What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Functions of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum The rough endoplasmic reticulum plays a number of roles within the cell, largely associated with protein synthesis. Polypeptides are synthesized, modified, folded into their correct 3-D shape and sorted towards an organelle or marked for secretion.
How are proteins assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum?
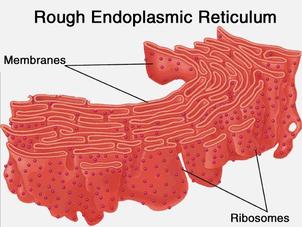
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough) Proteins are assembled at organelles called ribosomes. When proteins are destined to be part of the cell membrane or exported from the cell, the ribosomes assembling them attach to the endoplasmic reticulum, giving it a rough appearance.
Where is the endoplasmic reticulum found in a cell?
The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum occurs in most eukaryotic cells, but is absent from red blood cells and spermatozoa . There are two types of ER: rough endoplasmic reticulum ( RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum ( SER ).
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Electron micrograph showing smooth ER (arrow) in mouse tissue, at 110,510× magnification. In most cells the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (abbreviated SER) is scarce. Instead there are areas where the ER is partly smooth and partly rough, this area is called the transitional ER.

What proteins does the rough ER produce?
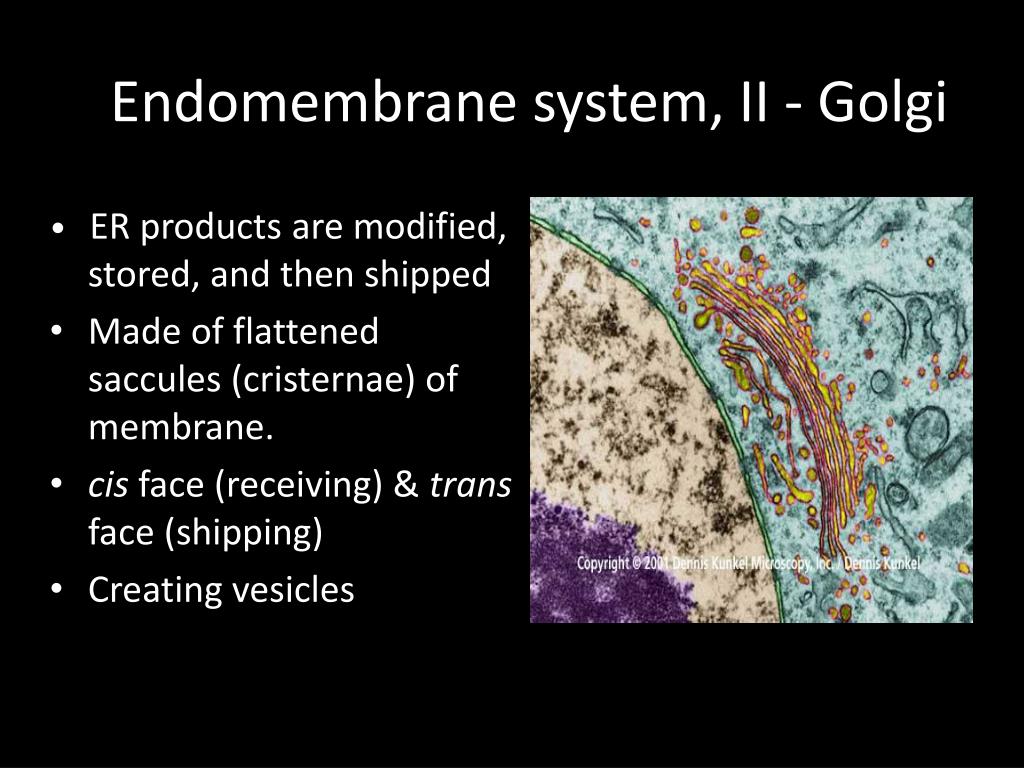
Proteins synthesized by the rough ER include the prominent milk protein casein, and whey proteins. These proteins are packaged into secretory vesicles or large micelles and travel through the Golgi network before fusing with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents into milk ducts.
Where is the rough endoplasmic reticulum produced?
The RER is also located near the Golgi apparatus, which transports, modifies, and packages proteins for delivery to targeted destinations. Many proteins that are synthesized in the RER are packaged into vesicles and transported to the Golgi apparatus.
Which of the following is a function of the rough ER?
The major function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum is protein synthesis and their folding into proper quaternary structures. The major functions of the Golgi bodies involve modifying, sorting, and packaging of proteins produced by the ribosomes.
Is rough endoplasmic reticulum in plant and animal cells?
There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER). Both types are present in plant and animal cells. The two types of ER often appear as if separate, but they are sub-compartments of the same organelle.
Where are proteins produced other than on ribosomes?
The mitochondria that is a yes. The mitochondria can make some of its own proteins. So our only correct answer here is letter D. The mitochondria.
Does the rough ER make ribosomes?
Narration. The endoplasmic reticulum can either be smooth or rough, and in general its function is to produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has on it ribosomes, which are small, round organelles whose function it is to make those proteins.
Where is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum located?
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum like the rough endoplasmic reticulum is connected to the nuclear envelope. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum comprises tube-like structure located near the cell periphery. These tubules or tubes sometimes branch forming a network that is reticular in appearance.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside a cell through which proteins and other molecules move.
Why is the endoplasmic reticulum engorged?
They're retained and the endoplasmic reticulum becomes engorged because it seems to be constipated, in a way, ...
Which organelle is a workhorse in producing proteins and substances needed by the rest of the cell?
So the endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that's really a workhorse in producing proteins and substances needed by the rest of the cell. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
Endoplasmic reticulum, a continuous membrane system in eukaryotic cells that plays an important role in the biosynthesis, processing, and transport of proteins and lipids. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Read More on This Topic. cell: The rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Which type of reticulum lacks ribosomes?
This feature distinguishes it superficially and functionally from the other major type of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER), which lacks ribosomes and is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids. RER occurs in both animal and plant cells. endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum, a continuous membrane ...
What is the RER in eukaryotic cells?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), series of connected flattened sacs, part of a continuous membrane organelle within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, that plays a central role in the synthesis of proteins.
Where are secretory proteins released?
Some proteins, such as secretory proteins, which are released by cells, are packaged in vesicles and move to the Golgi apparatus. Other proteins remain in the ER, where they carry out their specified functions. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
Why is the rough ER called the rough ER?
Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, which is due to the ribosomes attached to its outer (cytoplasmic) surface. Rough ER lies immediately adjacent to the cell nucleus, and its membrane is continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. The ribosomes on…
What happens to a protein as it grows?
As the protein grows, if it contains a signal sequence at its amino-terminal end, it will become bound to a signal recognition particle, which carries the ribosome to the RER membrane. Once bound to the RER, the signal recognition particle dissociates, and protein translation continues.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and flattened sacs that serve a variety of functions in plant and animal cells . The two regions of the ER differ in both structure and function. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes.
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum serves as a transitional area for transport vesicles. It also functions in carbohydrate and lipid synthesis. Cholesterol and phospholipids are examples.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
It plays a major role in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and lipids. The ER produces transmembrane proteins and lipids for its membrane and many other cell components including lysosomes, secretory vesicles, ...
How are proteins sent to the Golgi apparatus?
Some proteins are sent to the Golgi apparatus by special transport vesicles. After the proteins have been modified in the Golgi, they are transported to their proper destinations within the cell or exported from the cell by exocytosis .
What is the smooth ER?
Typically, the smooth ER is a tubule network and the rough ER is a series of flattened sacs. The space inside of the ER is called the lumen. The ER is very extensive extending from the cell membrane through the cytoplasm and forming a continuous connection with the nuclear envelope. Since the ER is connected with the nuclear envelope, ...
Which structure helps support the cell and aids in organelle movement?
Cytoskeleton: a network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm that helps support the cell and aids in organelle movement.
Which protrusions from a cell aid in movement and cellular locomotion?
Cilia and flagella: protrusions from a cell that aid in movement and cellular locomotion.
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER rough) is part of the cell’s endomembrane system and a subset of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This organelle is mainly concerned with the synthesis, folding, and modification of proteins, especially those that have to be delivered to different organelles within the cell or secreted by the cell. The rough ER is also involved in the cell’s response to unfolded proteins and plays a role in the induction of apoptosis due to its close interaction with mitochondria.
What happens to the rough ER after the cytoskeleton is rebuilt?
If the microtubule structure is temporarily disrupted, the ER network collapses and only re-forms after the cytoskeleton has been rebuilt. Changes in the microtubule polymerization pattern are also reflected in changes in ER morphology. Furthermore, when ribosomes separate from the rough endoplasmic reticulum layers, these structures can disintegrate and form tubular cisterns.
What is the role of the rough ER proteome?
The rough ER proteome reflects its specific role within the cell. It contains enzymes involved in RNA metabolism that bind and modify RNA. This is necessary since the organelle is involved in the translation of RNA into protein. It also contains proteins that recognize various signal sequences within a growing polypeptide and aid in its translocation. The glycosylation enzymes and proteins that act as molecular chaperones that ensure proper folding of the synthesized polypeptides are also important proteins within this organelle. Occasionally, ER induces apoptosis in response to excess protein deployed within the cell. This function is mediated in consort with the mitochondria.
Why are some proteins removed from the system?
Despite these mechanisms to ensure that proteins are correctly folded, some must be removed from the system, either due to translation errors or genetic mutations that lead to the production of defective proteins . This is accomplished through quality control systems within the ER, which “check” the newly synthesized proteins. If the polypeptide does not fold in its native state, the molecular chaperones reattach the polypeptide and make another attempt to fold the protein into its correct form. If repeated attempts fail, misfolded proteins can be exported to the cytosol and removed by ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation by the proteasome.
What are the edges of the ER panels?
The edges of the ER panels have a strong curvature that must be stabilized. Proteins are known as reticules and DP1 / Yop1p play an important role in this stabilization. These proteins are integral membrane proteins that form oligomers to form the lipid bilayer. In addition, they also use a structural motif that is inserted into a membrane sail and reinforces its curvature. These two classes of proteins are superfluous because the overexpression of one protein seems to compensate for the lack of the other protein.
What is the role of rough ER in the digestive system?
Thus, the rough ER is prominently represented in liver cells that secrete serum albumin, cells of the digestive system that secrete enzymes, endocrine cells that synthesize and secrete protein hormones (such as insulin), and in cells that they form the proteins of the extracellular matrix. . Rough ER protein synthesis is also important for membrane-bound proteins, especially those such as G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which contain multiple hydrophobic segments and cross the membrane more than once by hairpin bends in their structure. The precise role of ER-resident proteins and translocons in coping with the complex task of translating these proteins is not fully understood.
What is the rough ER?
Rough ER is characterized by the presence of membrane-bound ribosomes, which give it a distinctive appearance under the microscope. These ribosomes look like studs and distinguish the organelle from the smooth sections of the ER. Some proteins are also synthesized from ribosome chains called polysomes. The rough ER can also be identified by its morphology: it often consists of tortuous, flattened sac-like structures that arise near the nucleus. The lumen of the rough ER is adjacent to the perinuclear space and the membranes of the rough ER are connected to the outer nuclear membrane.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells contain an ER. In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: ...
Who introduced the term "endoplasmic reticulum"?
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, Porter and colleagues Helen P. Thompson and Frances Kallman introduced the term endoplasmic reticulum to describe the organelle. Porter later worked with Romanian-born American cell biologist George E. Palade to elucidate key characteristics of the ER. Kara Rogers.
What is the ER in eukaryotic cells?
All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. Differences in certain physical and functional characteristics distinguish the two types of ER, known as rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, ...
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the liver?
In cells of the liver, it contributes to the detoxification of drugs and harmful chemicals. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a specialized type of smooth ER that regulates the calcium ion concentration in the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
Why is the rough ER called the rough ER?
Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, which is due to the ribosomes attached to its outer (cytoplasmic) surface. Rough ER lies immediately adjacent to the cell nucleus, and its membrane is continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope.
What are the two types of ER?
Differences in certain physical and functional characteristics distinguish the two types of ER, known as rough ER (RER) and smooth ER (SER). Ribosomes on RER, which give RER its rough appearance, specialize in the synthesis of proteins that possess a signal sequence that directs them specifically to the ER for processing.
What percentage of the membrane content of an animal cell is ER?
In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell.
Where is the endoplasmic reticulum found?
The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa .
Where are the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum located?
The membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum forms large double-membrane sheets that are located near, and continuous with , the outer layer of the nuclear envelope. The double membrane sheets are stacked and connected through several right- or left-handed helical ramps, the "Terasaki ramps", giving rise to a structure resembling a multi-story car park. Although there is no continuous membrane between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, membrane-bound transport vesicles shuttle proteins between these two compartments. Vesicles are surrounded by coating proteins called COPI and COPII. COPII targets vesicles to the Golgi apparatus and COPI marks them to be brought back to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum works in concert with the Golgi complex to target new proteins to their proper destinations. The second method of transport out of the endoplasmic reticulum involves areas called membrane contact sites, where the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles are held closely together, allowing the transfer of lipids and other small molecules.
What are the dark circles in the endoplasmic reticulum?
Dark small circles in the network are mitochondria.
Which type of reticulum is most abundant in gonad cells?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is especially prominent in cells such as hepatocytes. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes and functions in lipid synthesis but not metabolism, the production of steroid hormones, and detoxification. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is especially abundant in mammalian liver and gonad cells.
What is the function of the phospholipid membrane?
The functions of the endoplasmic reticulum can be summarized as the synthesis and export of proteins and membrane lipids, but varies between ER and cell type and cell function.
What are dark circles in the ER?
Dark small circles in the network are mitochondria . The endoplasmic reticulum ( ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( RER ), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum ( SER ).
How long is the animation of the secretory pathway?
A 2-minute animation showing how a protein destined for the secretory pathway is synthesized into the rough endoplasmic reticulum, which appears at the upper right approximately halfway through the animation.