
Proto-Indo-European phonology
The phonology of the Proto-Indo-European language has been reconstructed by linguists, based on the similarities and differences among current and extinct Indo-European languages. Because PIE was not written, linguists must rely on the evidence of its earliest attested descendants, such as Hittite, Sanskrit, Ancient Greek, and Latin, to reconstruct its phonology.
How do you improve phonological memory?
While reading, your working memory helps you to:
- figure out what’s going on in the story
- hold on to what’s just happened
- remember reading rules
- come up with the correct pronunciation of long words
How to improve phonological memory?
Poor phonological memory can hinder a student’s ability to accomplish most tasks including:
- mastering early reading skills
- learning new vocabulary words
- comprehending new and lengthy material
- following multi-step directions
How to pronounce phonological?
Here are 4 tips that should help you perfect your pronunciation of 'phonological':
- Break 'phonological' down into sounds : [FOH] + [NUH] + [LOJ] + [I] + [KUHL] - say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them.
- Record yourself saying 'phonological' in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen. ...
- Look up tutorials on Youtube on how to pronounce 'phonological'.
What does it mean to be phonetic or phonological?
The study of human sounds is called phonetics, while phonology refers to the way sounds are categorized within a language or language system. The phonotactics process deals with the combinations of sounds that can occur in a syllable and how they can be combined.
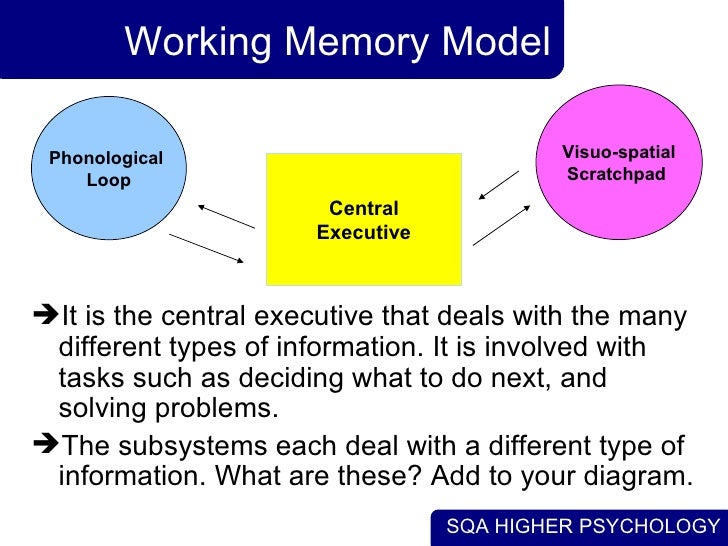
How can I increase my phonological memory?
It may seem unnatural at first, but practicing listening to, recalling, and repeating nonsense words provided by the teacher is a way for students to strengthen their phonological working memory.
What is phonological memory used for?
Phonological memory is the ability to hold information (numbers, sounds, words) in working or short-term memory for temporary storage. Students must be able to hold information long enough to process it, use it, and then transfer it to long-term memory.
Why is phonological memory important for reading?
Phonological memory predicted word identification and decoding. In addition, phonological awareness and rapid automatized naming predicted every aspect of reading assessed, supporting the notion that phonological processing is a core contributor to reading ability.
What is phonological short-term memory?
Phonological short-term memory (PSTM) can be defined as the ability to maintain verbal information in the working memory for a few seconds, that is, to recognize and remember phonological elements and the order of their occurrence.
What is phonological memory example?
Phoneme segmentation requires breaking a word into its sounds by tapping out or counting the sounds, for example, “How many phonemes in block?” (four: /b/ /l/ /o/ /ck/). The ability to hold on to speech-based information in short-term memory is called phonological memory.
How do you support phonological memory in the classroom?
Phonological memory can be supported by developing strategies to compensate for the underlying phonological weakness.Break words into bigger units, using chunking. ... Teach learners how to use rehearsal e.g. saying words or sounds over and over again while they are working out the sounds that they need to manipulate.
What is a symptom of a problem with phonological working memory?
Difficulty following multi-step directions. Difficulty staying engaged in class. Test anxiety, especially on multiple choice tests. A need for more time and repetition.
Is phonological processing dyslexia?
Phonological dyslexia is extreme difficulty reading that is a result of phonological impairment, meaning the ability to manipulate the basic sounds of language. The individual sounds of language become 'sticky', unable to be broken apart and manipulated easily. This type of dyslexia is synonymous with dyslexia itself.
How is phonological working memory measured?
Phonological working memory is assessed using 'digit span', 'digit span-running', and 'nonword repetition' tasks. The 'digit span' task requires children to repeat lists that vary in length from 2-8 digits. This task is presented to children in the context of playing a copycat game with a robot.
Is verbal memory the same as phonological memory?
While phonological short-term memory (or immediate memory span for auditory–verbal information) is generally reported to be at or above the level predicted by mental age (Porter & Coltheart, 2005), verbal working memory (being able to hold and manipulate auditory–verbal information in mind) is generally at, or below, ...
What does phonological processing mean?
Definition. The ability to quickly and correctly hear, store, recall, and make different speech sounds.
What are phonological difficulties?
Phonological disorder is a type of speech sound disorder. Speech sound disorders are the inability to correctly form the sounds of words. Speech sound disorders also include articulation disorder, disfluency, and voice disorders.
What does phonological processing mean?
Definition. The ability to quickly and correctly hear, store, recall, and make different speech sounds.
What is a symptom of a problem with phonological working memory?
Difficulty following multi-step directions. Difficulty staying engaged in class. Test anxiety, especially on multiple choice tests. A need for more time and repetition.
What is phonological processing?
Phonological processing is the use of the sounds of one's language (i.e., phonemes) to process spoken and written language (Wagner & Torgesen, 1987). The broad category of phonological processing includes phonological awareness, phonological working memory, and phonological retrieval.
Is phonological processing dyslexia?
Phonological dyslexia is extreme difficulty reading that is a result of phonological impairment, meaning the ability to manipulate the basic sounds of language. The individual sounds of language become 'sticky', unable to be broken apart and manipulated easily. This type of dyslexia is synonymous with dyslexia itself.
What is phonological processing?
Phonological processing is the use of the sounds of one's language (i.e., phonemes) to process spoken and written language (Wagner & Torgesen, 1987).The broad category of phonological processing includes phonological awareness, phonological working memory, and phonological retrieval.
What is phonological retrieval?
Phonological retrieval is the ability to recall the phonemes associated with specific graphemes, which can be assessed by rapid naming tasks (e.g., rapid naming of letters and numbers). This ability to recall the speech sounds in one's language is also integral to phonological awareness.
Why is phonological processing important?
All three components of phonological processing are important for speech production as well as the development of spoken and written language skills. Therefore, it is important and necessary to monitor the spoken and written language development of children with phonological processing difficulties.
What is the term for the ability to analyze and manipulate sound structures?
Phonological awareness is the umbrella term; phonemic awareness applies when the units being manipulated are phonemes, rather than words, onset-rime segments, or syllables.
