
The Profit Split Method examines the terms and conditions of these types of controlled transactions by determining the division of profits that independent enterprises would have realized from engaging in those transactions. An example of this method is shown in this image: In the above example, we see two comparable joint ventures.
What are the different types of profit split?
It can be applied in three different ways: the comparable profit split method, contribution profit split method, and residual profit split method. Companies select an approach based on how the transaction is structured and the data available.
What is the difference between contribution profit split and residual profit split?
The residual profit split method is generally preferred over the contribution profit split method owing to two reasons. Firstly, this method breaks up the complicated issue of transfer pricing into two simpler steps easing the work.
What is profit split method (PSM)?
The Profit Split Method (PSM) With An Example Posted on: March 1, 2019 The profit split method (PSM) is one of the five transfer pricing methods, which are used to ensure that transactions between related companies are carried out at “arm’s length,” or a fair market price.
How is a fair profit split calculated?
A fair profit split is then determined based on those contributions. The residual profit split method looks at total profits, removes the profits made by the routine functions of both parties—computed using the comparable profits method —and residual profits are split, generally based on each party’s investments and relative spending.
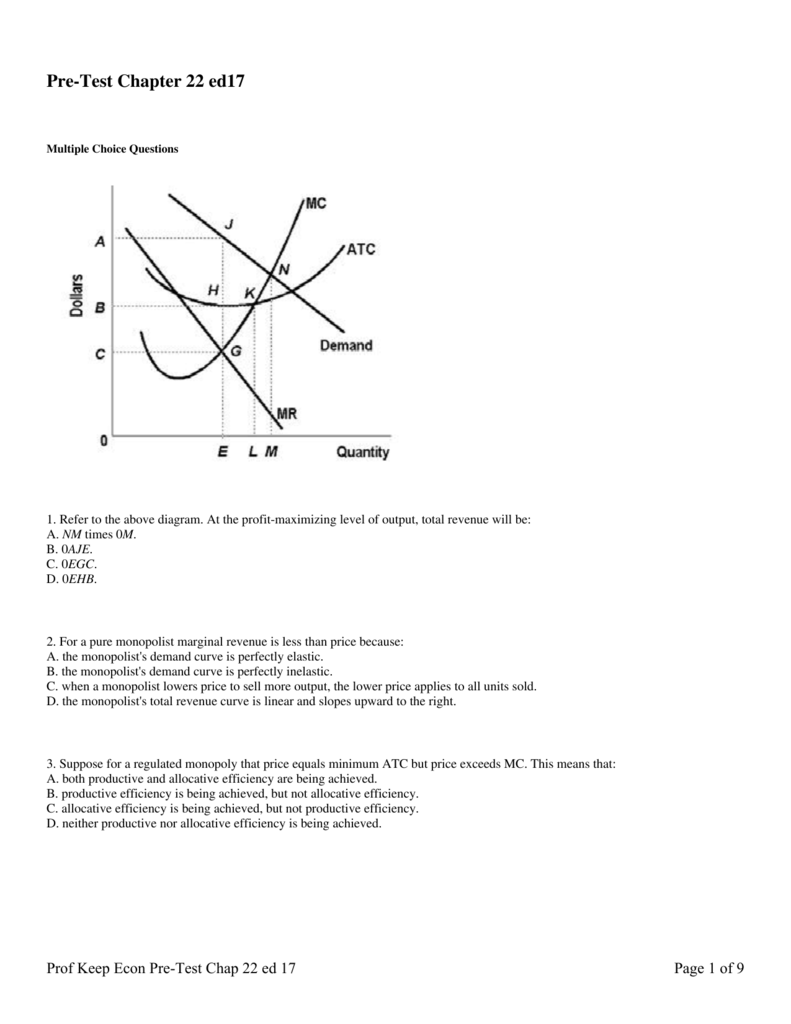
What is profit split method?
A method that identifies the relevant profits to be split for of associated enterprises from a controlled transaction and then splits those profits between the associated enterprises on an economically valid basis that approximates the division of profits that would have been agreed at arm's length.”
What is profit split analysis royalty rate?
Profit split – rule of thumb One of the most widely cited is the 25% rule, which states that in licensing transactions the licensee should pay a royalty to the licensor equal to about 25% of the licensee's pretax profit from exploiting the licensed intangible.
What are the different methods of transfer pricing?
Here are five widely used transfer pricing methods your business should consider.Comparable Uncontrolled Price. ... Cost-Plus. ... Resale-Minus. ... Transactional Net Margin (TNMM) ... Profit Split.
What is routine profit?
“Routine” profit is the profit a third party would expect to earn for performing a particular set of functions and activities on an outsourcing basis.
What is the 25% rule licensing?
The “25 percent rule” is a general rule of thumb that suggests, as a starting point in a negotiation, that a licensee would pay 25 percent of its expected profits as a royalty for products that incorporate the licensed intellectual property (IP).
What is the 25 percent rule?
The 25% rule is the concept that a local government's long-term debt should not exceed 25% of its annual budget. Any debt beyond this threshold is considered excessive and poses a potential risk, as the municipality may have trouble servicing the debt.
What are the three types of transfer pricing?
Generally, companies can determine transfer prices three different ways: market-based transfer prices, cost- based transfer prices, and negotiated transfer prices.
What is CPM in transfer pricing?
The Comparable Profits Method (“CPM”) is a common method for establishing an amount charged in a controlled transaction based on objective measures of profitability. The CPM is a specified transfer pricing method that compares the Taxpayer's operating results with those of uncontrolled taxpayers.
What is arm's length price?
The price at which a willing buyer and a willing unrelated seller would freely agree to transact or a trade between related parties that is conducted as if they were unrelated, so that there is no conflict of interest in the transaction.
What is amount a Pillar 1?
Amount A of Pillar One introduces a new taxing right over a portion of the profit of large and highly profitable enterprises for jurisdictions in which goods or services are supplied or consumers are located. Comments on the consultation documents are due by 10 June 2022.
What are routine returns?
The routine return represents the profit a business might have made if it did not have access to unique IP and other intangible assets.
Who does Pillar 2 apply to?
Pillar 2 applies to the constituent entities (CEs), i.e., subsidiaries included in the consolidation and permanent establishments (PEs), including branch operations and entities that are disregarded for US income tax purposes.
How do you split band royalties?
We recommend to split royalties and rights evenly between each band member to keep things easy. In hip hop, the producer will usually request 50%, while the other top liners will split the remaining 50%.
How are streaming royalties split?
Overall, for every $1 a streaming service pays in royalties, rights holders collectively earn about 73 cents, creators take a little over 25 cents and the PRO gets a little over 1 cent. Breaking that down for recorded music revenue, the artist receives about 16 cents and the label takes about 64 cents.
How do you split royalties with a featured artist?
If the artist has no money up front to pay, then it's typically a 50/50 split of royalties – and usually ownership. But if the producer is going to get ownership then they should sign something saying that the Artist can admin the track.
What is relief from royalty method?
The Relief from Royalty Method is one of the business valuation methods used for the valuation of some intangible assets such as trademarks and trade names. The method is based on the premise that the only value that a purchaser of the assets receives is the exemption from paying a royalty for its use.
Why should profits be split?
Profits should be split on an economically valid basis that reflects the relative contributions of the parties to the transaction and thus approximates the division of profits that would have obtained at arm’s length.
Why is profit splitting challenging?
It is challenging in profits split as it is subjective to determine the relevant profits to be split and what is the profit splitting factors.
Which method is most appropriate for determining the compensation for the products sold by Company A to Company B?
Under these circumstances, the PSM is likely to be the most appropriate method for determining the compensation for the products sold by Company A to Company B as both parties make unique and valuable contributions to the transaction.
Is economic risk separately assumed?
Various economically significant risks in relation to the transaction are separately assumed by the parties, but those risks are so closely inter-related and/or correlated that the playing out of the risks of each party cannot reliably be isolated.
Should my company apply the Profit split method?
One or more of the following indicators can indicate the need to consider the PSM:
What is profit split method?
Both variations rely on the contribution of the parties to a transaction to the combined operating profit or loss associated with the business activity in question.
Is profit allocated to any particular member of a controlled group necessarily limited to the total operating profit of the group?
The profit allocated to any particular member of a controlled group is not necessarily limited to the total operating profit of the group from the relevant business activity. For example, in a given year, one member of the group may earn a profit while another member incurs a loss.
When to use the Profit Split Method?
The Profit Split Method works only under specific circumstances and therefore, one must firstly brainstorm on the following points, before proceeding with this method, to ensure the viability of its results:
What basis is profit split?
The basis on which the profit may be split would vary according to transaction depending on its nature. Where transactions involve heavy investments and form the key factor of the transaction, the profit may be split according to the amount invested.
What is residual profit?
The balance profits remaining after distribution are known as the Residual Profits which are distributed amongst the associated enterprises based on the facts and circumstances of the transactions. The residual profits can be allocated to the enterprise providing the tangible or intangible assets necessary if the same is held by one enterprise only. Any similar reasonable basis may be adopted for the allocation of special profits or the residual profits at step 2. These profits combined with the costs incurred form the Transfer Price.
Why is residual profit split preferred?
The residual profit split method is generally preferred over the contribution profit split method o wing to two reasons. Firstly, this method breaks up the complicated issue of transfer pricing into two simpler steps easing the work. Where the first step analyses the comparables and decides the basic returns, the second step considers special points and value of tangible or intangible assets to determine the distribution of residual profits. The second reason is the potential conflict if any raised by the tax authorities, the same is often reduced to the residual profits only, and thereby, a comparatively small figure becomes the controversial point of a tax arbitration, instead of encircling the entire transaction.
What is step 5 of residual profit split?
Step 5 – Distribute the contribution profit, or the basic and special profits in case of residual profit split method, according to the basis of distribution determined in stage 3.
What is contribution in project?
The contribution is the gross amount of profits earned before considering the fixed expenses. In case of a joint project performed by associated enterprises, the total contribution of the project can be arrived at after considering the sale value and the directly attributable expenses. These expenses may also be the ones which have been incurred jointly by the enterprises involved. At the contribution stage the profit is split and the same can be added to the share of direct costs to arrive at the Transfer Price.
How many stages of profit splitting?
There are two stages at which the profit may be split resulting into two different variations of the method – by analysis of contribution profit or by analysis of residual profits.
What is profit split?
The profit split method evaluates whether the allocation of the combined operating profit or loss attributable to one or more controlled transactions is arm's length by reference to the relative value of each controlled taxpayer 's contribution to that combined operating profit or loss. The combined operating profit or loss must be derived from the most narrowly identifiable business activity of the controlled taxpayers for which data is available that includes the controlled transactions (relevant business activity).
Is direct allocation made?
To the extent direct allocations are not made, the reliability of the results derived from the application of this method is reduced relative to the results of a method that requires fewer allocations of costs, income, and assets.
Does the allocation of income to the controlled taxpayer's routine contributions reflect profits attributable to each controlled taxpayer's?
The allocation of income to the controlled taxpayer 's routine contributions will not reflect profits attributable to each controlled taxpayer 's contributions to the relevant business activity that are not routine (nonroutine contributions).
What is profit split?
The Profit Split Method examines the terms and conditions of these types of controlled transactions by determining the division of profits that independent enterprises would have realized from engaging in those transactions.
Which method is preferred over transactional profit?
A taxpayer should select the most appropriate method. In general, the traditional transaction methods is preferred over the transactional profit methods and the CUP method over any other method.
What Transfer Pricing Methods Are There?
The good thing about transfer pricing is that the principles and practices are quite similar all around the world. The OECD Transfer Pricing Guidelines ( OECD Guidelines) provide 5 common transfer pricing methods that are accepted by nearly all tax authorities.
What is transactional profit?
The transactional profit methods don’t measure the terms and conditions of actual transactions. In fact, these methods measure the net operating profits realized from controlled transactions and compare that profit level to the profit level realized by independent enterprises that are engaged in comparable transactions.
Why are transactional profit methods less precise than traditional transaction methods?
The reason is that application of the traditional transaction methods, which is preferred, requires detailed information and in practice this information is not easy to find. In short:
What is traditional transaction method?
Traditional transaction methods measure terms and conditions of actual transactions between independent enterprises and compares these with those of a controlled transaction.
Which method is preferred for transfer pricing?
However, if a traditional transaction method and a transactional profit method are equally reliable, the traditional transaction method is preferred.
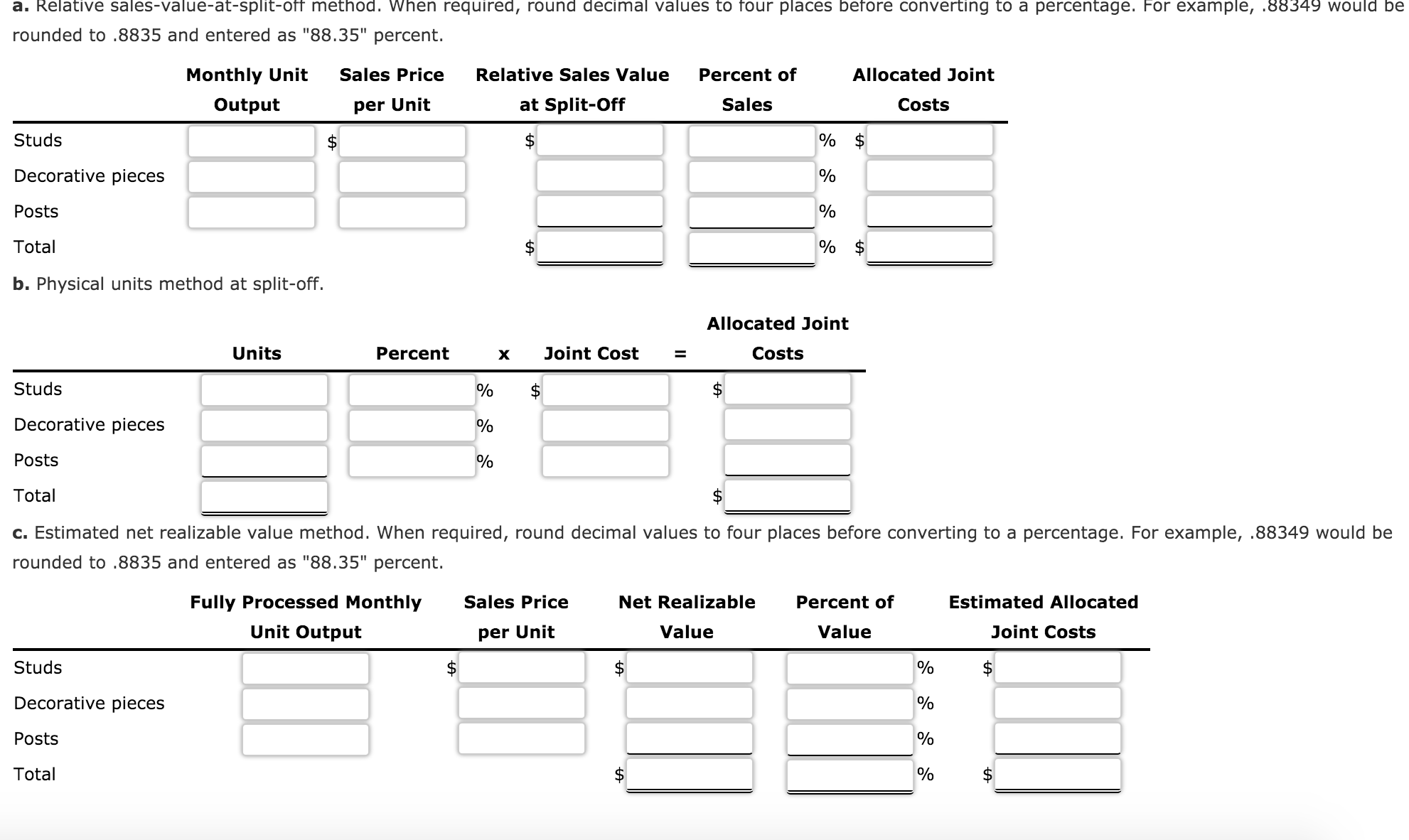
What Is The Profit Split Method?
Variations of Profit Split Method
- There are two stages at which the profit may be split resulting into two different variations of the method – by analysis of contribution profit or by analysis of residual profits. 1. Contribution Profit Split Method– The contribution is the gross amount of profits earned before considering the fixed expenses. In case of a joint project performed by associated enterprises, the total contribution o…
Computation of Arm’S Length Price Under The Profit Split Method
- Step 1 – Determine the Sale Price of the transaction and the associated direct costs and indirect costs incurred by each enterprise jointly or individually. The difference between the sale price and joint costs or direct costs would provide the contribution. Step 2 – Determine the variation of profit split to be used. In the case of contribution profit split, the profit would have to be split at o…
Advantages and Disadvantages of The Profit Split Method
- Advantages: 1. The method is suitable when the transactions are highly integrated and the transfer price cannot be decided on the basis of one-sided approach. 2. It ensures that the transfer price does not result in extreme results for either of the entities if the residual profit split variation is followed. 3. This method carefully deals with the synergies involved in the transactio…
When to Use The Profit Split Method?
- The Profit Split Method works only under specific circumstances and therefore, one must firstly brainstorm on the following points, before proceeding with this method, to ensure the viability of its results: 1. Complex Integrated Transactions–The Profit Split Method will have to be used when the transactions are highly interconnected and it is practically impossible to evaluate the transa…