What is the prognosis for riboflavin deficiency?
Usually, when someone has a riboflavin deficiency, levels of other B-vitamins in the body are also low. This condition is treatable with riboflavin supplementation to restore levels of riboflavin and other B-vitamins, along with lifestyle changes to reduce the risk that the deficiency will recur.
How can riboflavin deficiency be prevented?
If you are riboflavin deficient, you will need a higher dose and should consult with your doctor on what is best. And the dose will depend on whether you’re trying to prevent riboflavin deficiency or treat an already existing case of it, as well as the severity of the deficiency. Standard doses range from 5-30 mg per day .
Is riboflavin deficiency the root cause of MTHFR?
Thus, if someone has a riboflavin deficiency, then will also have an FAD deficiency, which in turn can affect MTHFR. In addition, autoimmune conditions such as Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are characterized by proinflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress.
What are symptoms of too much B2?
- Upset stomach
- Diarrhea
- Increased risk of bleeding
What causes a riboflavin deficiency?
The causes of riboflavin deficiency (ariboflavinosis) are mainly related to malnourished and malabsorptive states, including GI infections. Treatment with some drugs, such as probenecid, phenothiazine, or oral contraceptives (OCs), can also cause the deficiency.
What happens when you have a deficiency in riboflavin?
Riboflavin deficiency can cause skin disorders, sores at the corners of your mouth, swollen and cracked lips, hair loss, sore throat, liver disorders, and problems with your reproductive and nervous systems.
What foods are high in riboflavin?
Riboflavin is found mostly in meat and fortified foods but also in some nuts and green vegetables.Dairy milk.Yogurt.Cheese.Eggs.Lean beef and pork.Organ meats (beef liver)Chicken breast.Salmon.More items...
What deficiency disease is caused by lack of vitamin B2?
deficiency, known as ariboflavinosis, is unlikely without the simultaneous deficiency of other nutrients. After several months of riboflavin deprivation, symptoms include cracks in the skin at the corners of the mouth, fissures of the lips, and an inflamed, magenta-coloured tongue.
How do you treat riboflavin deficiency?
(Vitamin B2 Deficiency) Treatment consists of oral or, if needed, intramuscular riboflavin. ). Riboflavin is essentially nontoxic. Dietary sources include milk, cheese, liver, meat, eggs, and enriched cereal products.
Which fruit is richest source of riboflavin?
More Fruits High in Riboflavin8% DV in 1 cup of bananas.8% DV in 1 cup of grapes.6% DV in 1 cup of navel oranges.
Is riboflavin vitamin B12?
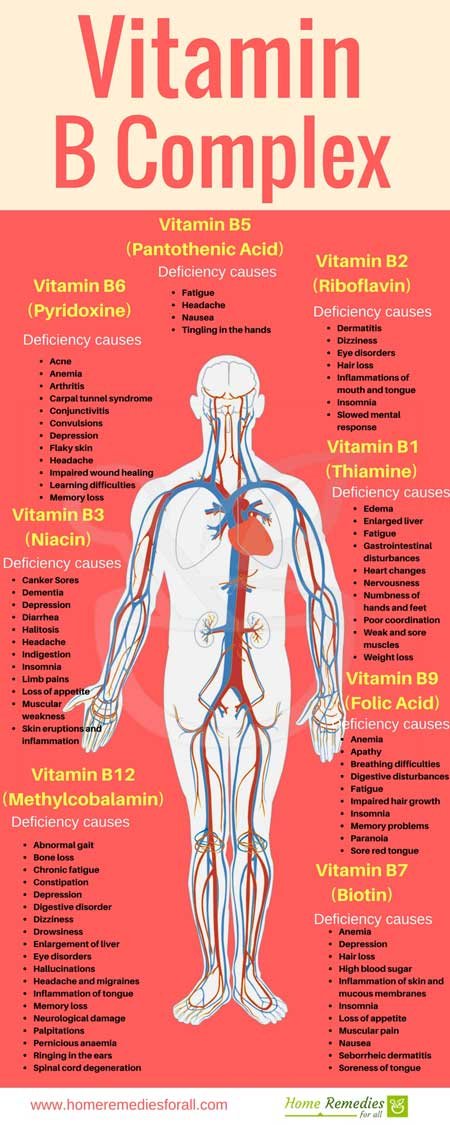
Vitamin B complex generally includes vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B3 (niacin/niacinamide), vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), and folic acid.
How is riboflavin deficiency diagnosed?
Riboflavin deficiency can be confirmed by measuring the riboflavin-dependent enzyme erythrocyte glutathione reductase. Activity coefficients greater than 1.2–1.4 are suggestive of riboflavin deficiency. Urinary riboflavin excretion and serum levels of plasma and red cell flavins can also be measured.
What vegetable is high in riboflavin?
This article provides a list of foods highest in riboflavin per serving and per 100 grams. For reference, the current daily value for riboflavin is 1.3 mg for adults and children over the age of four (1)....17) Spinach.SpinachPer Cup (30g)Per 100 GramsAmount of riboflavin0.057 mg0.189 mg% Daily value4% DV15% DVJun 10, 2020
Why would a doctor prescribe riboflavin?
Increased need for riboflavin should be determined by your health care professional. Claims that riboflavin is effective for treatment of acne, some kinds of anemia (weak blood), migraine headaches, and muscle cramps have not been proven. Oral forms of riboflavin are available without a prescription.
How do you know if you have riboflavin deficiency?
Symptoms of riboflavin deficiency may vary. Most commonly, people appear pale and have painful cracks in the corners of the mouth and on the lips. The mouth and tongue are sore, and the tongue may turn magenta.
What is the best way to correct a deficiency in riboflavin?
High doses of riboflavin supplements, usually taken by mouth, can correct the deficiency. The vitamin riboflavin (vitamin B2) is essential for the processing (metabolism) of carbohydrates (to produce energy) and amino acids (the building blocks for proteins). It also helps keep mucous membranes (such as those lining the mouth) healthy.
What are the conditions that affect the absorption of food?
Chronic disorders (such as recurrent diarrhea, liver disorders, and chronic alcoholism) Impaired absorption of food ( malabsorption disorders) Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis—procedures that filter the blood. Use of barbiturates for a long time.
Which vitamin is essential for metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as for normal nerve and heart function
Vitamin E Excess. Vitamin K Deficiency. Vitamin K Excess. Test your knowledge. Thiamin. Thiamin, vitamin B1 , is widely available in common foods. This vitamin is essential for metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as for normal nerve and heart function.
Can you take riboflavin with hemodialysis?
Sometimes riboflavin given by injection. As a preventive measure, people who are undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis or who have a malabsorption disorder should take riboflavin supplements or a daily multivitamin. People who have riboflavin deficiency are given high doses of riboflavin, taken by mouth, until symptoms resolve.
Is riboflavin toxic?
Riboflavin is not toxic, so consuming excess amounts of riboflavin is not a concern. Good sources of riboflavin include milk, cheese, liver, meat, fish, eggs, and enriched cereals.
Can riboflavin be taken with vitamin B?
Relief of symptoms when riboflavin supplements are taken. Doctors may suspect riboflavin deficiency in people who have typical symptoms and other vitamin B deficiencies. The diagnosis of riboflavin deficiency is based on symptoms and evidence of general undernutrition. The diagnosis is confirmed by measuring riboflavin excreted in urine ...
What is riboflavin deficiency?
Riboflavin deficiency is relatively uncommon in the developed world but in developing countries mild deficiency can be seen in up to 50% of the population. Riboflavin deficiency can be associated with inadequate dietary intake, malabsorptive conditions, for example, celiac disease, but is often seen in combination with a generalized B vitamin deficiency. Riboflavin deficiency (sometimes called ariboflavinosis) causes stomatitis of the mouth and tongue, cheilosis (chapped and fissured lips) and a scaly rash on the genitalia. It has also been associated with visual disturbances including night blindness, migraine headaches, mild anemia, and psychological effects including depression.1 Treatment is by dietary modification or supplements; usually combined vitamin B supplements in view of the association of riboflavin deficiency with deficiencies of the other B vitamins.
What causes ariboflavinosis?
Ariboflavinosis can result from such primary and secondary factors as commonly affect supply or utilization of other nutrients as well. Inadequate dietary intake most commonly related to limited availability of food, but sometimes exacerbated by poor storage or processing, remains the major cause.
How much riboflavin is needed for a healthy diet?
Riboflavin is destroyed on exposure to light and signs of deficiency occur if daily intake is less than 0.2–0.3 mg, although 2 mg is considered ideal for an adult . Riboflavin-poor staple diets, such as polished rice, are common in developing countries. Large amounts of riboflavin occur in liver, kidney, milk, cheese and eggs.
Is riboflavin a dietary requirement?
Riboflavin is not synthesized by higher animals and is therefore an absolute dietary requirement. The co-enzymes of flavin mono- and dinucleotide are synthesized from riboflavin, forming the prosthetic groups of several enzymes important in electron transport. Riboflavin is destroyed on exposure to light and signs of deficiency occur if daily intake is less than 0.2–0.3 mg, although 2 mg is considered ideal for an adult. Riboflavin-poor staple diets, such as polished rice, are common in developing countries. Large amounts of riboflavin occur in liver, kidney, milk, cheese and eggs.
Can riboflavin deficiency cause neurodegeneration?
Severe riboflavin deficiency in rats and chickens can lead to neurodegeneration, in some cases linked with peripheral nerve demyelination. This may arise from impaired energy generation and deranged lipid metabolism, but this remains conjectural. Evidence of neurodegeneration in humans, arising from riboflavin deficiency, is lacking.
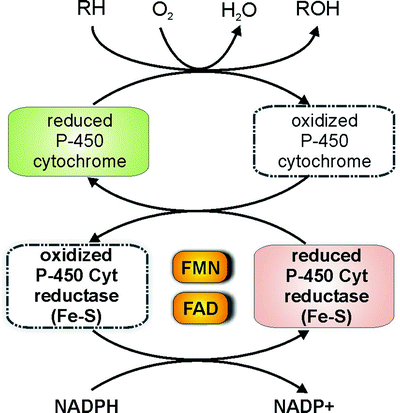
Is riboflavin converted to FMN?
This contrasts with heterozygous β -thalassemia, in which there is an inherited slow erythrocyte conversion of riboflavin to FMN, a decrease in subsequent FAD, and a high stimulation of the erythrocyte glutathione reductase by extraneous FAD.
Does riboflavin increase excretion?
The relationship of the vitamin to protein status has long been recognized. Also, certain antibiotics and phenothiazine drugs increase excretion of riboflavin.
What is Riboflavin
Riboflavin, or vitamin B2, is among the eight B vitamins that are vital for maintaining your health. It plays a crucial role in absorbing other nutrients, breaking food components, and preserving tissue health.
Role of Riboflavin in Your Body
Riboflavin is an indispensable part of enzymes that regulate cellular function, energy production, and the metabolism of drugs and fats.
Recommended Dietary Allowance
The recommended daily allowance of riboflavin for men is 1.3 mg a day, and for women, it is 1.1 mg a day. The need increases during pregnancy and lactation, when the doses are 1.4 mg and 1.6 mg a day, respectively.
Causes of Riboflavin Deficiency
As mentioned before, riboflavin is widely present in many food items, so deficiency is rare.
Consequences of Riboflavin Deficiency
Now that you know a little about the vitamin, let's understand what happens when you are deficient.
Sources of Riboflavin
Many food items are rich in riboflavin. Some options that are easy to incorporate to help prevent riboflavin deficiency are:
Conclusion
Riboflavin, or vitamin B2, is extremely important for health and various body functions. It also aids in the absorption of other nutrients.
What are the symptoms of riboflavin deficiency?
The signs and symptoms of riboflavin deficiency (also known as ariboflavinosis) include skin disorders, hyperemia (excess blood) and edema of the mouth and throat, angular stomatitis (lesions at the corners of the mouth), cheilosis (swollen, cracked lips), hair loss, reproductive problems, sore throat, itchy and red eyes, and degeneration of the liver and nervous system [ 1-3, 8 ]. People with riboflavin deficiency typically have deficiencies of other nutrients, so some of these signs and symptoms might reflect these other deficiencies. Severe riboflavin deficiency can impair the metabolism of other nutrients, especially other B vitamins, through diminished levels of flavin coenzymes [ 3 ]. Anemia and cataracts can develop if riboflavin deficiency is severe and prolonged [ 1 ].
What happens when you eat too much riboflavin?
When excess amounts are consumed, they are either not absorbed or the small amount that is absorbed is excreted in urine [ 3 ]. Bacteria in the large intestine produce free riboflavin that can be absorbed by the large intestine in amounts that depend on the diet.
How much riboflavin is in breast milk?
In well-nourished women, riboflavin concentrations in breast milk range from 180 to 800 mcg/L and concentrations of riboflavin in breast milk increase over time [ 27, 28 ]. In developing countries, in contrast, riboflavin levels in breast milk range from 160 to 220 mcg/L [ 27 ].
Where is riboflavin absorbed?
Most riboflavin is absorbed in the proximal small intestine [ 4 ].
Does the FDA require riboflavin?
FDA does not require food labels to list riboflavin content unless riboflavin has been added to the food. Foods providing 20% or more of the DV are considered to be high sources of a nutrient, but foods providing lower percentages of the DV also contribute to a healthful diet.
Is riboflavin deficiency a measure of FAD?
Riboflavin status is not routinely measured in healthy people. A stable and sensitive measure of riboflavin deficiency is the erythrocyte glutathione reductase activity coefficient (EGRAC), which is based on the ratio between this enzyme’s in vitro activity in the presence of FAD to that without added FAD [ 1, 6, 7 ].
Does riboflavin produce more riboflavin?
More riboflavin is produced after ingestion of vegetable-based than meat-based foods [ 2 ]. Riboflavin is yellow and naturally fluorescent when exposed to ultraviolet light [ 1 ]. Moreover, ultraviolet and visible light can rapidly inactivate riboflavin and its derivatives.
Etiology of Riboflavin Deficiency
Primary riboflavin deficiency results from inadequate intake of the following:
Symptoms and Signs of Riboflavin Deficiency
The most common signs of riboflavin deficiency are pallor and maceration of the mucosa at the angles of the mouth (angular stomatitis) and vermilion surfaces of the lips (cheilosis), eventually replaced by superficial linear fissures. The fissures can become infected with Candida albicans, causing grayish white lesions (perlèche).
Diagnosis of Riboflavin Deficiency
The lesions characteristic of riboflavin deficiency are nonspecific. Riboflavin deficiency should be suspected if characteristic signs develop in a patient with other B vitamin deficiencies.
Treatment of Riboflavin Deficiency
Riboflavin 5 to 10 mg orally once a day is given until recovery. Other water-soluble vitamins should also be given.
Key Points
Riboflavin deficiency causes various nonspecific skin and mucosal lesions, including maceration of mucosa at the angles of the mouth (angular stomatitis) and surfaces of the lips (cheilosis).
Why is my riboflavin yellow?
It is also a sign your body is excreting unneeded vitamin B2, and do not have a problem with riboflavin deficiency.
Why is riboflavin important?
Riboflavin is needed in high amounts to allow other B vitamins to work properly. Together, B vitamins are responsible for heart and blood health, eye and skin health, nerve health, digestion, metabolism, hormonal function, and reducing inflammation.
What is the best vitamin for free radicals?
Vitamin B2 acts as an antioxidant, which can prevent free radical damage. Riboflavin is needed for the production of the antioxidant glutathione. Glutathione helps detoxify the liver and kills free radicals.
What are the symptoms of vitamin B2 deficiency?
Other signs and symptoms of vitamin B2 deficiency include: Fatigue. Mouth or lip sores, or cracks. Nerve damage.
What is B2 in the body?
Vitamin B2 is also called riboflavin, and it is responsible for many important functions within the body. It’s health benefits include maintenance of healthy blood cells, preventing free radical damage, and boosting energy levels. Vitamin B2 combines with other B vitamins to form B Vitamin Complex.
Is riboflavin deficiency common in the Western diet?
Vitamin B2 is needed for the functioning of every single cell in the body, and a lack of riboflavin in the diet can create various adverse effects. Riboflavin or vitamin B2 deficiency is not very common in the Western diet because many refined carbohydrates contain fortified vitamin B2.
Does riboflavin help with migraines?
It also helps reduce homocysteine levels for protection against heart disease. Riboflavin can also improve muscle function, prevent cramping, and reduce the frequency of migraine headaches.
What is riboflavin deficiency?
Riboflavin transporter deficiency is caused by mutations in the SLC52A2 gene or the SLC52A3 gene. Some authors have proposed a classification system of types of riboflavin transporter deficiency depending on the underlying genetic cause, with those having a mutation in the SLC52A2 gene classified as type 2 and those having a mutation in ...
What is riboflavin transporter deficiency?
Riboflavin transporter deficiency is a progressive neurodegenerative disease characterized by paralysis of the cranial nerves, sensorineural deafness, and signs of damage to other nerves. Symptoms may begin from infancy to early adulthood and worsen over time. [1] [2] When the condition begins in infancy, the first symptom often is breathing ...
What is riboflavin deficiency?
A deficiency of riboflavin can be primary – poor vitamin sources in one's daily diet – or secondary, which may be a result of conditions that affect absorption in the intestine, the body not being able to use the vitamin, or an increase in the excretion of the vitamin from the body.
How much riboflavin is in a riboflavin supplement?
An estimated 23% consume a riboflavin-containing dietary supplement that provides on average 10 mg. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services conducts National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey every two years and reports food results in a series of reports referred to as "What We Eat In America.".
How much riboflavin is absorbed?
The body absorbs little riboflavin from single doses beyond 27 mg. When excess amounts are consumed, they are either not absorbed or the small amount that is absorbed is excreted in urine.
How much riboflavin is in a multivitamin?
Multi-vitamin dietary supplements often contain 100% of the U.S. Daily Value (1.3 mg) for riboflavin, and can be used by persons concerned about an inadequate diet. Over-the-counter dietary supplements are available in the United States with doses as high as 100 mg, but there is no evidence that these high doses have any additional benefit for healthy people.
What is the name of the vitamin that is found in food?
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B 2 and, previously, as vitamin G is a vitamin found in food, sold as a dietary supplement, and used in food fortification programs in countries where deficiency is common.
Does riboflavin cause toxicity?
Side effects. In humans, there is no evidence for riboflavin toxicity produced by excessive intakes, in part because it has lower water solubility than other B vitamins, because absorption becomes less efficient as doses increase, and because what exceeds the absorption is excreted via the kidneys into urine.
Is riboflavin a nutrient?
Riboflavin is continuously excreted in the urine of healthy individuals, making deficiency relatively common when dietary intake is insufficient. Riboflavin deficiency is usually found together with other nutrient deficiencies, particularly of other water-soluble vitamins . A deficiency of riboflavin can be primary – poor vitamin sources in one's daily diet – or secondary, which may be a result of conditions that affect absorption in the intestine, the body not being able to use the vitamin, or an increase in the excretion of the vitamin from the body.