Why refrigeration cycle is called reverse Carnot cycle?
Unlike the Carnot heat engine, the Carnot refrigeration cycle undergoes a process with opposite direction which is referred as reverse carnot cycle (since it under goes path opposite to that of carnot cycle and hence the name reverse carnot cycle).
What does Carnot's ideal cycle mean?
The Carnot Cycle is an ideal cycle which means that did not exist and impossible to construct so, it is just a theoretical concept. The isothermal process says that the temperature is constant but the Carnot Cycle explains there will be heat addition in the isothermal expansion process which is not possible.
Why is reversed Carnot cycle not possible for refrigeration?
This is because that the isentropic process of Carnot cycle requires a high speed of air while the isothermal process of Carnot cycle requires extremely slower speed. This large variation in speed of air is simply not possible. - What are the temperature limitations for refrigeration cycle (Reversed Carnot)?
Why is the reversed Carnot cycle impractical?
- isentropic compression
- isothermal heat rejection
- isentropic expansion
- isothermal heat absorption.
What is Carnot reversible cycle?
A Carnot heat-engine cycle described is a totally reversible cycle. That is, all the processes that compose it can be reversed, in which case it becomes the Carnot heat pump and refrigeration cycle. This time, the cycle remains exactly the same except that the directions of any heat and work interactions are reversed.
What is difference between Carnot cycle and reversed Carnot cycle?
The Carnot Cycle is used to convert the convert the heat into the mechanical work whereas; the Reversed Carnot Cycle (or refrigeration system) is used to absorb the heat from the system and rejects to the surroundings (or environment) to maintain the system cool (which we called refrigeration effect).
Where is reverse Carnot cycle used?
Refrigerators and heat pumps are essentially the same device; they only differ in their objectives. Reversing the Carnot cycle does reverse the directions of heat and work interactions. A refrigerator or heat pump that operates on the reversed Carnot cycle is called a Carnot refrigerator or a Carnot heat pump.
What is reverse power cycle?
Reversed cycles are used either to extract heat from bodies colder than the surroundings (cooling effect), referred to as refrigeration cycles, or to heat spaces by extracting heat from low-temperature sources (heating effect), called heat pump cycles.
What are the limitations of reversed Carnot cycle?
Reversed Carnot refrigeration cycle with liquefaction and vaporization of the refrigerant. There are two major drawbacks to the reversed Carnot cycle with phase-change refrigerant: 1. The adiabatic compression between Tlow and Thigh occurs in the liquid–vapor region, which is why it is called wet compression.
Why is reverse Carnot cycle not feasible?
The Carnot cycle is reversible whereas the real engines are not reversible due to different reasons like friction, heat transfer to the insulating wall etc. In the Carnot cycle, all the reversible processes are extremely slow while real machines work faster.
Which of the following is an example of a reversed Carnot cycle?
A refrigerator operates on Reversed Carnot cycle. What is the power required to drive the refrigerator between temperatures of 42°C and 4°C, if heat at the rate of 2 kJ/s is extracted from the low-temperature region? Q5.
Which of the following components is the reverse Carnot cycle?
Explanation: The reversed Carnot cycle has 4 processes namely, isothermal compression process, isentropic compression process, isentropic expansion process and isothermal expansion process.
Why is the Carnot engine reversible?
In order to approach the Carnot efficiency, the processes involved in the heat engine cycle must be reversible and involve no change in entropy. This means that the Carnot cycle is an idealization, since no real engine processes are reversible and all real physical processes involve some increase in entropy.
How does reverse power work?
Reverse Power Relay is a directional protective relay that prevents/protect the generator from motoring effect (going to reverse direction). It is used where generator runs in parallel with other utility or generator.
What is reverse Joule cycle?
Reversed Joule cycle is also known as Reversed Brayton cycle or Bell Coleman cycle. The working fluid of the Bell Coleman refrigeration cycle is air. This system of refrigeration is used for Air-craft refrigeration and it has lightweight.
Which of the following is an example of a reversed Carnot cycle?
A refrigerator operates on Reversed Carnot cycle. What is the power required to drive the refrigerator between temperatures of 42°C and 4°C, if heat at the rate of 2 kJ/s is extracted from the low-temperature region? Q5.
What is the difference between heat pump and refrigerator?
A refrigeration system cools the external fluid flowing through the evaporator, whereas a heat pump heats the external fluid flowing through the condenser. The main difference between a refrigerator and a heat pump is in the manner of operation regarding cooling or heating.
What is Carnot cycle with diagram?
The Carnot cycle consists of the following four processes: A reversible isothermal gas expansion process. In this process, the ideal gas in the system absorbs qin amount heat from a heat source at a high temperature Thigh, expands and does work on surroundings....T-S Diagram.ProcessΔTΔSIVThigh−Tlow0Full Cycle003 more rows•Aug 15, 2020
What is the process of reversible carnot?
Firstly, the compression process in the reversible Carnot cycle involves the wet compression of the liquid-vapor mixture. In practice, when a reciprocating compressor is used, wet compression is not found suitable. After evaporation of refrigerant, it enters the compressor. Due to the appreciable speed of the compressor, the piston reciprocates so quickly that the vapor-bound liquid may remain in the cylinder, which may cause mechanical damage to the compressor valves and even to the cylinder.
What is a thermodynamic cycle?
Thermodynamic cycles allow the reciprocal conversion in a continuous manner of thermal energy into other kinds of energy. A work-supplying cycle is referred to as the power cycle (Fig. 1 ). Such cycles are traced clockwise and they remove heat from the hot reservoir, supply work, and reject heat to the cold reservoir. A reversed cycle is traced counterclockwise and consumes external work in order to cool the cold reservoir by transferring heat to the high-temperature reservoir ( Fig. 1 ).
What is the reciprocal conversion of thermal energy into other kinds of energy?
Thermodynamic cycles allow the reciprocal conversion in a continuous manner of thermal energy into other kinds of energy. A work-supplying cycle is referred to as the power cycle ( Fig. 1 ). Such cycles are traced clockwise and they remove heat from the hot reservoir, supply work, and reject heat to the cold reservoir.
What is the Carnot cycle?
Carnot Cycle. The Carnot cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that is known for the best possible efficiency. Carnot cycle changes the energy available in the form of heat to produce useful reversible-adiabatic (isotropic) and other processes. Carnot engine efficiency is one minus the ratio of the temperature of the hot thermal reservoir to ...
Why is the Carnot cycle important?
Carnot states that the efficiency of the heat engine is independent of the type of fluid and only depends upon the maximum and minimum temperatures during the cycle. Thus the efficiency of the heat engine is higher when operates on super-heated steam temperature.
What is a reversible cycle?
Refrigerators and heat engines that work on reversible cycles are considered as models for comparing the actual heat engines and refrigerators. In the development of the actual cycle, the reversible cycle serves as a starting point and modified in order to meet the requirement.
Who invented the Carnot cycle?
The Carnot cycle is named after “N. L. Sadi Carnot” who invented it in 1824. Sadi Carnot is referred to as the founder of thermodynamics for discovering the heat and work relationship. Carnot was one of the first to realize that heat is essentially works in a different form.
How can cycle efficiency be maximized?
The cycle efficiency can be maximized by utilizing the processes that requires the least amount of work and deliver the most by using the reversible processes. Practically, reversible cycles cannot be achieved due to irreversibility associated with each process which cannot be eliminated.
What is the reversible Carnot cycle?
The reversible Carnot cycle provides an upper limit for the heat engine. In the Carnot cycle, the greatest possible share of the heat produced by combustion is converted into work. The Carnot process consists of two isothermal and two isentropic steps.
What are the problems with a reversible Carnot compressor?
Problems in Compression. Firstly, the compression process in the reversible Carnot cycle involves the wet compression of the liquid-vapor mixture. In practice, when a reciprocating compressor is used, wet compression is not found suitable. After evaporation of refrigerant, it enters the compressor.
What is the entropy of a reversible process?
The entropy of a reversible process is equal to the heat absorbed during the process, divided by the temperature at which the heat is absorbed ( Equation (9.3) ). Reversibility denotes a process that is carried out under near-equilibrium conditions and therefore means that it is carried out most efficiently.
What is the power cycle of a heat engine?
In practice, a heat engine operates in a power cycle between a heat source and a heat sink. The second law of thermodynamics states that the conversion of heat into work is never 100%. The maximum yield is achieved in an ideal Carnot reversible cycle1 consisting of two adiabatic and two isothermal transformations.
Who introduced the second law of thermodynamics?
The second law of thermodynamics, as was introduced by Clausius and Kelvin, is formulated on the basis of theoretical analyses of reversible cycles established by Carnot ( Knacke et al., 1991). From the reversible Carnot cycle, it follows mathematically that the reversible exchange of heat, dQrev between systems and surroundings, divided by the absolute temperature T is a total differential d S, where S is the property of the state called entropy, that is,
Let us see here first reversed Carnot heat engine cycle
Following figure, displayed here, indicates the reversed Carnot heat engine cycle. There are four processes in reversed Carnot heat engine cycle as shown in figure, now we will see here the each process of reversed Carnot heat engine cycle.
Process 1 to 2: Adiabatic compression process
Process 1 to 2 will be the adiabatic compression process or isentropic compression process. Working fluid will be compressed here during the adiabatic compression process or isentropic compression process 1 to 2 by receiving work energy W from surrounding.
Process 2 to 3: Isothermal compression process
Process 2 to 3 will be the isothermal compression process and therefore working fluid will be compressed here by keeping temperature constant.
Process 3 to 4: Adiabatic expansion process
Process 3 to 4 will be the adiabatic expansion process or isentropic expansion process. During this adiabatic expansion process or isentropic expansion process, pressure and temperature of working fluid will be reduced while volume of working fluid will be increased during this process.
Process 4 to 1: Isothermal expansion process
Process 4 to 1 will be the isothermal expansion process and therefore working fluid will be expanded here by keeping temperature constant. Pressure of working fluid will be reduced and volume of working fluid will be increased during this isothermal expansion process.
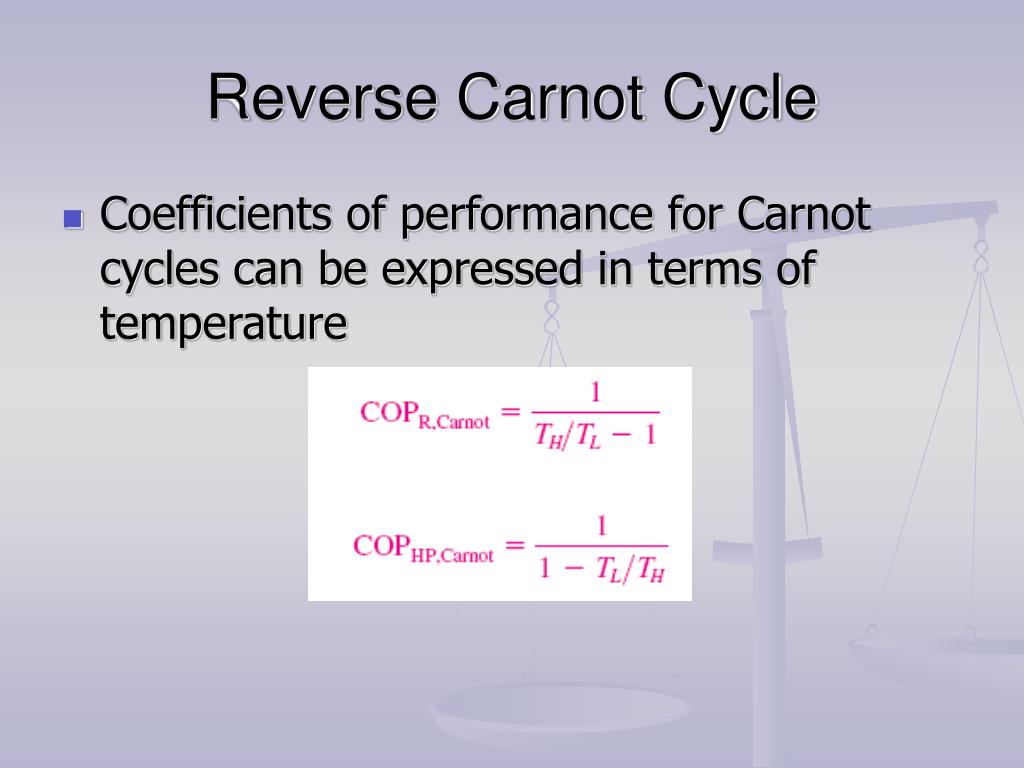
Coefficient of performance of a refrigerator (C.O.P)
We will see another topic i.e. "What are the corollaries of Carnot Theorem? in our next post in the category of thermal engineering.
What is a reversed Carnot cycle?
When a Carnot cycle runs reversely , it is called a reversed Carnot cycle. A refrigerator or heat pump that acts on the reversed Carnot cycle is called a Carnot refrigerator or Carnot heat pump respectively. In the first stage of this cycle, the refrigerant absorbs heat isothermally from a low-temperature source, TL, in the amount QL. Next, the refrigerant is isentropically compressed and its temperature rises to that of the high-temperature source, TH. Then at this high temperature, the refrigerant rejects heat isothermally in the amount QH. Also during this stage, the refrigerant changes from a saturated vapor to a saturated liquid in the condenser. Lastly, the refrigerant expands isentropically until its temperature falls to that of the low-temperature source, TL.
What is the first stage of the refrigerant cycle?
In the first stage of this cycle, the refrigerant absorbs heat isothermally from a low-temperature source, TL, in the amount QL. Next, the refrigerant is isentropically compressed and its temperature rises to that of the high-temperature source, TH.
What are the components of a gas compression cycle?
As there is no condensation and evaporation intended in a gas cycle, components corresponding to the condenser and evaporator in a vapor compression cycle are the hot and cold gas-to-gas heat exchangers .
What is an air cycle machine?
The air cycle machine is very common, however, on gas turbine -powered jet airliners since compressed air is readily available from the engines' compressor sections. These jet aircraft's cooling and ventilation units also serve the purpose of heating and pressurizing the aircraft cabin .
Do air cycle coolers work in terrestrial refrigeration?
Because of their lower efficiency and larger bulk, air cycle coolers are not often applied in terrestrial refrigeration.
