See more

What is SLT replication Server?
SLT is the an ETL ( Extract , Transform , Load ) tool which allows us to load and replicate data in real-time or schedule data from SAP source system or Non SAP System into SAP HANA Database. SAP SLT server uses a trigger-based replication approach to pass data from source system to target system.
What is SAP replication Server?
Move, manage, and integrate data from the most popular SAP and third-party data sources in real time using SAP Replication Server software, which feeds your IT investments with high-quality data that's always where you need it. Business continuity enabled by “zero-downtime” disaster recovery.
What happens when you stop a replication in SAP landscape transformation?
If you deactivate a configuration, the initial load and / or the replication process will stop immediately – however, database triggers in the source systems will continuously record changes in the logging tables. If you activate the configuration, the data transfer jobs resume.
What is the difference between SLT and SDI?
Nevertheless, SDI comes second with almost equal number of transform options available to integrate and cleanse data. While the tool as such has a long way to go, it may acquire new transform options with each release. SLT, on the other hand, has very minimal transformation options that can be done only through ABAP.
What is the use of replication Server?
Replication Servers are lightweight Amazon EC2 instances that are used to replicate data between your source servers and AWS. Replication Servers are automatically launched and terminated as needed.
What is the function of a replication server?
Replication Server works to distribute data over a network by: Providing application developers and system administrators with a flexible publish-and-subscribe model for marking data and stored procedures to be replicated. Managing replicated transactions while retaining transaction integrity across the network.
Why SLT is used in SAP?
SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server is part of SAP Business Technology Platform, supporting real-time replication of data from SAP or third-party systems to SAP HANA to help you run applications and analyze data quickly.
Can replication replace backup?
Data backup and data replication are commonly confused. While these processes are related, they're not interchangeable.
What does SLT stand for in SAP?
SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server (SLT) – A Cost Saving Use Case | NTT DATA Business Solutions (UK) Ltd.
Is SAP SDI an ETL tool?
SAP Smart Data Integration (SDI) is an ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) tool that comes as part of SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA Database. You can use it to integrate different types of source systems into SAP HANA Cloud, and SAP HANA Database without the need to install an ETL application.
How do you replicate a table in SLT?
If it exists, click on Data Provisioning, provide the table, select Stop Load/Replication and then continue. This would remove the table from SLT. Add the table again, Data Provisioning --> Provide the table --> Start Replication. This would create triggers/logging tables and replicate the table again.
What is logging table in SLT?
Logging tables are created by the source system for every table to be replicated. During the initial load itself, SLT identifies changes on source using database triggers, saves changes to logging tables and writes them to the target when the initial load is done.
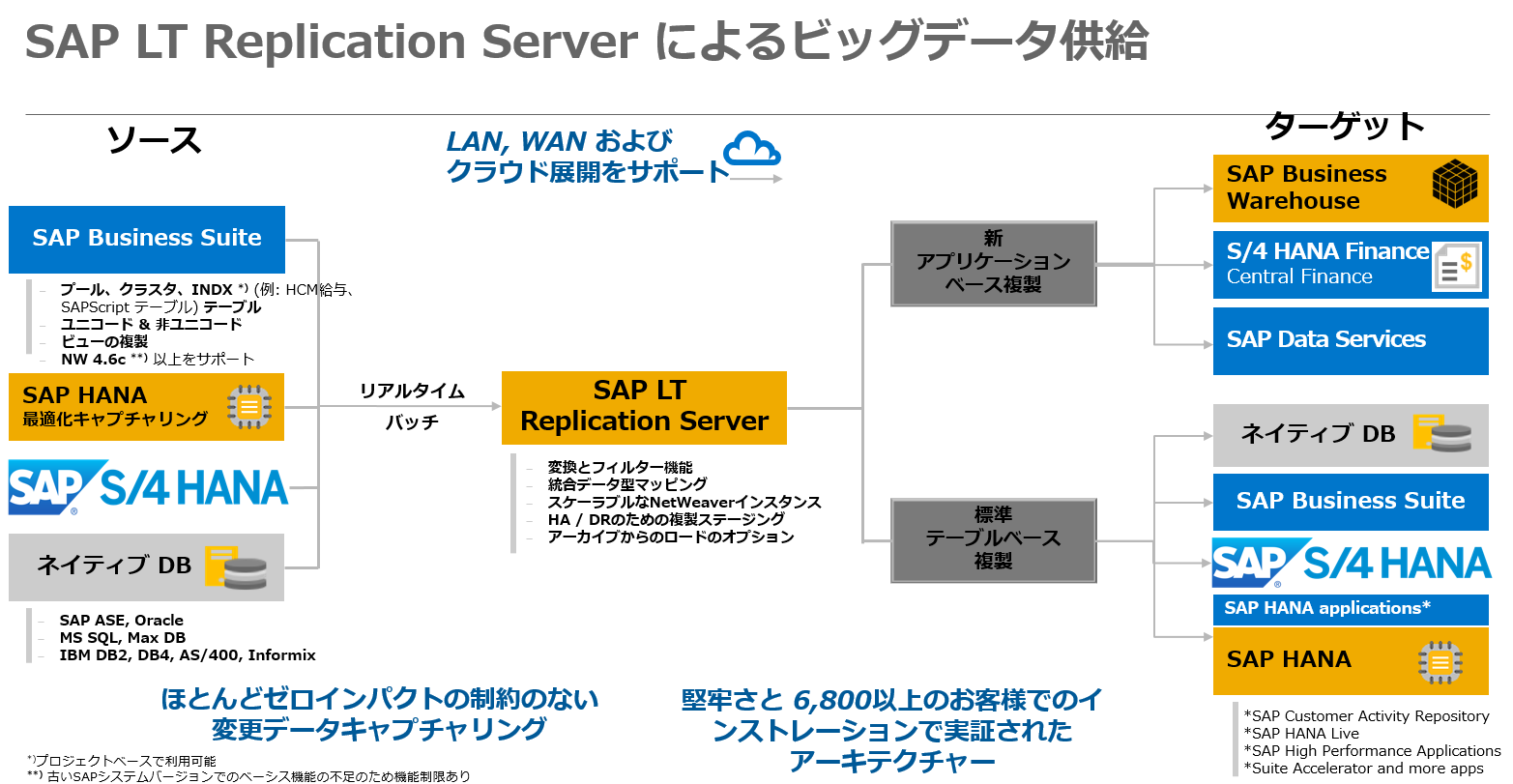
What is SAP LT replication server?
SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server is part of SAP Business Technology Platform, supporting real-time replication of data from SAP or third-party systems to SAP HANA to help you run applications and analyze data quickly.
What is Sybase replication server?
Sybase Replication Server is a 'data movement' product, which moves data from one place to another. More specifically, it captures database transactions in one database and then applies these to another database.
How does replication work in SAP HANA?
SAP HANA System Replication is controlled by the SAP HANA database Kernel. It is done using two separate systems with the exact same number of active HANA nodes. Once system replication is setup between the two HANA systems, one is defined as the primary system and the other being the secondary system.
What is replication in data storage?
Data replication is the process by which data residing on a physical/virtual server(s) or cloud instance (primary instance) is continuously replicated or copied to a secondary server(s) or cloud instance (standby instance). Organizations replicate data to support high availability, backup, and/or disaster recovery.
What is SAP SLT Replication Server?
SAP SLT Replication Server transforms all metadata table definitions from the non-ABAP source system to SAP HANA.
What is SLT in SAP?
SLT is the an ETL tool that allows you to load and replicate data in real-time or schedule data from SAP source system or Non SAP System into SAP HANA Database.
What is the connection between SAP SLT and SAP Source?
The connection between SAP SLT and SAP Source is established as RFC connection.
Where is the read engine created?
Read engine is created in the SAP SLT Replication server.
Where is SLT installed?
SLT server can be installed on the separate system or on SAP ECC System.
What does "stop replication" mean?
It stops the current replication process for a table. It removes database trigger and logging table completely.
What happens after data load?
After data load, Status will be changed to “Executed”. The table will be created in “SLTECC” schema with data.
What happens after SLT load?
After the initial load is complete, SLT continues to monitor the tables in the source system and replicates data changes (also known as delta data) in the source system to the target system in real-time. As long as the SLT system is functioning correctly, temporary downtimes of the source or target systems do not result in the loss of any business data. If the target system were to become temporarily unavailable, SLT continues to record any changes to the source system in the log tables, and updates the relevant target system tables when the system is back online.
What is SAP Replication Server?
Although the SAP Replication Server is a real-time replication tool for non- SAP source systems, it also supports the SAP Business Suite 7.20 and higher (Unicode-only).
What is SLT in SAP?
SLT is positioned as the standard real-time replication tool for big data for SAP ABAP-based source systems—unicode and non-unicode—to SAP HANA, to all databases supported by SAP, to the SAP Business Suite and to SAP applications. However, it also supports non-SAP sources. Although the SAP Replication Server is a real-time replication tool ...
How does SLT work?
SLT loads existing data or a defined subset of it from the source system to the target system (the initial load), and the source system sets up logging tables for each table to be replicated. You can run the initial load of data while the source system is active. In parallel to the initial load, by means of database triggers, SLT detects any data changes that occur while the initial load process is running.
What is SLT in data replication?
SLT is a real-time replication tool with trigger-based technology that captures all updates, inserts, and deletes for a table that is in replication. The cornerstone of SLT’s replication technology is both an effective, zero-impact data change capturing technology and a robust data replication process.
What is the process of replication?
The replication process corresponds to the real-time movement of data. This means that data is speedily synchronized from a source system to a target system.
Does SAP have real time replication?
SAP offers several real-time replication tools, and it may be difficult for a customer to distinguish among the offerings and find the right tool or the right combination of tools that best satisfies their organization's requirements.
What is SLT in SAP?
SAP LT Replication Server (aka ‘SLT’) is the software which is considered as the standard way of moving data within the varied systems within the same network, might be Local Area Network, Wide Area Network or into the Cloud so as to retrieve an information in the correct point of time and at the right place.
How many tables are replicated?
Most Tables Replicated – 12000 tables in one landscape, in one configuration, is 500 tables.
Is SAP LT a replication server?
Moreover SAP LT Replication Server is an asset of SAP and moreover, it has its own importance in the Software industry as discussed above.
What is SLT used for?
SLT is also used for Real time replication of source documents, supported via CFIN interface, e.g.:
What is SAP SLT?
SAP SLT server uses a trigger-based replication approach to capture the data to be passed in real-time from source system to target system.
What is duplicate posting in SLT?
Duplicate posting can occur when SLT transfer a change from source to target but cannot mark the processed record as “processed” in the source system. Then SLT could transfer the same record again (that will be recognized by the AIF-interface as a duplicate posting and marked as erroneous).
What is standard check for duplicate posting?
Duplicate Posting Issue –Standard does a check to ensure a document is already posted . This check is against the database but if same document is passed by SLT in 2 separate AIF jobs, it can result in duplicate posting. Please have a look at the following Note: 2918829 – Central Finance: Duplicate postings due to parallel processing of AIF messages
What is LT replication?
In a CFIN project SAP LT Replication Server collects data written to databases in the source systems (i.e. posted documents) and feeds this data into the corresponding Central Finance accounting interface via real-time replication.
Why does CFIN have a check?
CFIN has a standard check to help prevent the posting of documents, multiple times.
Why does SLT assume records were not transferred?
RFC-connection problems can cause SLT to assume that records were not transferred and to try again. Look into alerts on RFC related errors in SLT to prevent them in future.
