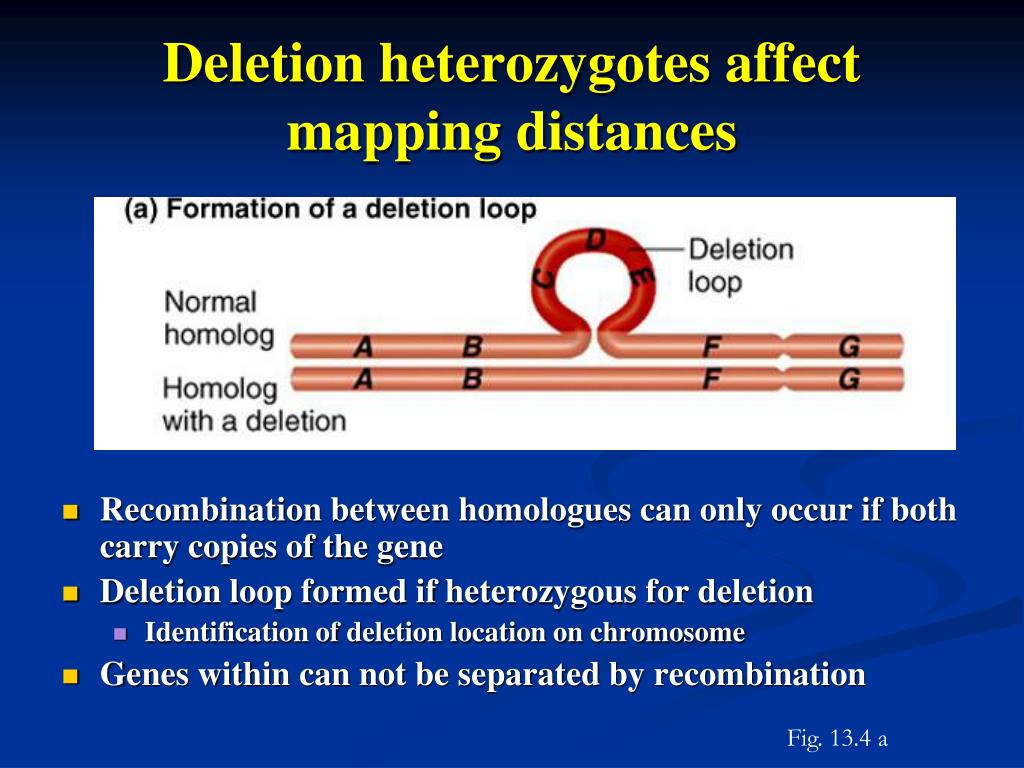
How is recombination frequency used in genetic mapping?
Genetic mapping exploits the recombination frequency between genes to measure the relative distance between genes. In bacterial genetics, the probability that recombination did not occur between genes is usually determined. If recombination does not occur between two genes, the genes will be coinherited.
What is recombination of genes?
Recombination is enhanced by the phenomenon of crossing over, in which gene sequences called linkage groups are disrupted, resulting in an exchange of segments between paired chromosomes that are undergoing separation.
When does recombination take place?
Recombination takes place during meiosis, when maternal and paternal genes are regrouped in the formation of gametes (sex cells).
Why is genetic recombination important in meiosis?
Genetic recombination is a programmed feature of meiosis in most sexual organisms, where it ensures the proper segregation of chromosomes. Because the frequency of recombination is approximately proportional to the physical distance between markers, it provides the basis for genetic mapping.
How do you read a recombination map?
5:519:49Genetic Recombination and Gene Mapping - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's say the frequency of recombination is less than that that means the genes are closer togetherMoreLet's say the frequency of recombination is less than that that means the genes are closer together what if the frequency of recombination is greater than that means that it's farther apart.
What recombination means?
Recombination is a process by which pieces of DNA are broken and recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms.
What is recombination and example?
Recombination occurs when two molecules of DNA exchange pieces of their genetic material with each other. One of the most notable examples of recombination takes place during meiosis (specifically, during prophase I), when homologous chromosomes line up in pairs and swap segments of DNA.
What is linkage mapping?
A linkage map (also known as a genetic map) is a table for a species or experimental population that shows the position of its known genes or genetic markers relative to each other in terms of recombination frequency, rather than a specific physical distance along each chromosome.
What is the importance of recombination?
Genetic recombinations provide a constant DNA homogenization within the species and, therefore, the species integrity as an elementary structure responsible for the preservation and rise in the level of ecological stability of organisms in evolving lineages.
What is another name for recombination?
What is another word for recombination?reunificationreintegrationreadditionreassimilationrejoiningreunitingrealliancerecombiningremergingreunion6 more rows
What are the 2 types of recombination?
What Are the Types of Recombination?Homologous recombination – occurs during meiosis, when a part of the chromosome is exchanged between two homologous chromosomes.Non-homologous recombination – exchange of genetic information between dissimilar chromosomes.More items...
What are the three types of recombination?
There are three types of recombination; Radiative, Defect, and Auger. Auger and Defect recombination dominate in silicon-based solar cells. Among other factors, recombination is associated with the lifetime of the material, and thus of the solar cell.
What are two causes of recombination?
There are two distinct genetic mechanisms that lead to recombinant offspring: independent assortment and crossing over.
What is the purpose of genetic mapping?
Genetic mapping provides a powerful approach to identify genes and biological processes underlying any trait influenced by inheritance, including human diseases.
What is linkage and recombination?
In linkage, two or more genes linked together are always inherited together in the same combination for more than two generations, whereas in recombination the genetic material is exchanged between different organisms which leads to the production of offsprings with the combination of traits.
What is gene mapping with example?
Gene mapping refers to the process of determining the location of genes on chromosomes. Today, the most efficient approach for gene mapping involves sequencing a genome and then using computer programs to analyze the sequence to identify the location of genes.
What do you mean by recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA technology involves using enzymes and various laboratory techniques to manipulate and isolate DNA segments of interest. This method can be used to combine (or splice) DNA from different species or to create genes with new functions. The resulting copies are often referred to as recombinant DNA.
What causes recombination of genes?
In eukaryotes, recombination during meiosis is facilitated by chromosomal crossover. The crossover process leads to offspring having different combinations of genes from those of their parents, and can occasionally produce new chimeric alleles.
How does DNA recombination work?
General recombination (also called homologous recombination) allows large sections of the DNA double helix to move from one chromosome to another, and it is responsible for the crossing-over of chromosomes that occurs during meiosis in fungi, animals, and plants.
What is recombination in molecular biology?
Recombination is the exchange of genetic information between two chromosomes or between two parts of the same chromosome. Recombination is mainly of four types: Homologous recombination – occurs during meiosis, when a part of the chromosome is exchanged between two homologous chromosomes.
What is a recombination frequency of 1%?
A recombination frequency of 1% is equivalent to 1 genetic map unit or centimorgan (cM), named after Morgan, who described crossover of genes. The linkage map is not a physical map of genes. Rather, it provides a rough estimate of the physical distance. The relation between the distance of genes and recombination frequency is as follows:
How does the position of genes affect the inheritance of a chromosome?
The position of the genes in a chromosome exerts vital effect in its inheritance. Genes on different chromosomes or located farer on a same chromosome are said to be unlinked and assort independent of each other, known as independent assortment. On the contrary, location of genes on the same chromosome causes them to be linked and inherited together, known as genetic linkage. The lesser the distance between 2 genes, the lesser the chances of recombination of them. Hence, the proportion of recombinant offspring gives an idea of the distance between the 2 genes.
What is recombination in genetics?
Recombination, in genetics, primary mechanism through which variation is introduced into populations.
How does recombination contribute to genetics?
Laboratory study of recombination has contributed significantly to the understanding of genetic mechanisms, allowing scientists to map chromosomes, identify linkage groups, isolate the causes of certain genetic anomalies, and manipulate recombination itself by transplantation of genes from one chromosome to another.
What is the primary mechanism through which variation is introduced into populations?
Recombination, in genetics, primary mechanism through which variation is introduced into populations. Recombination takes place during meiosis, when maternal and paternal genes are regrouped in the formation of gametes (sex cells).
Is recombination rare?
The detection of recombination (exchange of material between chromosomes) or mutation in human families is complicated by questions of paternity. In spite of the large number of families that have been studied, it is an extremely rare occurrence. The paucity of examples may indicate that the recombinant and…
Does recombination ensure constant variability?
Thus, although a normal daughter cell produced in meiosis always receives half of the genetic material contained in the parent cell (i.e., is haploid), recombination acts to ensure constant variability: no two daughter cells are identical, nor are any identical in genetic content to the parent cell. Read More on This Topic.
How many map units are there between A and B genes?
For example: A distance between A and B genes is estimated to be 3.5 map units. It is equal to 3.5 centimorgans or 3.5 % or 0.035 recombination frequency between the genes.
What is the unit of distance in genetics?
The unit of distance in a genetic map is called a map unit (m.u). One map unit is equivalent to one percent of crossing over (Figure 4.). One map unit is also called a centimorgan (cM) in honour of T.H. Morgan. 100 centimorgan is equal to one Morgan (M).
What is the process of crossing over?
Crossing over is a biological process that produces new combination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous pair of chromosomes. The term ‘crossing over’ was coined by Morgan (1912).
What stage of meiosis does crossing over occur?
It takes place during pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis. Usually crossing over occurs in germinal cells during gametogenesis. It is called meiotic or germinal crossing over. It has universal occurrence and has great significance. Rarely, crossing over occurs in somatic cells during mitosis. It is called somatic or mitotic crossing over.
When are homologous chromosomes aligned?
Intimate pairing between two homologous chromosomes is initiated during zygotene stage of prophase I of meiosis I. Homologous chromosomes are aligned side by side resulting in a pair of homologous chromosomes called bivalents. This pairing phenomenon is called synapsis or syndesis. It is of three types,
What organisms cross over?
Crossing over occurs in all organisms like bacteria, yeast, fungi, higher plants and animals. Its importance is
What happens after crossing over chiasma?
After crossing over, chiasma starts to move towards the terminal end of chromatids. This is known as terminalisation. As a result, complete separation of homologous chromosomes occurs. (Figure 3.10)
What is genetic recombination?
Genetic recombination refers to the rearrangement of DNA sequences by the breakage and rejoining of chromosomes or chromosome segments. It also describes the consequences of such rearrangements, that is, the inheritance of novel combinations of alleles in the offspring that carry recombinant chromosomes. Genetic recombination is a programmed feature of meiosis in most sexual organisms, where it ensures the proper segregation of chromosomes. Because the frequency of recombination is approximately proportional to the physical distance between markers, it provides the basis for genetic mapping. Recombination also serves as a mechanism to repair some types of potentially lethal damage to chromosomes.
How does recombination work?
Genetic recombination is the physical breakage, exchange, and rejoining of two DNA molecules. Homologous or general recombination can be mediated by several different pathways in bacteria. Each of these pathways requires the RecA protein to align the DNA molecules between regions of substantial DNA sequence identity. The DNA molecules are broken between random but matching nucleotides, and then the DNA fragments are exchanged and rejoined to form two new combinations of genes. For example, recombination between two DNA molecules with the genotypes a+b and ab+ can yield two recombinant DNA molecules with the genotypes a+b+ and ab. Owing to the efficiency of gene transfer and the ability to work with large populations of bacteria, recombination analysis can be sufficiently sensitive to detect recombination events between adjacent base pairs.
What is a homologous recombination?
Homologous recombination can occur between homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids in mitotic cells as well. In addition, essentially analogous events may take place between homologous sequences that are present at different locations on nonhomologous chromosomes; this is often called ‘ectopic recombination’. Recombination that involves very limited or no hom ology between the interacting DNA sequences is termed illegitimate or nonhomologous recombination. Sometimes, a few matched base pairs (bp) are seen precisely at illegitimate recombination junctions, and these are called microhomologies. An event supported by homologies of 100 bp or more would typically be classified as homologous; a match of 10 bp or fewer would be nonhomologous; and there is evidently a gray area in between.
Why is recombination important?
Because the frequency of recombination is approximately proportional to the physical distance between markers, it provides the basis for genetic mapping. Recombination also serves as a mechanism to repair some types of potentially lethal damage to chromosomes.
How many copies of a chromosome are reduced in a conservative recombination?
In conservative recombination events, the number of copies of the interacting chromosomes or DNA sequences is maintained through the process, while in nonconservative events, two original copies are reduced to one in the product. This distinction can be made for both homologous and nonhomologous recombination.
What is the role of DNA double strand breaks in recombination?
In recent years, DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) have emerged as an important lesion that can initiate and stimulate meiotic and mitotic homologous recombination.
What do vertical bars mean in DNA?
Vertical bars indicate individual chromatids (i.e., DNA mole cules); ovals are centromeres. We imagine two pairs of sister chromatids after premeiotic DNA synthesis that are distinguished by color and by genetic markers at locations A/a and B/b. If meiosis were to proceed without recombination, the markers would segregate 2:2 in linked pairs in ...
What factors play into recombination?
Two factors play into this. The first is the distance of the genes. The second is the location of the recombination breakpoint, which does not always fall inbetween both genes, usually above or below , which can lead to no recombination
Which part of the genome is recombined more often?
Humans tend to have more recombiantion towards the telomere then the centromere. If the genes are the same distance apart, then the one by the telomere is recombined more often
What is the probability of independent recombination?
For independent recombination, the probability is 50%, with all possibilties being 25%. For dependnet assortment, there is a 0% recombination factor, as they always divide together
Does the distance between genes tell what orientation is?
False, while it does give the distance between the genes, it does not say what the orientation might be. However, the more dat one has, the more accurate the placement becomes
