What is it called when salt water and fresh water mix?
When Salt and Fresh Water mix it is called a mixing zone. Sometimes in a cave system, we see two Haloclines at different levels. So there is a higher fresh water level. Then brackish water in the Mixing Zone. Then salt water in the lower level. What does a place where Fresh Water meets Salt Water look like?
What happens when saltwater and fresh water mix?
When Salt and Fresh Water mix it is called a mixing zone. Sometimes in a cave system, we see two Haloclines at different levels. So there is a higher fresh water level. Then brackish water in the Mixing Zone.
What happens when freshwater and saltwater meet in an estuary?
When freshwater and saltwater meet in an estuary, they do not always mix very readily. Because freshwater flowing into the estuary is less salty and less dense than water from the ocean, it often floats on top of the heavier seawater. When river water meets sea water, the lighter fresh water rises up and over the denser salt water.
What is the difference between fresh and salt water?
From a physicist’s point of view, the density difference between fresh and salt water makes estuaries interesting. When river water meets sea water, the lighter fresh water rises up and over the denser salt water.
What does Halocline mean?
What is the Mixing Zone?
What is the name of the place where salt and fresh water meet?
What is the difference between a thermocline and a halocline?
How does the temperature of the cenotes in Mexico feel?
How to get the best visual effect?
Why do waves rise and fall?
See 2 more

Halocline - Wikipedia
In oceanography, a halocline (from Greek hals, halos 'salt' and klinein 'to slope') is a cline, a subtype of chemocline caused by a strong, vertical salinity gradient within a body of water. Because salinity (in concert with temperature) affects the density of seawater, it can play a role in its vertical stratification.Increasing salinity by one kg/m 3 results in an increase of seawater ...
Where is the place where fresh water meets ocean salty water?
Answer (1 of 14): The mouth of a river is where the fresh water drains into salt water, in an ocean or bay. If the tides are strong compared with the current the river than flood tides will bring salt water up river; ebb tides will have fresh water past the mouth of the river. If the river curr...
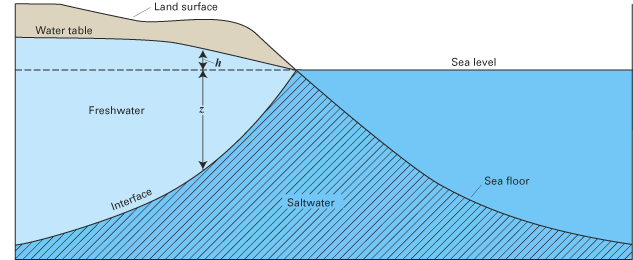
The Process of Saltwater Intrusion | U.S. Geological Survey
The Process of Saltwater Intrusion: The figure above illustrates how the process of saltwater intrusion into an aquifer system can occur. The boundary between fresh groundwater and saline groundwater is referred to as the freshwater/saltwater interface.
What is the dividing line between the Ashley River and the Cooper River?
On Ashley River (PDF) the dividing line is the confluence of Popper Dam Creek directly across from Magnolia Gardens. On Cooper River (PDF) the dividing line is the seaward shoreline of Old Back River at the confluence of Old Back River downstream from Bushy Park Reservoir. Wando River (PDF) is saltwater for its entire length.
Where is the dividing line on the Intracoastal Waterway?
On the Intracoastal Waterway (PDF) in Horry County the dividing line is the bridge across the Intracoastal Waterway at the intersection of S.C. Highway 9 and U.S. Highway 17.
What is the dividing line for freshwater and saltwater?
Except as otherwise provided below, the freshwater/saltwater dividing line is U.S. Highway 17. The Freshwater/Saltwater dividing line as depicted is an approximation of the line described in South Carolina Code Section 50-5-80. (Numbers below correlate to the map above):
Where is the dividing line on the Savannah River?
On Savannah River (PDF) the dividing line is the abandoned Seaboard Railroad track bed located approximately one and three-fourths miles upstream from the U.S. Highway 17A bridge.
Is saltwater considered freshwater?
The dividing line between saltwater and freshwater on the rivers listed is defined in this section, and all waters of the rivers and their tributaries, streams, and estuaries lying seaward of the dividing lines are considered saltwaters, and all waters lying landward or upstream from all dividing lines are considered freshwaters for purposes of licensing and regulating commercial and recreational fishing.
How does an estuary work?
When river water meets sea water, the lighter fresh water rises up and over the denser salt water. Sea water noses into the estuary beneath the outflowing river water, pushing its way upstream along the bottom.
What are the problems of estuaries?
While the problems of American estuaries are complicated and expensive, they pale in comparison to Asian estuaries. The entire nation of Bangladesh lies within the estuary and lower floodplain of the Ganges-Brahmaputra River. Other Asian rivers such as the Mekong, Chiang Jiang (or Yangtze), and Huang Ho (or Yellow River) are crowded and strained by concentrated human settlements. Global sea-level rise is causing a loss of land, increased flooding, and increased salt intrusion in these estuaries.
Why is salt intrusion so important?
The landward intrusion of salt is carefully monitored by engineers because of the potential consequences to water supplies if the salt intrusion extends too far. For instance, the city of Poughkeepsie, N.Y., 60 miles north of the mouth of the Hudson River, depends on the river for its drinking water. Roughly once per decade, drought conditions cause the salt intrusion to approach the Poughkeepsie freshwater intake. The last time this happened, in 1995, extra water had to be spilled from dams upstream to keep the salt front from becoming a public health hazard.
What is the effect of estuaries on the environment?
An estuary, with all of its dynamic stirrings, has one attribute that promotes its own destruction: It traps sediment. When suspended mud and solids from a river enter the estuary, they encounter the salt front. Unlike fresh water, which rides up and over the saline layer, the sediment falls out of the surface layer into the denser, saltier layer of water moving into the estuary. As it drops, it gets trapped and accumulates on the bottom. Slowly, the estuary grows muddier and muddier, shallower and shallower.
What is the role of scientists in the estuary?
As scientists, one of our roles is to predict changes in the environment, given different natural and human-induced influences. To foresee the health of estuaries in the future, we have some fundamental questions to answer about the present and the past. How far will salt intrude if river flow is cut in half? Do changes in river flow increase or decrease the rate at which sediments shoal the estuary? What effect do such changes have on the fish that spawn in fresh water?
How long does sediment accumulate in the Hudson River?
Sediment cores in the Hudson River indicate that sediment may accumulate for 10, 20, or even 50 years, laying down layers every year like tree rings. But then a hurricane or big snowmelt floods the river, wipes out the layers of sediment, and sends the mud out to sea.
How does salt change in the Fraser River?
Often, as in the Fraser River, this occurs at an abrupt salt front. Across such a front, the salt content (salinity) and density may change from oceanic to fresh in just a few tens of meters horizontally and as little as a meter vertically.
What does Halocline mean?
The word comes from Greek. Halo means salt, and Cline means slope or graduation. It is where the higher fresh water, that has fallen as rain, meets the lower salt water, that comes in from the sea.
What is the Mixing Zone?
When Salt and Fresh Water mix it is called a mixing zone. Sometimes in a cave system, we see two Haloclines at different levels. So there is a higher fresh water level. Then brackish water in the Mixing Zone. Then salt water in the lower level.
What is the name of the place where salt and fresh water meet?
What is a Halocline ? Where Fresh Water and Salt Water Meet is called a Halocline. A Halocline is defined as, the level where the amount of dissolved salt changes sufficiently to be able to see. We see this phenomenon in the caves of the Yucatan while scuba diving.
What is the difference between a thermocline and a halocline?
What’s the difference between a Thermocline and a Halocline? A thermocline is a change in temperature, whereas a Halocline is a change in salinity, in the level of water. There is a change in temperature in a halocline. In the cenotes, in Mexico, the temperature rises a degree or two as we descend into the salt water layer.
How does the temperature of the cenotes in Mexico feel?
In the cenotes, in Mexico, the temperature rises a degree or two as we descend into the salt water layer. At the end of a long cave dive, if we spend time in the nice warm salty water, it can feel quite cold going back up into the colder fresh water.
How to get the best visual effect?
To get the best visual effect we position ourselves with our eyes just on the Halocline. The salt water is warmer so we have a warm body but a cold head. It looks crazy, stunning. Words cannot fully describe the beauty. As we rise and fall gently with each breath, we slowly propel ourselves through the layer keeping it fresh and clean. We see concentrated horizontal beams of light and the rocks behind distort as if in a hall of mirrors at a fairground.
Why do waves rise and fall?
When it’s undisturbed we can see waves rising and falling caused by the slightly faster flowing fresh water. It looks like another surface to the water. It’s best to shine your light across the layer to see it better. The refraction works better.
