
What are the two segments of the ascending loop of Henle?
There are two segments of the ascending loop of Henle. They are thin ascending limb and thick ascending limb. Thick ascending limb is thicker than the thin ascending limb. Thin ascending limb is the lower part of the ascending loop of Henle and it is lined by simple squamous epithelium.
What is the function of the ascending limb of the Henle?
Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle. Salt (NaCl) is actively extruded from the ascending limb into the surrounding interstitial fluid. This is not accomplished, however, by the same process that occurs in the proximal tubule. Instead, Na+ diffuses from the filtrate into the cells of the thick portion of the ascending limb,...
Why is the ascending loop of Henle function impermeable to water?
The ascending loop of Henle function is impermeable to water. In this, sodium chloride is transported from a thick portion of the ascending limb without accompanying water so an osmotic gradient of approximately 200 mosm/kg is generated.
What substances pass through the loop of Henle?
The liquid entering the loop of Henle is the solution of salt, urea, and other substances passed along by the proximal convoluted tubule, from which most of the dissolved components needed by the body—particularly glucose, amino acids, and sodium bicarbonate—have been reabsorbed into the blood.
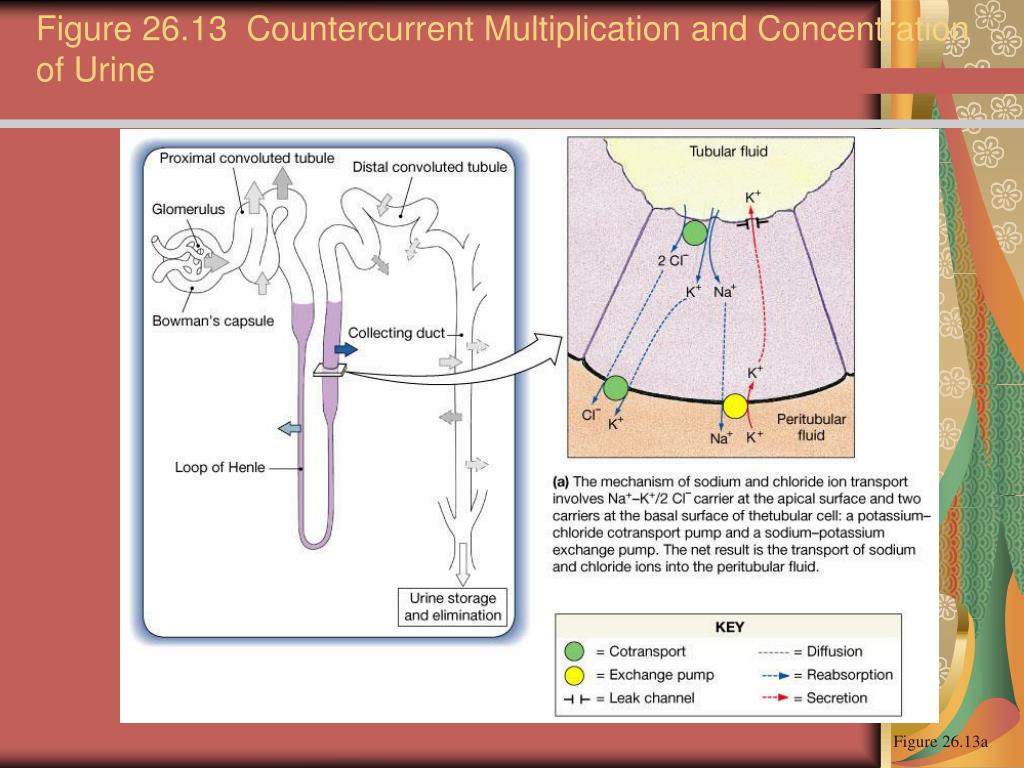
What is reabsorbed and secreted in the descending loop of Henle?
This part of the nephron is called the loop of Henle. Its main function is to reabsorb water and sodium chloride from the filtrate. This conserves water for the organism, producing highly concentrated urine.
What is secreted in the descending loop of Henle?
The descending loop contains AQP1 and is therefore permeable to water but impermeable to salt. As urine descends into the medulla, the high interstitial solute concentration osmotically draws water from the descending limb and concentrates salt within the lumen.
What substance is reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle?
Thick ascending limbs of Henle's loop have at least three major roles: (1) They reabsorb sodium chloride which dilutes the urine.
What substances are reabsorbed or secreted in the ascending loop?
Reabsorption in the thick ascending limb: A further 25% of the sodium and potassium is reabsorbed through the walls of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle via: Three-ion cotransporter (sodium/potassium/chloride) and the sodium/potassium ATPase, which as before maintains the sodium concentration gradient.
What is the difference between ascending and descending loop of Henle?
The key difference between ascending and descending loop of Henle is that ascending loop of Henle is the thicker segment of the loop of Henle located just after the sharp bend of the loop while descending loop of Henle is the thinner segment located just before the sharp bend of the loop.
What is the function of ascending limb of Henle?
The thick ascending limb occupies a central anatomic and functional position in human renal physiology, with critical roles in the defense of the extracellular fluid volume, the urinary concentrating mechanism, calcium and magnesium homeostasis, bicarbonate and ammonium homeostasis, and urinary protein composition.
What substance is reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle quizlet?
Na+ is actively being pumped out of thick ascending limb of LOH to be reabsorbed. This gradient is used by the collecting ducts under the influcence of ADH to control the amount of water that is excreted or reabsorbed.
What is the function of the ascending loop of Henle quizlet?
What is the role of the loop of Henle? responsible for reabsorbing approximately 25% of the filtered NaCl and water and a small amount of bicarbonate. However, another major function of the loop of Henle is to enable the kidney to produce either a dilute or a concentrated urine.
Is urea reabsorbed in the ascending loop of Henle?
Urea is secreted in the thin ascending limb of Henle loop, so significant amounts of urea reach the distal nephron. In the collecting ducts, urea is reabsorbed together with water.
Which substances are secreted by which regions of the nephron?
Secreted substances largely include hydrogen, creatinine, ions, and other types of waste products, such as drugs. Tubular secretion is the transfer of materials from peritubular capillaries to the renal tubular lumen and occurs mainly by active transport and passive diffusion.
What is reabsorbed and secreted in the nephron?
The filtrate absorbed in the glomerulus flows through the renal tubule, where nutrients and water are reabsorbed into capillaries. At the same time, waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubule. This process is called secretion.
What occurs in the descending limb of the loop of Henle quizlet?
What is the main event in the Descending Loop of Henle? Is reabsorption of water in response to the osmolarity of the interstitium. What happens to TF concentration of NaCl in the Descending Loop of Henle?
Where hydrogen and potassium ions are secreted into the urine?
proximal tubuleSecretion, which occurs in the proximal tubule section of the nephron, is responsible for the transport of certain molecules out of the blood and into the urine. Secreted substances include potassium ions, hydrogen ions, and some xenobiotics.
What does the proximal tubule secrete?
The cells of the proximal tubule also secrete organic acids and bases (transporter not shown). This secretion is the basis for the use of PAH for the clearance estimation of renal plasma flow. In addition, this secretion can be a major route for the elimination of certain drugs, such as penicillin, from the body.
1. What are the major functions of the loop of henle?
Loop of Henle is found in the kidney location and has three major functions.Re-absorption: It absorbs 15% of filtered water and 25% of the filtered...
2. What activity happens in the ascending loop of henle?
The ascending loop of Henle carries a thin and thick segment. It helps in draining urine into the distal convoluted tubule. The sodium reabsorption...
3. What is the role of the ascending loop of henle?
The ascending Loop of Henle is impermeable to water. Here, the sodium chloride is transported from a thick portion of the ascending limb without ac...
4. What are the functions of nephron?
The primary function of the Nephron is to flush out the waste products such as solid waste and other excesses from the blood. Nephron is a basic st...
5. Mention one essential part of nephron?
An essential part of Nephron is Henle’s Loop, also known as Loop of Henle. The Henle’s loop carries both the descending limbs of Loop of Henle and...
6. What is PCT?
PCT or Proximal Convoluted Tubule is an essential part of Nephron. PCT can be described as a system that helps in the absorption and the reabsorpti...
7. Where are study notes available?
Biology is an important subject and it is necessary to have clear concepts of all the chapters. Practice is important so as to be able to do well a...
8. What are the three essential parts of nephron?
Nephron carries three different parts of tubules for secretion purpose. These three are-1. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)The blood brought by the...
What is the ascending limb of the loop of Henle?
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a direct continuation from the descending limb of loop of Henle, and one of the structures in the nephron of the kidney. The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule .
Which is thicker, ascending or descending?
The ascending limb is much thicker than the descending limb . At the junction of the thick ascending limb and the distal convoluted tubule are a subset of 15-25 cells known as the macula densa that are part of renal autoregulation through the mechanism of tubuloglomerular feedback .
Which limb is impermeable to water?
Thick ascending limb. Functionally, the parts of the ascending limb in the medulla and cortex are very similar. The medullary ascending limb is largely impermeable to water. Sodium (Na + ), potassium (K +) and chloride (Cl −) ions are reabsorbed by active transport.
What is the function of Tamm Horsfall protein?
The function of this protein is not well understood, but is responsible for creating urinary casts .
Is the ascending limb impermeable to water?
The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water; but is permeable to ions allowing for some sodium reabsorption. Na/K-ATPase is expressed at very low levels in this segment and thus this reabsorption is likely through passive diffusion. Salt moves out of the tubule and into the interstitium due to osmotic pressure created by the countercurrent system.
What is the purpose of the loop of Henle?
The aims of the loop of henle is to reduce the volume of water and solutes within the urine but without changing the concentration. In doing this it creates a hypertonic medulla. This hypertonic medulla not only helps reabsorb water from the loop of henle but also aids the reabsorption of water from the collecting ducts as well as they pass ...
Why does excess water pass through the loop of the henle?
When there is excess water in the body, the excess fluid passes through the loop of henle because the fluid entering the loop is less concentrated already. The solutes only have so much osmotic potential and therefore are unable to draw the excess water from the lumen. This contributes to allowing the kidneys to produce dilute urine.
What happens to the osmolarity of blood as it ascends back out of the medulla?
As the blood ascends back out of the medulla, the osmolarity reduces until it is only slightly higher than when it entered . The conclusion drawn from this is that the solutes which are reabsorbed from the fluid mainly remain in the surrounding tissue and maintain the concentration gradient.
Why does salt enter the tubule?
Here salt enters the tubule passively due to the hypertonicity of the medulla creating a gradient. This results in a very high salt concentration at the bottom of the loop. The fluid moves on and enters the thick ascending limb. This has salt transporters and so salt is pumped into the medulla via active transport causing more water to leave ...
Which medulla helps reabsorb water from the loop of the Henle?
This is maintained by the vasa recta. This hypertonic medulla not only helps reabsorb water from the loop of henle but also aids the reabsorption of water from the collecting ducts as well as they pass through the medulla en-route to the renal pelvis.
Where does urea enter the medullary interstial fluid?
The urea from the collecting duct enters the medullary interstial fluid and diffuses into the loop of henle. As it passes back up the ascending limb of the loop of henle and reabsorption of other ions occurs the urea becomes even more concentrated. This recirculation can occur several times and steadily increases urea concentration in ...
Why is it important to return concentration to the same level as when it entered the loop?
This returning of the concentration back to the same level as when it entered the loop is important for retaining salt and also allows the concentration to be finely controlled by the collecting ducts without the loss of salt. When there is excess water in the body, the excess fluid passes through the loop of henle because the fluid entering ...
What occurs in ascending loop of Henle?
Thick ascending limbs of Henle’s loop have at least three major roles: (1) They reabsorb sodium chloride which dilutes the urine. (3) They reabsorb large amounts of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in an energy-efficient manner.
Does secretion occur in loop of Henle?
While much of the reabsorption and secretion occur passively based on concentration gradients, the amount of water that is reabsorbed or lost is tightly regulated. This control is exerted directly by ADH and aldosterone, and indirectly by renin. Most water is recovered in the PCT, loop of Henle, and DCT.
What is reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle?
The loop of Henle is the site of the majority of magnesium absorption from the kidneys. Approximately 60% to 70% of filtered magnesium is reabsorbed in the cortical thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
What cells are in the ascending loop of Henle?
The ascending limb is much thicker than the descending limb. At the junction of the thick ascending limb and the distal convoluted tubule are a subset of 15-25 cells known as the macula densa that are part of renal autoregulation through the mechanism of tubuloglomerular feedback.
What is the main function of loop of Henle?
The principal function of the loop of Henle is in the recovery of water and sodium chloride from urine. This function allows production of urine that is far more concentrated than blood, limiting the amount of water needed as intake for survival.
Why is thick ascending loop of Henle impermeable?
In the ascending portion, the loop becomes impermeable to water and the cells of the loop actively reabsorb solutes from the luminal fluid; therefore water is not reabsorbed and ions are readily reabsorbed.
Why loop of Henle is called countercurrent multiplier?
The descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to water but impermeable to solutes, due to the presence of aquaporin 1 in its tubular wall. The countercurrent flow within the descending and ascending limb thus increases, or multiplies the osmotic gradient between tubular fluid and interstitial space.
What is the function of the loop of henle?
The loop of Henle function is to reabsorb water and sodium chloride from the filtrate. This conserves water for the organism, resulting in highly concentrated urine. In other words, the Loop of Henle is a heterogeneous segment that comprises the pars recta of the proximal tubule, the thin descending and ascending limbs along ...
Where is the loop of henle located?
Loop of Henle is found in the kidney location and has three major functions.
Why does sodium reabsorption occur in ascending limbs?
The sodium reabsorption in a thin ascending limb is quite passive and occurs paracellularly because of the difference in osmolarity between the tubule and interstitium. Share this with your friends. Share.
What is the effect of water absorption on the descending limb?
The absorption of water within the descending limb leads to an increasing osmotic gradient within the tubule. The loop of Henle is supplied by two vasa recta which straight vessels closely accompany the tubule’s hairpin- are shaped course. These vessels carry blood in the opposite direction, similar to the tubular fluid- the countercurrent mechanism. These result in water absorbed on one hand, and solute on the other.
What is the first portion of the loop?
The first portion of the loop is the thin descending limb which is permeable to water. The descending loop of Henle is an important function. The liquid that reaches the bend of the loop is richer in salt and urea than the blood plasma. As the liquid returns through the thin ascending limb, sodium chloride diffuses out of the tubule into ...
What is the loop of heme called?
This part of the Nephron is called the Loop of Henle.
Which limb of the loop of Henle expresses sodium-potassium-chloride?
The thick descending limb of the loop of Henle expresses a sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter and helps reabsorb approximately a third of the filtered sodium and chloride from the fluid in the tubular lumen into the blood.
What is Ascending Loop of Henle?
Ascending loop of Henle is one of the two parts of the loop of Henle. It is located after the sharp bend of the loop, so it is the second part of the loop of Henle. It continues to the distal convoluted tubule and drains tubular fluid or urine to the distal convoluted tubule.
What are the Similarities Between Ascending and Descending Loop of Henle?
Ascending and descending loop of Henle are two parts of the Henle loop of the nephron.
What are the two parts of the loop of Henle?
The loop of Henle has two parts: the descending loop of Henle and the ascending loop of Henle. Descending loop of Henle is the first part located just before the sharp bend of the loop. Ascending loop of Henle is the second part located just after the sharp bend of the loop. The thickness of the ascending loop of Henle is higher than ...
What is the difference between a thin ascending limb and a thick ascending limb?
They are thin ascending limb and thick ascending limb. Thick ascending limb is thicker than the thin ascending limb. Thin ascending limb is the lower part of the ascending loop of Henle and it is lined by simple squamous epithelium. Thick ascending limb is the upper part and it is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium.
What is the function of the nephron?
The nephron is the basic functional unit of our kidney that filter blood and produces urine in order to remove waste and extra fluid from the body. Nephron has two major parts: renal corpuscle and renal tubule. Renal corpuscle consists of glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule.
Where does the renal tubule start?
Renal tubule starts from the capsule and the first part of the renal tubule is proximal convoluted tubule. Then a special area called Henle loop runs and enters the second part of the renal tubule known as the distal convoluted tubule.
Where does re-absorption take place?
Re-absorption takes place in both ascending and descending loop of Henle.

Overview
Structure
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a direct continuation from the descending limb of loop of Henle, and one of the structures in the nephron of the kidney. The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule.
The thin ascending limb is found in the medulla of the kidney, and the thick ascending limb can be divided into a part that is in the renal medulla and a part that is in the renal cortex. The ascending …
Function
The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water; but is permeable to ions allowing for some sodium reabsorption. Na/K-ATPase is expressed at very low levels in this segment and thus this reabsorption is likely through passive diffusion. Salt moves out of the tubule and into the interstitium due to osmotic pressure created by the countercurrent system.
Functionally, the parts of the ascending limb in the medulla and cortex are very similar.
Clinical significance
The thick ascending limb symporter: Na-K-Cl cotransporter.
See also
• Descending limb of loop of Henle
External links
• Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 7/7ch07/7ch07p11". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
• Histology image: 15804loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Overview at vet.cornell.edu