What is Planck's constant in simple terms?
The Planck constant (Planck's constant) says how much the energy of a photon increases, when the frequency of its electromagnetic wave increases by 1 (In SI Units). It is named after the physicist Max Planck. The Planck constant is a fundamental physical constant. It is written as h.
What is Planck's constant class 11?
Planck's constant is defined as A fundamental constant, equal to the energy of a quantum of electromagnetic radiation divided by its frequency. S.I unit of planck's constant is joule second. And the MKS unit is in eV second. It is represented by h.
What is Planck's constant called?
A photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant. Due to mass–energy equivalence, the Planck constant also relates mass to frequency. = 6.62607015×10−34 J⋅Hz−1....Planck constantCommon symbols, or for the reduced Planck constantDimension
What is Planck's constant class 12?
In the quantum of electromagnetism, Planck's constant is the physical constant that relates the energy carried by a single photon to its corresponding frequency. Represented by h and measure using J.s in the SI system and eV.
Why we use Planck's constant?
Today, scientists use Planck's constant to determine overall energy: they multiply Planck's constant by the frequency of a wave (E=hf). This is important – Planck's constant effectively defines quantum mechanics. It defines how the universe permits life, in any form, to exist.Mar 10, 2021
What is dimension of Planck's constant?
Thus the dimension of plank's constant h is [ML2T−1]
Is Planck constant constant?
The Planck constant h is constant, but it is not a constant in the usual sense - it is a unit of action required to make a Schrödinger wave complete a period.
How is Planck's constant derived?
Derivation – Planck Constant In classical format, the Planck constant can be derived from the Planck mass, Planck length and Planck time. In wave format, the Planck constant was derived from the Transverse Energy Equation and provided in detail on the page on the Planck relation (E=hf).
What is the meaning of h in physics?
(physics) Reduced Planck's constant. Has the value ℎ/2π (where ℎ is Planck's constant), or approximately 1.05457182×10-34 J⋅s. Synonym: Dirac constant.
What is Planck's quantum theory?
According to Planck's quantum theory, Different atoms and molecules can emit or absorb energy in discrete quantities only. The smallest amount of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation is known as quantum.
What is the dimensional formula of Planck’s constant?
The dimensional formula of Planck’s constant is ML 2 T -1 .
What is the use of Planck’s constant?
Planck’s constant is used for describing the behavior of particles and waves at an atomic scale. Planck’s constant is one of the reasons for the de...
What is Planck’s law?
Planck’s law states that the energy of electromagnetic radiation is confined to quanta which cannot be divided and has an energy equal to the produ...
Why is LED used to determine Planck’s constant?
LED is used for determining Planck’s constant because the color of LED has a different threshold voltage which produces electrons at a different vo...
Why do we use Planck’s constant?
We use Planck’s constant for measuring Planck length and Planck time.
Why is Planck's constant important?
Planck’s constant is one of the reasons for the development of quantum mechanics.
Why is LED used for Planck's constant?
LED is used for determining the Planck’s constant because the color of LED has a different threshold voltage which produces electrons at a different voltage. This voltage along with the emission wavelengths can be used for determining the value of the Planck’s constant.
What is fundamental constant?
A fundamental constant, equal to the energy of a quantum of electromagnetic radiation divided by its frequency.
What is Planck's constant?
Planck's constant defines the amount of energy that a photon can carry, according to the frequency of the wave in which it travels. Electromagnetic radiation and elementary particles "display intrinsically both particle and wave properties," explains Fred Cooper, an external professor at the Santa Fe Institute, ...
What would happen if Planck's constant was bigger?
But if Planck's constant was a significantly bigger or smaller number, "all the world around us would be completely different," explains Martin Fraas, an assistant professor in mathematics at Virginia Tech, by email. If the value of the constant was increased, for example, stable atoms might be many times bigger than stars.
What is the invisible world of the ultrasmall?
Planck and other physicists in the late 1800s and early 1900s were trying to understand the difference between classical mechanics — that is, the motion of bodies in the observable world around us, described by Sir Isaac Newton in the late 1600s — and an invisible world of the ultrasmall, ...
How is electromagnetic energy transferred?
Electromagnetic energy cannot be transferred continuously but is transferred by discrete photons of light whose energy E is given by E = h f, where h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency of the light.". Advertisement.
When did the kilograms come into force?
The size of a kilogram, which came into force on May 20, 2019, as agreed upon by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (whose French acronym is BIPM) is now based upon Planck's constant.
Who invented the constant?
The constant — devised in 1900 by a German physicist named Max Planck, who would win the 1918 Nobel Prize for his work — is a crucial part of quantum mechanics, the branch of physics which deals with the tiny particles that make up matter and the forces involved in their interactions.
Can a child swing at any constant range of energy?
Hence, the child can swing at any continuous range of energies from zero up to a certain point.". But when you get down to the level of quantum mechanics, things behave differently. "The amount of energy that an oscillator could have is discrete, like rungs on a ladder," Schlamminger says.
What is the Planck constant?
The Planck constant is related to the quantization of light and matter. It can be seen as a subatomic -scale constant. In a unit system adapted to subatomic scales, the electronvolt is the appropriate unit of energy and the petahertz the appropriate unit of frequency. Atomic unit systems are based (in part) on the Planck constant. The physical meaning of the Planck constant could suggest some basic features of our physical world. These basic features include the properties of the vacuum constants#N#μ 0 {displaystyle mu _ {0}}#N#and#N#ϵ 0 {displaystyle epsilon _ {0}}#N#. The Planck constant can be identified as
What is the resulting constant of Planck constant?
The resulting constant is called the reduced Planck constant .
What was Planck's goal in finding the Planck constant?
Planck tried to find a mathematical expression that could reproduce Wien's law (for short wavelengths) and the empirical formula (for long wavelengths). This expression included a constant, , which is thought to be for Hilfsgrösse (auxiliary variable), and subsequently became known as the Planck constant.
What is the energy of a photon?
A photon 's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant. Due to mass–energy equivalence, the Planck constant also relates mass to frequency. In metrology it is used, together with other constants, to define the kilogram, an SI unit.
What is a kibble balance?
A Kibble balance (formerly known as a watt balance) is an instrument for comparing two powers, one of which is measured in SI watts and the other of which is measured in conventional electrical units. From the definition of the conventional watt W90, this gives a measure of the product KJ2RK in SI units, where RK is the von Klitzing constant which appears in the quantum Hall effect. If the theoretical treatments of the Josephson effect and the quantum Hall effect are valid, and in particular assuming that RK = h/e2, the measurement of KJ2RK is a direct determination of the Planck constant.
What is the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons (called "photoelectrons") from a surface when light is shone on it. It was first observed by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel in 1839, although credit is usually reserved for Heinrich Hertz, who published the first thorough investigation in 1887. Another particularly thorough investigation was published by Philipp Lenard in 1902. Einstein's 1905 paper discussing the effect in terms of light quanta would earn him the Nobel Prize in 1921, after his predictions had been confirmed by the experimental work of Robert Andrews Millikan. The Nobel committee awarded the prize for his work on the photo-electric effect, rather than relativity, both because of a bias against purely theoretical physics not grounded in discovery or experiment, and dissent amongst its members as to the actual proof that relativity was real.
Why is there confusion when dealing with frequency?
Confusion can arise when dealing with frequency or the Planck constant because the units of angular measure (cycle or radian) are omitted in SI. In the language of quantity calculus, the expression for the value of the Planck constant, or a frequency, is the product of a numerical value and a unit of measurement.
What is Planck's quantum theory?
This theory states: Energy radiated or enwrapped is not perpetual, but in the form of packets called quanta. This energy is known as “Quantum of energy.”.
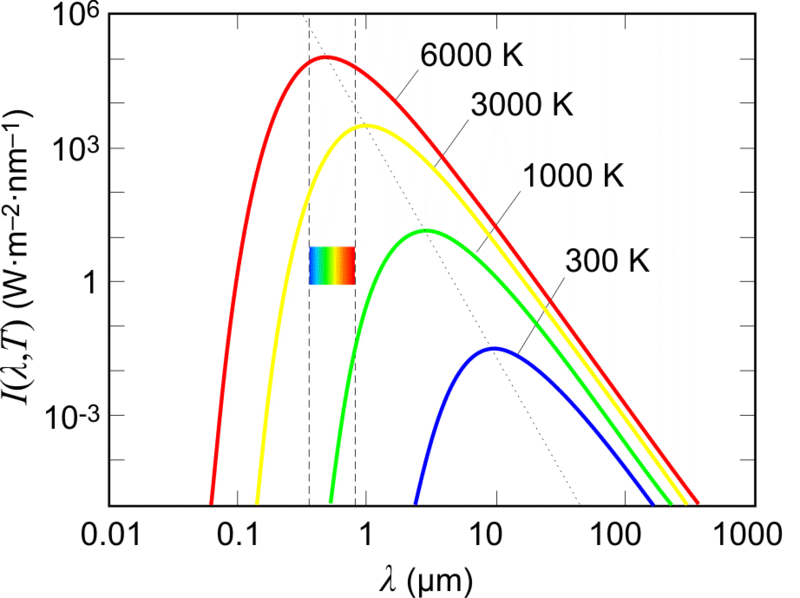
What is the Vmax of a graph?
The Vmax is the position shown as a peak in the graph is the visible light. What happens here is when we go further, the wavelength keeps on increasing, but the emission of waves keeps on decreasing and continues further, we see that the emission of waves is negligible, but not zero.
How is light formed?
Ans: Light is formed by the combination of the Magnetic and Electric field, and these two fields are perpendicular to each other, which means these two waves are oscillating in a direction perpendicular to each other and the wave is propagating in the direction perpendicular to these two fields.
Is the emission of waves maximum even when the wavelength is less?
The emission of waves is maximum even when the wavelength is less. There’s a lot of difference when the wavelength is less. The modification in the above concept was brought up by a great German theoretical physicist, named Dr. Max Planck.
What is Planck's law?
Planck’s Law: It states that electromagnetic radiation from heated bodies is not emitted as a continuous flow but is made up of discrete units or quanta of energy, the size of which involve a fundamental physical constant (Planck’s constant). Mathematically, Where, h = Planck’s Constant =. k = Boltzmann’s Constant = 1.381 × 10 -23 J/K.
How to find the energy of photons?
If the wavelength is known, you can calculate the energy by using the wave equation to calculate the frequency and then apply Planck’s equation to find the energy.
What is Planck's constant?
Planck’s constant, (symbol h ), fundamental physical constant characteristic of the mathematical formulations of quantum mechanics, which describes the behaviour of particles and waves on the atomic scale, including the particle aspect of light. The German physicist Max Planck introduced the constant in 1900 in his accurate formulation ...
What is the Planck scale?
The Planck scale is described as the arena in which both quantum mechanical and gravitational effects come into play. Brian Greene explains where the Planck values come from. This video is an episode in his Daily Equation series.
Who invented the constant?
The German physicist Max Planck introduced the constant in 1900 in his accurate formulation of the distribution of the radiation emitted by a blackbody, or perfect absorber of radiant energy ( see Planck’s radiation law ).
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...

Overview
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, is a fundamental physical constant denoted , and is of fundamental importance in quantum mechanics. A photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant. Due to mass–energy equivalence, the Planck constant also relates mass to frequency.
In metrology it is used, together with other constants, to define the kilogram, an SI …
Origin of the constant
Planck's constant was formulated as part of Max Planck's successful effort to produce a mathematical expression that accurately predicted the observed spectral distribution of thermal radiation from a closed furnace (black-body radiation). This mathematical expression is now known as Planck's law.
In the last years of the 19th century, Max Planck was investigating the proble…
Development and application
The black-body problem was revisited in 1905, when Rayleigh and Jeans (on the one hand) and Einstein (on the other hand) independently proved that classical electromagnetism could never account for the observed spectrum. These proofs are commonly known as the "ultraviolet catastrophe", a name coined by Paul Ehrenfestin 1911. They contributed greatly (along with Einstein's work on …
Photon energy
The Planck–Einstein relation connects the particular photon energy E with its associated wave frequency f:
This energy is extremely small in terms of ordinarily perceived everyday objects.
Since the frequency f, wavelength λ, and speed of light c are related by , the relation can also be expressed as
Reduced Planck constant
In applications where it is natural to use the angular frequency (i.e. where the frequency is expressed in terms of radians per second instead of cycles per second or hertz) it is often useful to absorb a factor of 2π into the Planck constant. The resulting constant is called the reduced Planck constant. It is equal to the Planck constant divided by 2π, and is denoted ħ (pronounced "h-bar"):
Value
The Planck constant has dimensions of angular momentum. In SI units, the Planck constant is expressed in joules per hertz (J⋅Hz or kg⋅m ⋅s ). Implicit in the dimensions of the Planck constant is the fact that the SI unit of frequency, the hertz, represents one complete cycle, 360 degrees or 2π radians, per second. An angular frequency in radians per second is often more natural in mathematics and physics and many formulas use a reduced Planck constant (pronounced h-bar).
Understanding the 'fixing' of the value of h
Since 2019, the numerical value of the Planck constant has been fixed, with a finite decimal representation. Under the present definition of the kilogram, which states that "The kilogram [...] is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of h to be 6.62607015×10 when expressed in the unit J⋅s, which is equal to kg⋅m ⋅s , where the metre and the second are defined in terms of speed of light c and duration of hyperfine transition of the ground state of an unperturbed caesium-133atom ΔνC…
Significance of the value
The Planck constant is related to the quantization of light and matter. It can be seen as a subatomic-scale constant. In a unit system adapted to subatomic scales, the electronvolt is the appropriate unit of energy and the petahertz the appropriate unit of frequency. Atomic unitsystems are based (in part) on the Planck constant. The physical meaning of the Planck constant could suggest some basic features of our physical world. These basic features include the properties …