A secondary ossification center is the area of ossification that appears after the primary ossification center has already appeared – most of which appear during the postnatal and adolescent years. Most bones have more than one secondary ossification center.
Where do you find primary and secondary ossification centers?
- one at the tip of the spinous process
- one at the tip of each transverse process (two in total)
- two as ring (or annular) epiphyses at the upper and lower surfaces of the vertebral bodies
What is the primary center of ossification?
The primary ossification center is the first place where the bone formation begins in the axle of a long bone or in the body of an irregular bone. Conversely, the secondary ossification center is the area of ossification that appears after the primary center of ossification at the epiphysis of edges of bones.
Where do secondary ossification centers occur?
The site where bone formation continues after beginning in the long shaft or body of the bone, usually in an epiphysis is a secondary ossification center. A secondary ossification center is the center of bone formation appearing later than the punctum ossificationis primarium, usually in epiphysis.
What are the three types of ossification?
What are the five injury classifications?
- Soft Tissue Injuries. Soft tissue injuries are some of the most common types of injuries.
- Broken Bones. Our bones support our bodies and help us move.
- Traumatic Brain Injuries. There are two types of brain injuries—traumatic brain injuries and non-traumatic brain injuries.
- Spinal Cord Injuries.
- Psychological Injuries.

Where are the secondary ossification centers?
epiphysesLater, usually after birth, secondary ossification centers form in the epiphyses. Ossification in the epiphyses is similar to that in the diaphysis except that the spongy bone is retained instead of being broken down to form a medullary cavity.
What is primary and secondary ossification center?
The primary ossification center is the first place where the bone formation begins in the axle of a long bone or in the body of an irregular bone. Conversely, the secondary ossification center is the area of ossification that appears after the primary center of ossification at the epiphysis of edges of bones.
What is secondary ossification and where does it occur?
Secondary ossification mostly occurs after birth (except for distal femur and proximal tibia which occurs during 9th month of fetal development). The epiphyseal arteries and osteogenic cells invade the epiphysis, depositing osteoclasts and osteoblasts which erode the cartilage and build bone, respectively.
What is an ossification center?
The site where bone begins to form in a specific bone or part of bone as a result of the accumulation of osteoblasts in the connective tissue. The site where bone begins to form in the shaft of a long bone or the body of an irregular bone; primary ossification center.
What are the two types of ossification?
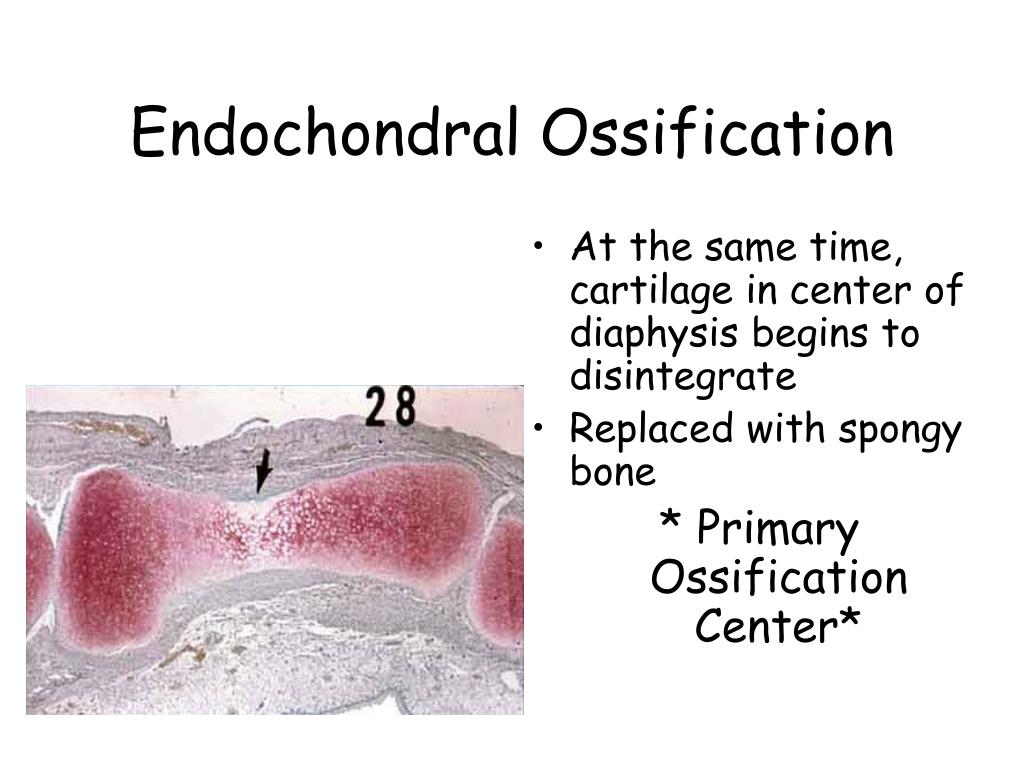
The formation of bone (ossification) occurs in one of two ways:Intramembranous ossification - bone is formed by direct replacement of mesenchyme.Endochondral ossification - cartilage model serves as the precursor of bone.
What is the difference between the primary growth center of a bone and a secondary growth center?
This primary center of ossification begins in the middle of a long bone as blood vessels invade into the cartilage model. With time, vessels then invade the periphery of the bone, establishing secondary centers of ossification.
Why is the secondary ossification center important?
Secondary ossification centers for epiphyses and apophyses go through different stages of growth from the initiation of ossification to complete fusion. This evolution leads to variations in fracture patterns based on mechanism and anatomical location.
Is the growth plate a secondary ossification center?
Abstract. Growth plate and articular cartilage constitute a single anatomical entity early in development but later separate into two distinct structures by the secondary ossification center (SOC). The reason for such separation remains unknown.
What are the 3 stages of ossification?
The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines, they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation, called proliferation, maturation of matrix, and mineralization.
What is the Centre of a bone called?
Bone marrow is found in the center of most bones and has many blood vessels. There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow. Red marrow contains blood stem cells that can become red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. Yellow marrow is made mostly of fat.
What is the last bone to ossify?
flat bones of the faceThe last bones to ossify via intramembranous ossification are the flat bones of the face, which reach their adult size at the end of the adolescent growth spurt.
What is unfused ossification center?
Unfused transverse process ossification center is a smooth well corticated and normally aligned lateral part of a vertebral process that failed to fuse to the proximal part of the transverse process.
Where does primary ossification occur?
Primary ossification occurs in the diaphysis of a long bone (in the womb), secondary ossification occurs in the epiphysis (after birth). Both primary and secondary ossification are endochondral (replacement) events.
What are the two types of bone ossification?
There are two types of bone ossification, intramembranous and endochondral. Each of these processes begins with a mesenchymal tissue precursor, but how it transforms into bone differs. Just so, where are the primary and secondary ossification centers? The primary ossification center is the first place where the bone formation begins in the axle ...
What is the ossification center?
An ossification center is a point where ossification of the cartilage begins. The first step in ossification is that the cartilage cells at this point enlarge and arrange themselves in rows. The matrix in which they are imbedded increases in quantity, so that the cells become further separated from each other.
What is secondary ossification?
A secondary ossification center is the area of ossification that appears after the primary ossification center has already appeared – most of which appear during the postnatal and adolescent years . Most bones have more than one secondary ossification center. In long bones, the secondary centers appear in the epiphyses .
What are the two types of ossification centers?
There are two types of ossification centers – primary and secondary.
Where are the primary centers of long bones?
In long bones the primary centers occur in the diaphysis /shaft and in irregular bones the primary centers occur usually in the body of the bone. Most bones have only one primary center (e.g. all long bones except clavicle) but some irregular bones such as the os coxa (hip) and vertebrae have multiple primary centers.
What is secondary ossification?
A secondary ossification center is the center of bone formation appearing later than the punctum ossificationis primarium, usually in epiphysis. Secondary ossification centers for epiphyses and apophyses go through different stages of growth from the initiation of ossification to complete fusion.
What is the name of the site where bone begins to form in the shaft of a long bone or the body of?
Abstract. The site where bone begins to form in the shaft of a long bone or the body of an irregular bone is called a primary ossification center. The site where bone formation continues after beginning in the long shaft or body of the bone, usually in an epiphysis is a secondary ossification center .
What are the two types of SOCs?
There are two types of SOCs, the epiphysis and the apophysis. The epiphysis typically forms the end extensions of long bones. Articular cartilage surrounds the epiphysis and typically no attachments for muscles or tendons are seen. The main function is longitudinal growth and facilitation of joint motion [ 2, 3 ].
Why are SOCs absent at birth?
As mentioned, the majority of the SOCs are absent at birth, with the exception being the distal femur epiphysis. This poses a problem because often these injuries can be missed or under treated. This is especially important as up to 50% of cases involving the distal humerus and distal femur are related to non-accidental trauma [ 4 ]. Other common causes include accidental trauma, falls and motor vehicle collisions.
Which imaging method best illustrates a physeal separation?
Ultrasound imaging better illustrates a physeal separation by identifying a bare area of the distal humerus not covered by epiphyseal cartilage [ 7 ]. An important identifier is the posteromedial displacement of the radius and ulna in relation to the distal humerus. Supakul et al. compared radiography vs. ultrasound in diagnosing distal humeral physeal separation. 56% of patients had a missed diagnosis using radiographs, while ultrasound diagnosed a distal humeral physeal separation in 75% patients. Additionally, ultrasound identified bucket handle fractures in 31% of the patients vs. 12.5% with radiographs [ 7 ].
When do capitellar SOCs appear?
Capitellar SOCs often do not appear until the close to the ninth postnatal month [ 9 ], often leading to a misdiagnosis of elbow dislocation. Radiographs will show a loss of relationship between the radioulnar articulation relative to the distal humerus, which can be appreciated in both dislocation and separation.
Does the apophysis contribute to longitudinal growth?
The apophysis does not participate in longitudinal growth or joint articulation. The apophysis typically serve as attachments sites for tendons and ligaments, providing function of added force production for movement and stability [ 1 ].
