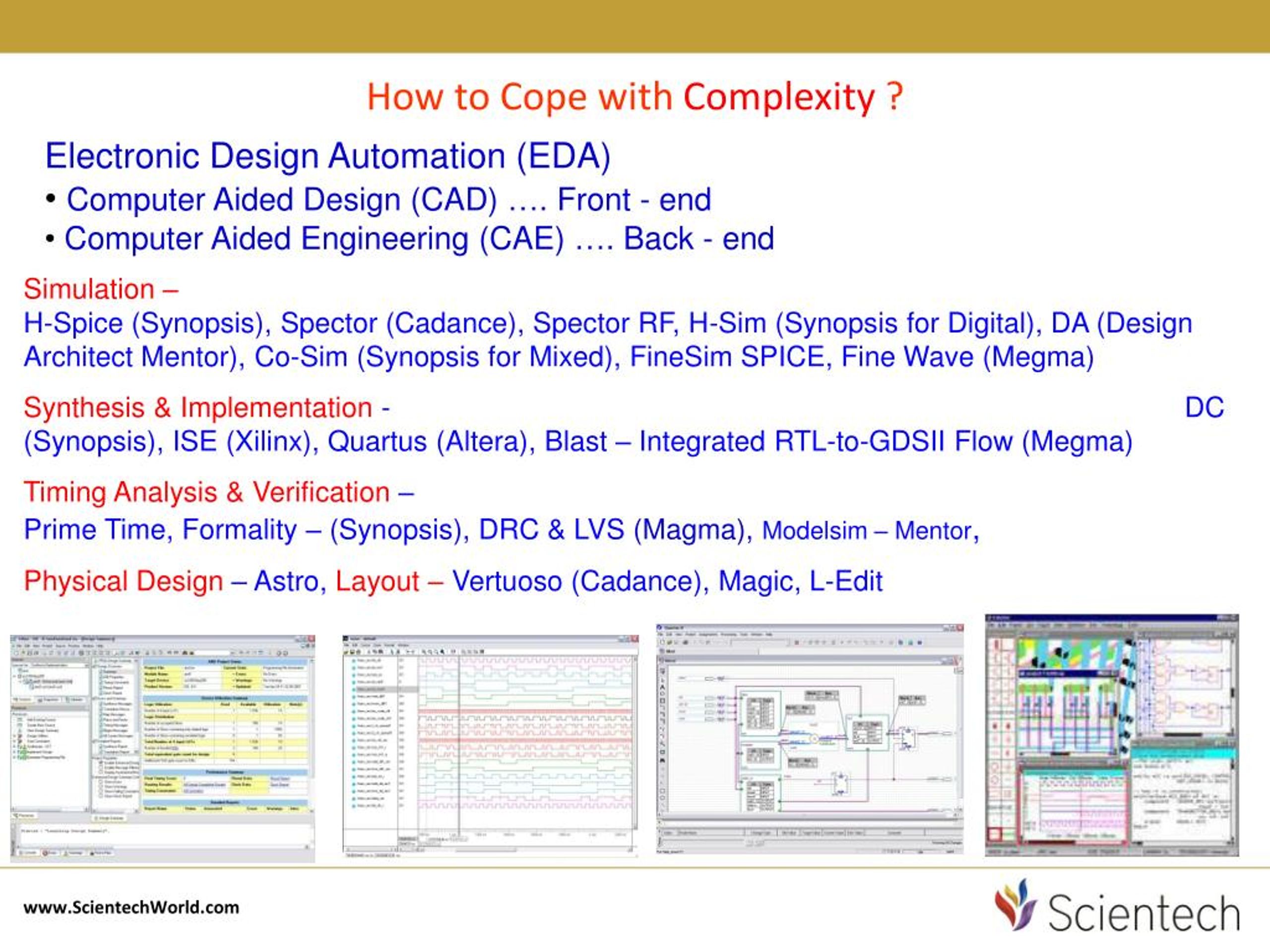
What is primetime in VLSI?
PrimeTime is a Static Timing Analysis (STA) tool from Synopsys. This is a simple description to use PrimeTime for VLSI class project. In Project #6, you will learn to find critical path using PrimeTime from your synthesized Verilog code.
What is Primetime static timing analysis?
Synopsys' PrimeTime static timing analysis tool provides a single, golden, trusted signoff solution for timing, signal integrity, power and variation-aware analysis.
What is the Primetime suite?
The PrimeTime® Suite delivers fast, memory-efficient scalar and multicore computing, distributed multi-scenario analysis and ECO fixing using POCV and variation-aware modeling. Synopsys' PrimeTime static timing analysis tool provides a single, golden, trusted signoff solution for timing, signal integrity, power and variation-aware analysis.
How to use primetime with Verilog?
The verilog file imported into PrimeTime must be a flattened one. Run the design first at an arbitrary clock period, the tool will report the slack as positive or negative. If the slack is negative you can fix it by increasing your clock period to make it positive. The tool also reports the power consumption.
What is a negative unate timing arc?
What unit is used for timing reports?
Can timing arcs be used to invert polarity?

For what is prime time tool used for?
Synopsys' PrimeTime static timing analysis tool provides a single, golden, trusted signoff solution for timing, signal integrity, power and variation-aware analysis.
What are the inputs of PrimeTime?
PrimeTime output is generated by giving input as netlist file of counter , SDF file of counter (both generated from Design Compiler) and clock period of 2 .
What is timing analysis in VLSI?
Static timing analysis (STA) is a way of evaluating a design's timing performance by testing for timing violations along all conceivable paths. Dynamic simulation, which determines the whole behaviour of the circuit for a given set of input stimulus vectors, is another technique to do timing analysis.
What is DMSA in VLSI?
Distributed Multi-Scenario Analysis (DMSA) allows multiple scenarios to be run concurrently, which reduces wall clock time and produces a single comprehensive timing report.
What is SDF file in VLSI?
Standard Delay Format (SDF) is an IEEE standard for the representation and interpretation of timing data for use at any stage of an electronic design process.
Is prime time one or two words?
prime′ time′ n. the hours, generally between 7 and 11 p.m., considered to have the largest television audience of the day.
What is path delay in VLSI?
Path delay. Path delay is also known as pin to pin delay. It is the delay from the input pin of the cell to the output pin of the cell.
What is skew in VLSI?
It's a difference between the clock arrival time across the chip. It's the time delta between the actual and expected arrival time of a clock signal. Clock skew is the timing differences between signals in a clock distribution system. Variation of arrival of clock at destination points in the clock Network.
What is clock gating in VLSI?
Clock gating is a power-saving feature in semiconductor microelectronics that enables switching off circuits. Many electronic devices use clock gating to turn off buses, controllers, bridges and parts of processors, to reduce dynamic power consumption.
What is Crosstalk in VLSI?
Crosstalk is a phenomenon, by which a logic transmitted in vlsi circuit or a net/wire creates undesired effect on the neighbouring circuit or nets/wires, due to capacitive coupling. Refer to the digram below to get a clear picture on the effect of coupling capacitance on functionality and timing of VLSI circuits.
What is Mmmc in VLSI?
Multi-mode multi-corner (MMMC) analysis refers to performing STA across multiple operating modes, PVT corners and parasitic interconnect corners at the same time.
What is margin in uncertainty in VLSI?
Setup Uncertainty: Pre-Cts = Jitter + Skew + Extra setup margin. Cts = Jitter + Extra setup margin. Hold Uncertainty: Pre-Cts = Skew + Extra hold margin.
What are primetime hours on TV?
NBC, CBS, and ABC have provided national programming from 8 p.m. to 11 p.m. — aka primetime — since the early days of television.
What is your prime time?
Here's the gist: Your biological prime time refers to a period of time when you feel your most focused and energized. For example, maybe you have the easiest time zoning in on your tasks between 8am and noon. That's your biological prime time. You might also hear it referred to as your “golden hours.”
What is considered prime time TV?
Traditional primetime is eight to 11 o'clock at night, Monday through Friday, but Nielsen finds that more Americans tune in from 9:15pm to 9:30pm than any other period during primetime. The tail end of primetime—10:45 to 11:00pm—is when the fewest viewers use their televisions.
STA – VLSI Tutorials
Basics -Setup and Hold time (coming soon)Recovery and Removal time (coming soon)Time borrowing in Latches (coming soon)Synthesis Timing constraints -How to constrain the input, output and internal path of a single clock designHow to constrain the input and output of a single clock design in different scenariosHow to constrain multiple synchronous clock designHow to constrain…
What is Static Timing Analysis in VLSI? - ChipEdge VLSI Training Company
Static timing analysis (STA) is a way of evaluating a design’s timing performance by testing for timing violations along all conceivable paths. Dynamic simulation, which determines the whole behaviour of the circuit for a given set of input stimulus vectors, is another technique to do timing analysis.
What is a negative unate timing arc?
A negative unate timing arc is one where a rising transition on an input causes the output to have a falling transition (or not to change) and a fall ing transition on an input causes the output to have a rising transition (or not to change). For example, the timing arcs for NAND and NOR type cells are negative unate.See Figure (b)
What unit is used for timing reports?
Most timing reports use ns for the time unit. However, you can use the PrimeTime commandreport_unitsto report all theunits, such as capacitance, resistance, time, and voltage units used by the design.
Can timing arcs be used to invert polarity?
One can take advantage of the non-unateness property of a timing arc, such as when an xor cell is used, to invert the polarity of a clock. See the exaample below (figure). If input POLCTRL is a logic-0, the clock DDRCLK on output of the cell UXOR0 has the same polarity as the input clock MEMCLK. If POLCTRL is a logic-1, the clock on the output of the cell UXOR0 has the opposite polarity as the input clock MEMCLK.
What is static timing analysis?
Static Timing Analysis (STA) is one of the techniques to verify design in terms of timing. This kind of analysis doesn’t depend on any data or logic inputs, applied at the input pins. The input to an STA tool is the routed netlist, clock definitions (or clock frequency) and external environment definitions. The STA will validate whether the design could operate at the rated clock frequency, without any timing violations. Some of the basic timing violations are setup violation and hold violation
How many timing paths does a NAND gate have?
The above example illustrates for 2-input NAND gate, it has two timing paths.More complex logic gates will have even more timing paths, e.g. 10 input MUX. Thus, the delay between Sender and Receiver is not constant, but will have range of values, as shown below.
Does data change between hold time H and M?
The data is not expected to change between hold time ‘H’ to ‘m’ and ‘M’ to (T clk – Setup time ‘S’). Data changes somewhere between ‘m’ and ‘M’, and becomes stable after that.
Which has higher precedence, POCV or LVF?
If both data types are present in the design then by default the file with single POCV coefficient has higher precedence than POCV slew-load table or LVF format file.
Which is more realistic, OCV or POCV?
POCV is more realistic approach than that of OCV and AOCV. This method does not use distance and depth based derate factor. It uses delay sigma to model the delay variation of the cell. An advantage of POCV over AOCV is also that it reduces the slack pessimism between Graph Based Analysis (GBA) and Path Based Analysis (PBA).
What is POCV advance variation?
POCV advance variation technology provides statistical benefits without the overhead of expansive statistical library characterization. In POCV instead of applying the specific derate factor to a cell, cell delay is calculated based on delay variation (σ) of the cell. In POCV it is assumed that the normal delay value of a cell follows the normal distribution curve. An example of a normal distribution curve and standard deviation of data from the mean is shown in figure-8.
Why is AOCV derate applied only on clock path?
In clock only mode, AOCV derate is applied only on the clock path so it has reduced effort and a fast runtime. Whereas in clock and data mode, AOCV derate is applied on full design. AOCV analysis requires an AOCV derate table for all the cells. Due to reduces timing pessimism in AOCV, it has been observed that huge time violation have fixed when we moved to clock only AOCV derate mode and the violations have further reduced when we moved to clock and data AOCV mode.
What is a negative unate timing arc?
A negative unate timing arc is one where a rising transition on an input causes the output to have a falling transition (or not to change) and a fall ing transition on an input causes the output to have a rising transition (or not to change). For example, the timing arcs for NAND and NOR type cells are negative unate.See Figure (b)
What unit is used for timing reports?
Most timing reports use ns for the time unit. However, you can use the PrimeTime commandreport_unitsto report all theunits, such as capacitance, resistance, time, and voltage units used by the design.
Can timing arcs be used to invert polarity?
One can take advantage of the non-unateness property of a timing arc, such as when an xor cell is used, to invert the polarity of a clock. See the exaample below (figure). If input POLCTRL is a logic-0, the clock DDRCLK on output of the cell UXOR0 has the same polarity as the input clock MEMCLK. If POLCTRL is a logic-1, the clock on the output of the cell UXOR0 has the opposite polarity as the input clock MEMCLK.