What is the perfect indicative in Greek?
The perfect tense in Greek is used to describe a completed action which produced results which are still in effect all the way up to the present. Sample translation: “I have believed.” Notice that the perfect tense carries two ideas: (1) completed action and (2) continuing results.
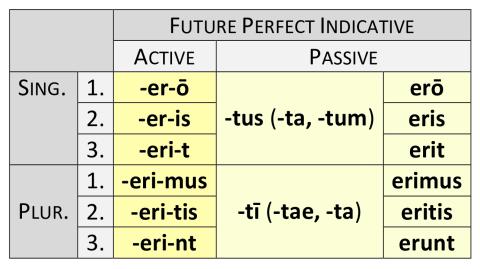
What is indicative perfect in Latin?
cecinit sDescription of FormLatin FormTranslation(s) in English Idiomperfect indicative activececinits/he sang, has sung, did singpluperfect indicative activececinerats/he had sungfuture perfect indicative activececinerits/he will have sungpresent indicative passivecaniturit is sung, is being sung21 more rows
Is present perfect indicative?
It's preterite because it refers to an action in the past, but in the present moment this action is perfect, it means “completed.” It's also compuesto (compound) because you form it with two words that I'll explain later. And it's indicative, as it expresses real actions and facts.
How is the present perfect indicative formed?
The present perfect of any verb is composed of two elements : the appropriate form of the auxiliary verb to have (present tense), plus the past participle of the main verb. The past participle of a regular verb is base+ed, e.g. played, arrived, looked.
What is perfect passive indicative?
2:059:08Ch. 19: Perfect Passive Indicative - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI was loved or I have been loved okay so two acceptable translations of the perfect passiveMoreI was loved or I have been loved okay so two acceptable translations of the perfect passive indicative.
What does imperfect indicative mean?
The Imperfect Indicative is a past tense. It is used to talk about ongoing past actions, habitual actions in the past, and lasting personal qualities or conditions. It is used when talking about what time it was in the past, moods/feelings/and emotions in the past, someone's age in the past, etc.
What is indicative example?
Indicative is defined as a grammar term for a verb or a sentence that either makes a statement or asks a question. An example of the indicative is the sentence, "The birds are singing."
What are the 4 types of present perfect tense?
have been and have gone.Present perfect with time adverbials.Present perfect continuous.Present perfect for future.
What is an example of a present indicative verb?
The indicative mood is a verb form that makes a statement or asks a question. For example: Jack sings every Friday. (This is a verb in the indicative mood.
What are the 10 examples of present perfect tense?
Examples of Present Perfect TenseI have written articles on different topics.He has read various kinds of books.They have played football.She has taken coffee.He has gone to the library.We have shopped in this market.We have watched movies in this Cineplex.You have shopped in that market.More items...
What means present indicative?
Indicative means to tell the facts. What you're doing by using present indicative in English is getting straight to the point and telling the person you are speaking to what's up.
How can you tell the difference between present perfect indicative and subjunctive?
Matchpresent perfect subjunctive. - used to describe actions that have occurred in the past that have an influence on the present or continue into the present. ... present perfect indicative. -formed with the present form of the verb haber and the past participle. ... present perfect.
What is the indicative form in Latin?
Latin verbs can state facts, give commands and express doubt The most common is indicative, which is used to make a simple statement of fact; the others are more expressive. The indicative mood is for stating facts, as in: "He is sleepy." The imperative mood is for issuing commands, as in: "Go to sleep."
What is indicative in Latin?
MOOD: Latin has four Moods: Indicative, Subjunctive, Imperative, Infinitive. a) Indicative: The Indicative is used for statements and questions: I love that book. Are you reading that book?
How do you form the perfect passive indicative in Latin?
To form the perfect passive, pluperfect passive and future perfect passive tense change the '-m' ending of the supine to '-s' to form the past participle. Remember that a past participle must agree with the word it modifies in gender, number and case and it declines like 'bonus, -a, -um' .
What is the perfect infinitive in Latin?
To form the perfect active infinitive of a verb, add '-sse' to the third principal part of the verb.
Perfect Active Indicative
Sorry my Greek text did not transfer over??? I still haven't figured that out. Just in case that is frustrating to you, it is more so to me!
Re: Perfect Active Indicative
Alan Patterson wrote: But, my concern is with the way Mounce translates the Perfect Active Indicative. Mounce is not putting the focus on the present stage of the result of having been loosed. His translation really does not require that the individual is currently loosed, whereas that is what the Greek emphasizes.
Re: Perfect Active Indicative
Alan, the perfect has something in it that is already completed, it is not just a present tense "I loose". It applies a completed action to the present.
Re: Perfect Active Indicative
Alan Patterson wrote: Per Mounce, leluka is I have loosed. What I am trying to do is give this gloss a present moment feel. Perhaps I should have said I loose, You loose, and He looses (there really is not a great gulf fixed between the Present and Perfect; this is what I am trying to indicate).
Re: Perfect Active Indicative
As a newcomer to Greek, I have just come across this same issue in my textbook. For example, my book's author translates μεμαρτυρηκα as, "have borne". Given Stephen's last post in this thread, is "have borne" the "least worst" English translation for the perfect active indicative?
Tense
Scholars propose three uses of tenses in Greek: Aktionsart, [1] aspect, [2] and time. Some argue that tenses strictly belong to one of these categories, while others propose a mixed use of tenses.
Voice
There are three voices in Greek: active, passive and middle. The voice shows the direction of the action. Active voice indicates that the subject carries out the action. It originates from the subject. Passive voice indicates that the action is done on or to the subject.
Mood
Mood refers to the manner in which the speaker relates the verbal idea to reality. There are four moods in Greek: Indicative mood affirms the actuality of the statement: God loves the world. Imperative mood expresses a command: Love your neighbor. Subjunctive mood expresses contingency: If you love God… Infinitive mood expresses a verbal idea without indicating person and number: To love is good..
Inflection
The word inflection comes from Latin inflecto “I bend.” See how “bending” occurs in English:
