How do you determine pKa?
- Now you want to calculate the pKa from the equation 2.3= pKa+ log (0.1/0.05). OK.
- pKa= 2.3- log (0.1/0.05)=
- PKa= 2.3- log (10/5)
- pKa= 2.3- log2
- = 2.303- 0.3010
- =2.0020. Ok.
- Now you got it and caught it ?
What does pKa tell us?
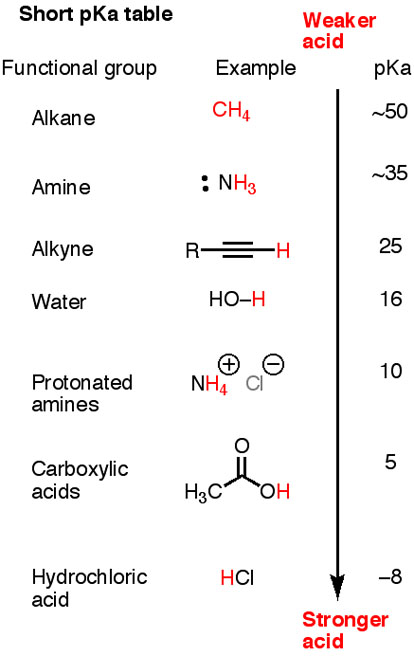
The pKa value is the pH at which a drug is found to be 50% ionised and 50% not ionised. It is able to tell us how a molecule will behave when it is put into something with a certain pH value. The concept of pKa is derived from something called the acid dissociation constant (Ka).
How to determine pKa values?
Find the dissociation constant with the formula Ka = (H+)²/ ( (HA) – (H+)), where Ka is the dissociation constant, and (HA) is the concentration of the acid before dissociation. In chemistry, the pKa value is really a way of measuring acidity. It is the negative logarithm from the equivalence constant once the solvent is water.
What does pKa tell you?
pKa is a property of a compound that tells us how acidic it is. The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid. Acids are neutral when protonated and negatively charged (ionized) when deprotonated. Bases are neutral when deprotonated and positively charged (ionized) when protonated.
What is pKa in chemistry simple?
In simple terms, pKa is a number that shows how weak or strong an acid is. A strong acid will have a pKa of less than zero. More precisely – pKa is the negative log base ten of the Ka value (acid dissociation constant). It measures the strength of an acid — how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid.
What is pKa and pH?
pKa and pH are two concepts in physical chemistry that refer to a system's acidity. The fundamental distinction between pKa and pH is that pKa denotes an acid's dissociation, whereas pH denotes a system's acidity or alkalinity.
What is pKa used for in chemistry?
The pKa value is one method used to indicate the strength of an acid. pKa is the negative log of the acid dissociation constant or Ka value. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid. That is, the lower value indicates the acid more fully dissociates in water.
Is pKa equal to pH?
Each dissociation has a unique Ka and pKa value. When the moles of base added equals half the total moles of acid, the weak acid and its conjugate base are in equal amounts. The ratio of CB / WA = 1 and according to the HH equation, pH = pKa + log(1) or pH = pKa.
Is higher pKa more acidic?
In addition, the smaller the pKa value, the stronger the acid. For example, the pKa value of lactic acid is about 3.8, so that means lactic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
What does high pKa mean?
pKa: If the pKa of an acid is high, it is a weak acid, and if the pKa of an acid is low, it is a strong acid. pH: If the pH of a system is high, the system is alkaline, but if the pH is low, that system is acidic.
Does high pKa mean strong base?
Using pKa values and the Principle of Acid-Base Mediocrity To Predict Acid-Base Reactions. With these two mental tools – the higher the pKa, the weaker the acid, and the Principle Of Acid Base Mediocrity, we are all set to use pKa values to predict the directions of acid-base reactions.
What is the unit of pKa?
Each pKa unit represents a 10-fold difference in acidity or basicity. The weaker an acid, the stronger is its conjugate base; the stronger an acid, the weaker is its conjugate base. For example, HCl is a very strong acid; it gives up its proton readily; its conjugate base, Cl–, has very little affinity for H+.
What does pKa strongest acidic mean?
The pKa value indicates the strength of an acid. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid i.e, the lower value indicates the acid more fully dissociates in water. ∴ Formic acid with lower pKa value of 3. 77 is the strongest acid.
Does Low pKa mean low pH?
where each bracketed term represents the concentration of that substance in solution. The stronger an acid, the greater the ionization, the lower the pKa, and the lower the pH the compound will produce in solution.
How is pKa different than pH?
Difference Between pKa and pH pKa is the negative value of the logarithm of Ka. pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid. pH indicates whether a system is acidic or alkaline.
What does a pKa of 7 mean?
pKa<3 is for a strong acid. 3
Does Low pKa mean low pH?
where each bracketed term represents the concentration of that substance in solution. The stronger an acid, the greater the ionization, the lower the pKa, and the lower the pH the compound will produce in solution.
How are pH and KA related?
Both Ka and pH are associated with each other. More the Ka, more would be its dissociation and thus stronger would be the acid. A strong acid has less pH value. Therefore, a larger Ka corresponds to a lesser pH value.
What happens when pH is less than pKa?
If the pH is lower than the pKa, then the compound will be protonated. If the pH is higher than the pKa, then the compound will be deprotonated. A further consideration is the charge on the compound. Acids are neutral when protonated and negatively charged (ionized) when deprotonated.
What is pH pKa and pKb?
pH, pKa, pKb, Ka, and Kb are used in chemistry to describe how acidic or basic a solution is and to gauge the strength of acids and bases. The pH scale is the most familiar measure of acidity and basicity, but pKa, pKb, Ka, and Kb are better for predicting acid and base strength and their reactions.
How do I calculate pKa?
pKa value is the negative base -10 logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of a solution. pKa = -log[Ka]
How does pKa change with temperature?
An endothermic reaction required heat during the reaction. Increase the dissociation constant (Ka) with an increase in temperature. Higher the valu...
Is high pKa more acidic?
No higher pka means lower acidity. So the higher the pKa the smaller Ka, and this means a weaker acid . Higher pKa indicates weaker acid.
What is the pKa of pure water at 25 ℃?
The pKa value of pure water at 25 ℃ is 14.
Why is pKa value important?
The quantitative behaviour of acids and bases in solution can be understood only if their pKa values are known. In particular, the pH of a solution...
What does pKa depend on?
pKa is dependent on the concentration of acid, conjugate base and H+.
Is the pKa value proportional to the pH?
It is important to remember that when the pH equals the pKa value, the conjugate base and conjugate acid proportions are identical. The fraction of...
What effect does temperature have on pKa?
As the temperature rises, the pKa decreases.
What happens if the pKa value is higher than the pH value?
We can predict whether a molecule will be protonated or deprotonated based on the connection between its pKa and the pH of its solution. The chemic...
How may the environment affect pKa values?
The pKa of an acid can be altered by altering the environment’s temperature.
What is pKa?
The pKa value is the negative base -10 logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of a solution.
Definition of pKa
pKa is a number that describes the acidity of a particular molecule. It measures the strength of an acid by how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. The lower the value of pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate its protons. describe the acidity of a particular molecule
Calulation of pKa
Let us consider a weak acid HA which ionizes in the aqueous solution as:
pKa and pH of buffer solution
Note: So weak acid may be used for preparing buffer solutions having pH values lying within the ranges pK a + 1 and pK a – 1.
Relation between pK a and pK b
Let us consider a weak acid HA which ionizes in the aqueous solution as:
Frequently Asked Questions on pKa
pKa value is the negative base -10 logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of a solution. pKa = -log [Ka]
What is pKa?
In simple terms, pKa is a number that shows how weak or strong an acid is. A strong acid will have a pKa of less than zero. More precisely – pKa is the negative log base ten of the Ka value (acid dissociation constant). It measures the strength of an acid — how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. The lower the value of pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate its protons.
What does pKa tell us about pH?
Essentially, pKa reveals what the pH needs to be in order for a chemical species to be able to donate or accept a proton. The relationship between pKa and pH is described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
How are pH and PKa related?
The lower the pH value, the higher the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution; therefore, the stronger the acid. pKa and pH are related as pKa helps predict what a molecule will do at a specific pH.
What is the difference between pKa and ka?
pKa and Ka. Ka denotes the acid dissociation constant. It measures how completely an acid dissociates in an aqueous solution. The larger the value of Ka, the stronger the acid as acid largely dissociates into its ions.
What is the pKa in organic chemistry?
The pKa in Organic Chemistry - Chemistry Steps. Let’s first define the meaning of a strong acid. According to the Arrhenius theory, acids dissociate in water to form protons (H + ). The general equation for the acid dissociation can be shown as: For a specific example, we can look at the dissociation of hydrochloric acid: ...
What is the p-K-A?
The p K a is the quantitative indicator of the acid strength. For our two compounds, we have
What is the weaker the acid or the conjugate base?
The stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base.
What happens when acid dissociates into a proton?
The more the acid dissociates into a proton, the stronger it is. We can also say, the stronger the tendency of a compound to donate a proton, the stronger acid it is. The same principle is applied for comparing the acidity of organic molecules. For example:
How much acid is in one vs the other?
One is ~19, and the other is ~9. That is a huge difference – 10 10 times more acidic.
Is propionic acid more acidic than phenol?
The p K a of carboxylic acids is ~5 and the p K a of phenol is ~10. Therefore, propionic acid is 10 5 more acidic than phenol.
Is acid dissociation a reversible reaction?
This is where the p K a comes into play. Acid-dissociation is a reversible reaction which is described by equilibrium constant ( K eq) and the p K a is derived from the K eq. Let’s see how that works:
What are the ka and pka?
Understanding Ka and pKa. Ka, pKa, Kb, and pKb are most helpful when predicting whether a species will donate or accept protons at a specific pH value. They describe the degree of ionization of an acid or base and are true indicators of acid or base strength because adding water to a solution will not change the equilibrium constant.
What is the Ka value of a weak acid?
The Ka value for most weak acids ranges from 10 -2 to 10 -14 . The pKa gives the same information, just in a different way. The smaller the value of pKa, the stronger the acid. Weak acids have a pKa ranging from 2-14.
What is the pH of a solution?
pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, [H+], in an aqueous (water) solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A low pH value indicates acidity, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a high pH value indicates alkalinity. The pH value can tell you whether you're dealing with an acid or a base, but it offers limited value indicating the true strength of the acid of a base. The formulas to calculate pH and pOH are:
How are Kb and Ka related?
Ka and Kb are related to each other through the ion constant for water, Kw: Ka is the acid dissociation constant. pKa is simply the -log of this constant. Similarly, Kb is the base dissociation constant, while pKb is the -log of the constant.
What does ka mean in math?
In the formulas, A stands for acid and B for base. Ka = [H+] [A-]/ [HA] pKa = - log Ka. at half the equivalence point, pH = pKa = -log Ka. A large Ka value indicates a strong acid because it means the acid is largely dissociated into its ions.
What is the Kb constant?
Kb is the base dissociation constant. The base dissociation constant is a measure of how completely a base dissociates into its component ions in water. A large Kb value indicates the high level of dissociation of a strong base. A lower pKb value indicates a stronger base.
What scales are used to measure acidic or basic?
There are related scales in chemistry used to measure how acidic or basic a solution is and the strength of acids and bases. Although the pH scale is most familiar, pKa, Ka, pKb, and Kb are common calculations that offer insight into acid-base reactions. Here's an explanation of the terms and how they differ from each other.
CORE Concepts
Topics Covered in Other Articles
What Is pKa?
- In simple terms, pKa is a number that shows how weak or strong an acid is. A strong acid will have a pKa of less than zero. More precisely – pKa is the negative log base ten of the Ka value (acid dissociation constant). It measures the strength of an acid — how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. The lower the value of pKa, the stronger th...
Pka and Ka
- Kadenotes the acid dissociation constant. It measures how completely an acid dissociates in an aqueous solution. The larger the value of Ka, the stronger the acid as acid largely dissociates into its ions.
Pka and Ph
- pHis a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution. The lower the pH value, the higher the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution; therefore, the stronger the acid. pKa and pH are related as pKa helps predict what a molecule will do at a specific pH. Essentially, pKa reveals what the pH needs to be in order for a chemical species to be able to donate or acc…
Pka of Some Weak & Strong Acids
- Hydrocyanic acid pKa = 9.21 (HCN, weak acid): Acetic acid pKa = 4.75 (weak acid) Hydrofluoric acid pKa = 3.14 (HF, weak acid) Hydrochloric acid pKa = -8 (HCl, strong acid): Sulfuric acid pKa ~ 3 (strong acid) Some more pKa’s are here.