What is the purpose of a percussive respiratory assessment?
Percussion is an advanced respiratory assessment technique that is used by advanced practice nurses and other health care providers to gather additional data in the underlying lung tissue. By striking the fingers of one hand over the fingers of the other hand, a sound is produced over the lung fields that helps determine if fluid is present.
What is the role of percussion in a respiratory examination?
A thorough respiratory examination requires multiple elements of objective assessments to aid diagnosis and inform treatment. Percussion plays a key role in such an examination, when performed in conjunction with other techniques such as auscultation, palpation and imaging .
What does percussion sound like in the lungs?
Percussion over normal, healthy lung tissue should produce a resonant note. Dull percussive sounds are indicative of abnormal lung density. Hyperresonance on percussion indicates too much air is present within the lung tissue. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
How are percussive sounds categorized in patients with pulmonary edema?
Percussion sounds should be categorized as follows: normal, dull, or hyperresonant. Location and quality of percussive sounds should be noted and recorded as part of the objective respiratory examination Percussion over normal, healthy lung tissue should produce a resonant note. Dull percussive sounds are indicative of abnormal lung density.

What is respiratory percussion?
Percussion is a manual technique used by respiratory physiotherapists to improve airway clearance by mobilizing secretions in one or more lung segments to the central airways. Percussion over an affected area produces an energy wave, which is transmitted to the lungs and airways.
What is percussion assessment?
Percussion is a method of tapping body parts with fingers, hands, or small instruments as part of a physical examination. It is done to determine: The size, consistency, and borders of body organs. The presence or absence of fluid in body areas.
What is normal percussion of the lungs?
Normal: The lung is filled with air (99% of lung is air). Hence, percussion of it gives a resonance. This step helps identify areas of lung devoid of air.
What is lung percussion test?
While auscultation is most commonly practiced, both percussion and inspection are equally valuable techniques that can diagnose a number of lung abnormalities such as pleural effusions, emphysema, pneumonia and many others.
How do you perform a percussion assessment?
0:111:31Percussion for Beginners - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPercussion is performed by placing the middle finger of your non-dominant hand over the area to beMorePercussion is performed by placing the middle finger of your non-dominant hand over the area to be per cust and applying pressure with your middle phalanges.
What are the 5 percussion sounds?
See Figure 1.9 for the expected location of percussion sounds and Table 1.2 for an explanation of the types of percussion sounds heard including resonance, hyperresonance, tympany, dullness, and flatness.
What is percussion of the chest?
Chest percussion is a form of physical therapy used frequently in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, to help clear the airways from mucus.
How do you Percuss the respiratory system?
0:304:06Percussion of the lungs | Respiratory Examination - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWith the index finger of one hand strike. The middle finger of the other hand just above the nail.MoreWith the index finger of one hand strike. The middle finger of the other hand just above the nail. Press your finger firmly on the patient's chest in the intercostal spaces. It is advisable not to let
What are the rules of percussion?
Percussion should always be done from a resonant to a dull area and not in the reverse direction. During percussion the movement should take place at the wrist joint only. Over clavicular area, percussion is done directly over the clavicle.
What are the abnormal sounds heard upon percussion of lungs?
The most commonly heard adventitious sounds include crackles, rhonchi, and wheezes.
How do you perform a respiratory assessment?
InspectionAssess the level of consciousness. ... Obtain the respiratory rate over a full minute. ... Observe the breathing pattern, including the rhythm, effort, and use of accessory muscles . ... Observe pattern of expiration and patient position. ... Observe the patient's color in their lips, face, hands, and feet.More items...
How do you practice percussion of the lungs?
0:262:44Percussion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWith a cupped hand and soft wrists you can start your percussion argue that on the side. Or the backMoreWith a cupped hand and soft wrists you can start your percussion argue that on the side. Or the back once you're doing this you need to ensure that your patient is comfortable throughout.
What is the principle of percussion?
It is based on the principle of setting tissue and spaces in between at vibration. The sound thus generated is used to determine if the tissue is healthy or pathological.
What are the 4 types of physical assessment?
Physical assessment: Observation/inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation are techniques used to gather information.
Why would the nurse perform percussion during the physical assessment of a patient?
Percussion involves tapping your fingers or hands quickly and sharply against parts of the patient's body to help you locate organ borders, identify organ shape and position, and determine if an organ is solid or filled with fluid or gas.
How do you do percussion lung therapy?
0:222:44Percussion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFrom here you know where to start your treatment. Place a folded towel over the area you wish toMoreFrom here you know where to start your treatment. Place a folded towel over the area you wish to treat. With a cupped hand and soft wrists you can start your percussion argue that on the side.
What is objective assessment of respiratory function?
A focused respiratory objective assessment includes interpretation of vital signs; inspection of the patient’s breathing pattern, skin color, and respiratory status; palpation to identify abnormalities; and auscultation of lung sounds using a stethoscope.
How to collect data for respiratory health assessment?
Collect data using interview questions, paying particular attention to what the patient is reporting. The interview should include questions regarding any current and past history of respiratory health conditions or illnesses, medications, and reported symptoms. Consider the patient’s age, gender, family history, race, culture, environmental factors, and current health practices when gathering subjective data. The information discovered during the interview process guides the physical exam and subsequent patient education. See Table 10.3a for sample interview questions to use during a focused respiratory assessment. [1]
What is the normal respiratory rate for an adult?
The normal range of a respiratory rate for an adult is 12-20 breaths per minute at rest, and the normal range for oxygen saturation of the blood is 94–98% (SpO₂) [3] is less than 12 breaths per minute, and is greater than 20 breaths per minute.
When assessing patients who are experiencing shortness of breath (or fatigue easily), it may be helpful to begin?
When assessing patients who are experiencing shortness of breath (or fatigue easily), it may be helpful to begin auscultation in the bases and progress upward to other lung fields as tolerated by the patient. This ensures that assessment of the vulnerable lower lobes is achieved prior to patient fatigue.
What does it mean when your respiratory rate is below 95%?
As a general rule of thumb, respiratory rates outside the normal range or oxygen saturation levels less than 95% indicate respiration or ventilation is compromised and requires follow-up. There are disease processes, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), where patients consistently exhibit below normal oxygen saturations; therefore, trends and deviations from the patient’s baseline normal values should be identified. A change in respiratory rate is an early sign of deterioration in a patient, and failing to recognize such a change can result in poor outcomes. For more information on obtaining and interpreting vital signs, see the “ General Survey ” chapter.
What is the role of a nurse in respiratory assessment?
With an understanding of the basic structures and primary functions of the respiratory system, the nurse collects subjective and objective data to perform a focused respiratory assessment.
How to listen to the movement of air through the airways during inspiration and expiration?
Auscultation. Using the diaphragm of the stethoscope, listen to the movement of air through the airways during inspiration and expiration. Instruct the patient to take deep breaths through their mouth. Listen through the entire respiratory cycle because different sounds may be heard on inspiration and expiration.
What is respiratory assessment?
A thorough respiratory assessment consists of inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation in conjunction with a comprehensive health history. Use a systematic approach and compare findings between left and right so the patient serves as his own control.
How to measure diaphragmatic excursion?
To measure diaphragmatic excursion, ask your patient to inhale and hold it. Percuss from the lower edge of his right scapula down toward the diaphragm ( see Technique for percussion ). When the note changes from resonant to dull, you've located your first landmark.
What are the sounds of the lung?
Listen for adventitious lung sounds. Crackles are distinct , noncontinuous sounds defined as "fine" (sound like popping) and "coarse" (sound like bubbling or gurgling and usually clear or decrease after coughing). Sibilant wheezes—high-pitched musical or whistling sounds—are commonly heard in patients with asthma, typically during or at the end of expiration. Sonorous wheezes, heard throughout inspiration and expiration, may be caused by airway secretions or bronchoconstriction.
How to assess for fremitus?
2. Assess for tactile fremitus by placing the ball or the ulnar surface of your hands on the right and left sides of his upper back. Ask him to say "99" and note any absent or asymmetric increased or decreased palpable vibrations transmitted through the bronchopulmonary tree to the thorax as you move your hands down and from the center to the periphery.
How to test for chest expansion?
Next, gently palpate his back with your fingers, noting any tenderness, masses, lesions, temperature changes, or crepitus—a coarse, crackling sensation that's palpable over the skin. To test for symmetric chest expansion, place your thumbs at the level of the 10th ribs with your fingers loosely grasping and parallel to the lateral rib cage. Then slide them medially just enough to create a small skin fold between your thumbs, as shown. Ask him to inhale deeply and note if your thumbs move apart symmetrically as you feel for the range and symmetry of the rib cage as it expands and contracts.
How many breaths per minute does a pigeon breathe?
Note his breathing. Respirations should be even, unlabored, and regular at a rate of 12 to 20 breaths per minute. Normally, inspiration is half as long as expiration and chest expansion is symmetrical.
Where do you hear Auscultate's breath?
Auscultate his breath sounds at the areas indicated, down to the sixth rib. Tracheal sounds, heard over the trachea in the neck, are relatively high-pitched, and very loud with inspiration and expiration of equal duration. Bronchial sounds are heard over the manubrium, if present.
Who invented percussion?
Percussion was first described by Dr. Josef Leopold Auenbrugger, an Austrian physician who first observed his father tapping on wine barrels in the cellar of his hotel to determine how much wine was left. The son applied this technique to patients when he became a physician. He is credited with bringing the technique of percussion to the field of medicine. Much of his work occurred around 1760 where he described that by percussing the thorax he could accurately predict the contents of what was inside, as confirmed with post-mortum studies he conducted.
What is a pulmonary exam?
Pulmonary Exam: Percussion & Inspection. The pulmonary exam is one of the most important and often practiced exam by clinicians. While auscultation is most commonly practiced, both percussion and inspection are equally valuable techniques that can diagnose a number of lung abnormalities such as pleural effusions, emphysema, ...
Who first described the pulmonary exam?
Historical Perspective of the Pulmonary Exam. Percussion was first described by Dr. Josef Leopold Auenbrugger, an Austrian physician who first observed his father tapping on wine barrels in the cellar of his hotel to determine how much wine was left. The son applied this technique to patients when he became a physician.
How many fingers are in a clinical pearl?
Clinical Pearl. Insert (in a normal individual) three fingers vertically in the space under the cricoid cartilage, and above the sternal notch. As the person breathes in, the space may reduce to two fingers at most (i.e. the fingers get "squeezed" as the sternum rises with inspiration).
How to perform percussion?
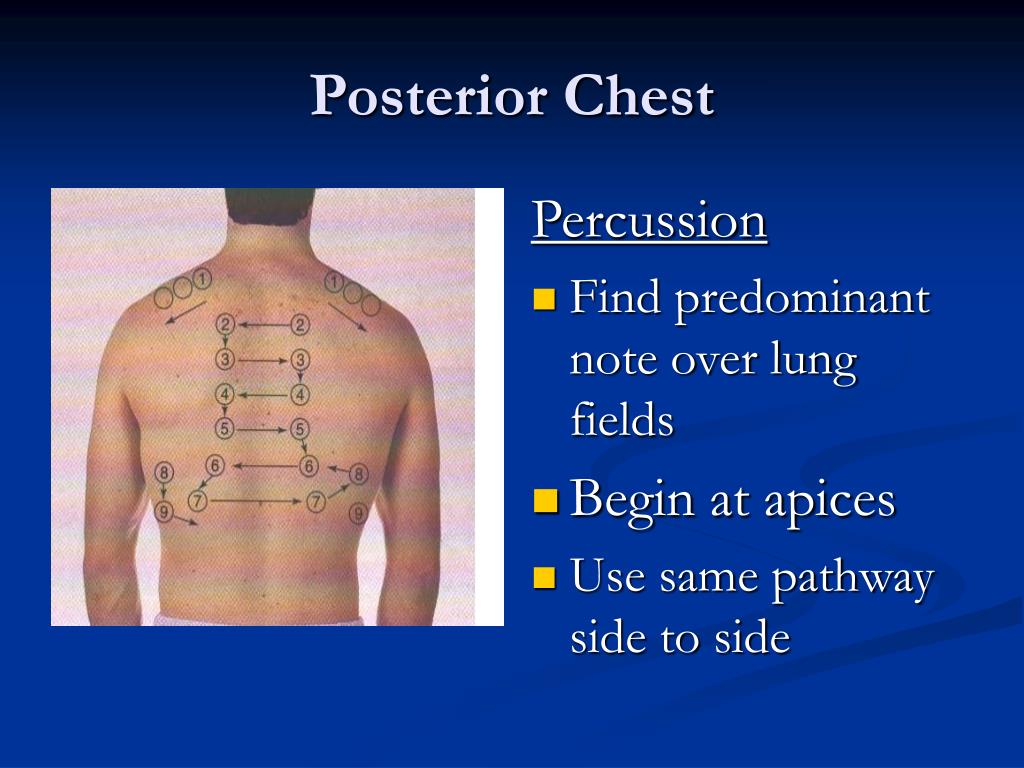
Percussion is performed by placing the middle finger of the nondominant hand against the chest wall. The tip of the middle finger on the dominant hand is used to strike the distal phalanx of the middle finger between the cuticle and the first joint. Percussion is helpful to determine the density of the underlying lung tissue and identify the position of the diaphragm during inspiration and expiration. Percuss the posterior chest in each intercostal space, avoiding the ribs and scapula, comparing one side with the other, using the side-to-side ladder pattern, striking in each place twice (Figure 1). Percussion sounds should be low-pitched, hollow, and long in duration, or resonant. In contrast, dullness occurs when fluid or solid tissue replaces the normally air filled lung and are thud-like with medium pitch and duration. Dull tones may indicate pneumonia, pleural effusion, or atelectasis. Very loud, lower pitch, and longer percussion sounds, hyperresonance, when unilateral may indicate emphysema or pneumothorax ( Bickley, 2012; Mansen & Gabiola, 2015 ).
Where to percuss in intercostal space?
Percuss the posterior chest in each intercostal space, avoiding the ribs and scapula, comparing one side with the other, using the side-to-side ladder pattern, striking in each place twice (Figure 1). Percussion sounds should be low-pitched, hollow, and long in duration, or resonant.
What are the sounds of the chest?
Listen for any adventitious or added sounds ( Table 3 ). Crackles are caused by the small airways reopening as the chest wall expands, forcing air through passages narrowed by fluid, mucous, or pus, and is heard most frequently in the bases due to hypoventilation. The sound of hair being rubbed between one's fingers simulates this sound. Rhonchi are coarse rattling respiratory sounds somewhat like snoring, usually caused by secretions in bronchial airways. A wheeze is a continuous, coarse whistling sound and suggests narrow airways (bronchospasm); and common in asthma, COPD, and bronchitis. If wheezing is heard on one side of the chest only, it may be the result of compression from a tumor or foreign body. Stridor is a medical emergency and is loud, rough, continuous, and high pitched due to upper airway obstruction, heard loudest over the trachea. Pleural friction rub is the squeaking or grating sound of the pleural linings rubbing together and can be described as the sound made by treading on fresh snow. This occurs when the pleural layers are inflamed and have lost their lubrication. Friction rub sounds that continue while the patient is holding their breath are most likely cardiac related ( Bickley, 2012; Mansen & Gabiola, 2015 ).
What is vocal fremitus?
Vocal fremitus is a vibration felt on the posterior chest using the ulnar side of the hand. Instruct the patient to say “baby” to create vibrations, each time the hands are moved from one area to another. Solid areas of consolidation such as with pneumonia or tumors will have increased vibration; air-filled areas such as with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pneumothorax will have less vibration. ( Bickley, 2012; Mansen & Gabiola, 2015 ).
Why is a physical exam important?
The health exam is an opportunity to explore patients' subjective symptoms and objective signs, screen for diseases, and identify risk for future medical problems. Although technology for disease detection is constantly improving, skilled physical assessment may lead to fewer unnecessary diagnostic tests and increased patient satisfaction ( Verghese & Horwitz, 2009 ). In addition, many clinical signs cannot be fully appreciated without a physical assessment, which is necessary to recognize subtle individual changes and ultimately improve patient outcomes ( Zambas, 2010 ). This article, the first in a four-part series, focuses on examination of the respiratory system.
What is the normal respiratory rate?
Normal adult respiratory rate is 14 to 20 with a regular rate and frequency and should be quiet. Breathing is considered abnormal if the rate is irregular, too fast, too slow, or shallow (Table 1). Observe the shape of the thorax; it should be symmetrical with equal chest movement.
Why are older adults at increased risk for respiratory disease?
Because older adults are at increased risk for respiratory disease due to loss of elasticity and decreased ventilation of the lower lobes, specifically inquire about fatigue, weight change, dyspnea on exertion, flu and pneumonia vaccine status, and change in number of pillows used at night (Hogstel & Curry, 2005).
What is a respiratory assessment?
In hypoxic patients or those with airway obstructions, a respiratory assessment provides important information about the patient’s status and clues about next treatment steps.
What does hearing the sounds of the patient breathing provide?
Hearing the sounds of the patient breathing provides vital information about the patient’s overall health. Auscultate the chest, back, and sides with a focus on signs of loud or labored breathing. Signs of abnormal breathing include:
How to check respiratory status?
Percussion can provide additional information about respiratory status. Use the middle or index finger of your dominant hand to tap the areas between each rib through the chest or back. Avoid touching the skin with your other fingers, since this can cause vibrations that compromise the assessment.
How to evaluate thorax?
Evaluate the thorax by positioning the palms over the thorax and feeling for bulging, tenderness, and retractions while breathing. Feel the ribs for lumps, scars, and swelling.
Do preterm babies have weaker respiratory muscles than adults?
Preterm infants, for example, have weaker respiratory muscles than children and adults, while infants and young children have a more rapid rate of respiration. Ensure you know what’s normal for the patient population you serve, as well as the specific patient you are treating.
Which lobe of the lung is a percussion?
Percussion – Percuss all lobes of the lung, front and back, listening for sounds that suggest complications like hyperinflation, consolidation, or effusion.
How to examine the respiratory system?
Examining the respiratory system consists of a number of components, namely inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Given the importance of the respiratory system, at least a basic exam should be conducted and documented on nearly all patients. Here’s a quick review of what you’re looking for: 1 Inspection – Inspect the external chest noting the chest shape (ex. barrel chest as seen in COPD), respiratory rate, signs of respiratory distress, nature of breathing, and external appearance of the skin. 2 Auscultation – Listen to lung sounds noting any abnormalities. 3 Percussion – Percuss all lobes of the lung, front and back, listening for sounds that suggest complications like hyperinflation, consolidation, or effusion. 4 Palpation – Check the position of the trachea, feel for symmetrical chest expansion, and test for tactile vocal fremitus.
What are the abnormalities on a respiratory exam?
Abnormals on a respiratory exam may include: Retractions, accessory muscle use, or nasal flaring. Chest wall tenderness, chest wall bruising, rib tenderness, sternal tenderness. Areas of increased or decreased tactile fremitus. Depression or protrusion of the sternum (pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum)
What is chest inspection?
Inspection – Inspect the external chest noting the chest shape (ex. barrel chest as seen in COPD), respiratory rate, signs of respiratory distress, nature of breathing, and external appearance of the skin.
What are the components of the respiratory system?
What You’re Looking For. Examining the respiratory system consists of a number of components, namely inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Given the importance of the respiratory system, at least a basic exam should be conducted and documented on nearly all patients.
Where is the respiratory abnormality located?
You may note, for example, abnormal lung sounds at the lung bases vs. the apex, or on the right vs. the left side of the chest .
Do you need to document a respiratory exam?
For patients presenting with respiratory complaints, or known respiratory system abnormalities, you will want to document a complete respiratory exam. For patients presenting with non-related problems, you can keep your respiratory system documentation to a minimum. The example provided here falls somewhere in the middle of this spectrum.