies are initially white and become blue green, gray green, olive gray, yellow or pinkish in time . The plate reverse is usually pale to yellowish [ 531, 1295, 2144, 2202 ].
What are the secondary branches of conidiophores?
Metulae are secondary branches that form on conidiophores. The metulae carry the flask-shaped phialides. The organization of the phialides at the tips of the conidiophores is very typical. They form brush-like clusters which are also referred to as “penicilli”.
What is a penicillium?
Penicillium. Penicillium is a genus consisting of a group of fungi, which include 354 accepted species. Some Penicillium species are considered doctor fungus as some of the members produce antibiotics, which can inhibit the growth of certain bacteria. Penicillium species are ubiquitous, where many produce potential mycotoxins, ...
What is the purpose of the penicillium species?
Penicillium species are ubiquitous, where many produce potential mycotoxins, few produce medically useful antibiotics, and some are important in cheese production. Due to the non-distinct sexual phase of Penicillium species are also termed “ Deuteroalsomycetes or Fungi imperfecti ”.
What temperature does a penicillium grow?
They achieve maximum growth at a temperature of 23 degrees Celsius. The water activity must be in a range of 0.78 – 0.88.
How does the Penicillium species affect the economy?
It can also affect the economy, as it may grow on fabrics, leather, wood etc.
What is the antibiotic used to treat dimorphic fungi?
Later, another antibiotic was introduced as “ Griseofulvin ” from Penicillium griseofulvum and used as an antifungal agent to inhibit the activity of dimorphic fungi. Culturing: It can be cultured on Czapek Dox agar and 2% Malt extract agar at a temperature between 23-25 degrees Celsius.
How to identify a penicillium?
Identification. One of the easiest ways to identify Penicillium species is through the branching pattern of the conidiophore. The conidiophores give rise to the secondary branches (metullae) that further give rise to the tertiary branches (phialides or sterigmata), making them distinct from the other groups of fungi.
Where did the term "penicillium" come from?
Origination. Penicillium is a term derived from the Latin word Penicillus (means paintbrush), as its structure is very similar to a paintbrush. Penicillin was the first antibiotic introduced by Alexander Fleming, which he isolated from the species ( P. notatum ).
What is the purpose of the penicillium fungus?
Penicillium is a latin root meaning "painter's brush", which is used as a descripitor for the chains of conidia produced by this genus that resemble a broom.
Why are some penicillium species considered bioremediation?
Some Penicillium species have gained attention in the field of bioremediation for the ability to breakdown pollutants that are toxic to humans called xenobiotic compounds.
What is the purpose of the fungus genus?
This genus is used extensively in fungal resistance testing to assess various substances' ability to either prevent the growth of fungi or to assess the ability of the fungi to use the substance as a substrate for growth .
Where is Penicillium marneffei found?
Penicillium marneffei infection found in both immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. P marneffei found in Southeast Asia and southern China. Mold, septate hyphae 1.5-5 um in diameter. May be cultured from a variety of specimens including blood. Penicillium spp. other than P marneffei occur worldwide.
What is the most common filamentous fungus?
Penicillium spp. are among the most common filamentous fungi found in nature. These blue-green molds grow rapidly in the mycology laboratory and produce fine septate hyphae with 1.5-5 um wide elements. In tissue specimens, the mycelial elements are somewhat larger at 15-20 um in width and exhibit branching at ~ 45° angles.
Is Penicillium spp. rare?
Infection caused by Penicillium spp. other than P mar neffei occurs almost exclusively among profoundly immunosuppressed patients and is exceedingly rare. Penicillium spp. lack the necessary virulence factors to commonly cause human infection, and only in the setting of extreme immunodeficient states can invasive infection occur.
Can penicillium be recovered?
Penicillium spp. are ubiquitous in nature and may be recovered with ease from a variety of sources within the hospital environment. These molds commonly contaminate clinical specimens and cause contamination in the laboratory. Colonization of nonsterile anatomical sites in humans is common.
Is penicilliosis transmitted in Thailand?
Infection is acquired via inhalation, inoculation of the skin, and possibly ingestion. Person-to-person transmission does not occur.
Does P marneffei resemble tuberculosis?
Differential Diagnosis. P marneffei may closely resemble tuberculosis, particularly in patients with HIV infection. The disease also closely resembles histoplasmosis and cryptococcosis as it occurs in HIV-infected patients.

Overview
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Some members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria. Other spe…
Taxonomy
The genus was first described in the scientific literature by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in his 1809 work Observationes in ordines plantarum naturales; he wrote, "Penicillium. Thallus e floccis caespitosis septatis simplicibus aut ramosis fertilibus erectis apice penicillatis", where penicillatis means "having tufts of fine hair". Link included three species—P. candidum, P. expansum, and P. glaucum—all …
Characteristics
The thallus (mycelium) consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated, usually colourless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical constricted units called conidia. These propagules play a significant role in reproduction; conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
Ecology
Species of Penicillium are ubiquitous soil fungi preferring cool and moderate climates, commonly present wherever organic material is available. Saprophytic species of Penicillium and Aspergillus are among the best-known representatives of the Eurotiales and live mainly on organic biodegradable substances. Commonly known in America as molds, they are among the main causes of food spoilage, especially species of subgenus Penicillium. Many species produce highl…
Economic value
Several species of the genus Penicillium play a central role in the production of cheese and of various meat products. To be specific, Penicillium molds are found in Blue cheese. Penicillium camemberti and Penicillium roqueforti are the molds on Camembert, Brie, Roquefort, and many other cheeses. Penicillium nalgiovense is used in soft mold-ripened cheeses, such as Nalžovy (ellischau) …
Reproduction
Although many eukaryotes are able to reproduce sexually, as much as 20% of fungal species had been thought to reproduce exclusively by asexual means. However recent studies have revealed that sex occurs even in some of the supposedly asexual species. For example, sexual capability was recently shown for the fungus Penicillium roqueforti, used as a starter for blue cheese production. This finding was based, in part, on evidence for functional mating type (MAT) genes t…
External links
• Asan, A. (2004). "Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Related Species Reported from Turkey" (PDF). Mycotaxon. 89 (1): 155–7.
• Samson, R.A.; Pitt, J.I. (2000). Integration of Modern Taxonomic Methods For Penicillium and Aspergillus Classification. CRC Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-9058231598.
Taxonomic Classification
Description and Natural Habitats
- With only one exception (Penicillium marneffei, which is thermally dimorphic), the members of the genus Penicillium are filamentous fungi. Penicillium spp. are widespread and are found in soil, decaying vegetation, and the air. Showing again how it is distinct from other species in this genus, Penicillium marneffeiis endemic specifically in Southeast Asia where it infects bamboo rats whic…
Species
- The genus Penicillium has several species. The most common ones include Penicillium chrysogenum, Penicillium citrinum, Penicillium janthinellum, Penicillium marneffei, and Penicillium purpurogenum. Identification to species level is based on macroscopic morphology and microscopic features [531]. See the summary of species and synonyms for the Penicillium spp.
Pathogenicity and Clinical Significance
- Penicillium spp. are occasional causes of infection in humans and the resulting disease is known generically as penicilliosis. Penicillium has been isolated from patients with keratitis [581], endophtalmitis, otomycosis, necrotizing esophagitis, pneumonia, endocarditis, peritonitis, and urinary tract infections. Most Penicillium infections are enco...
Macroscopic Features
- The colonies of Penicillium other than Penicillium marneffei are rapid growing, flat, filamentous, and velvety, woolly, or cottony in texture. The colonies are initially white and become blue green, gray green, olive gray, yellow or pinkish in time. The plate reverse is usually pale to yellowish [531, 1295, 2144, 2202]. Penicillium marneffei is thermally dimorphic and produces filamentous, f…
Microscopic Features
- For species other than Penicillium marneffei, septate hyaline hyphae (1.5 to 5 µm in diameter), simple or branched conidiophores, metulae, phialides, and conidia are observed. Metulae are secondary branches that form on conidiophores. The metulae carry the flask-shaped phialides. The organization of the phialides at the tips of the conidiophores is very typical. They form brus…
Histopathologic Features
- Intracellular arthroconidial yeast-like cells are observed inside the macrophages in infected tissues [531].
Compare to
- Paecilomyces Gliocladium Scopulariopsis Penicillium differs from Paecilomyces by having flask-shaped phialides and globose to subglobose conidia; from Gliocladium by having chains of conidia; and from Scopulariopsis by forming phialides. Penicillium marneffeidiffers as well by its thermally dimorphic nature.
Susceptibility
- Available data are very limited. For Penicillium chrysogenum, MICs of amphotericin B, itraconazole, ketoconazole, and voriconazole are acceptably low, while the denoted MICs for Penicillium griseofulvum are higher than those for Penicillium chrysogenum [2432]. Notably, Penicillium marneffei isolates may yield considerably high MICs for amphotericin B, flucytosine, …