Site-directed mutagenesis is a PCR-based method to mutate specified nucleotides of a sequence within a plasmid vector. This technique allows one to study the relative importance of a particular amino acid for protein structure and function.
What are the applications of site-directed mutagenesis?
Site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) is a method to create specific, targeted changes in double stranded plasmid DNA. There are many reasons to make specific DNA alterations (insertions, deletions and substitutions), including:
What is B-factor-based site-directed mutagenesis?
Site-directed mutagenesis is a molecular biology method that is used to make specific and intentional changes to the DNA sequence of a gene and any gene products. Site-directed mutagenesis is one of the most important techniques in laboratory for introducing a mutation into a DNA sequence.
Does site-directed mutagenesis with synthetic DNA oligonucleotides yield unexpected deletions and insertions?
Site-directed mutagenesis plays an important role in the advancement of biochemical and catalytic properties of proteins, and is one of the most widely used strategies for the molecular modification of enzymes [25, 26]. Selection and identification of the mutation site is the most important and crucial step in the site-directed mutagenesis process.
What is the PMID for site-directed mutagenesis?
Apr 05, 2019 · There are numerous applications of site-directed mutagenesis in gene therapy and gene-editing technology. It’s a kind of technique that tells you Yes or No about the assay. For instance, if a protein is correctly expressed or not; if a gene is working finely or not. So basically scientists can do many things using the SDM- Site-Directed Mutagenesis.
What are the advantages of site-directed mutagenesis?
Why is site-directed mutagenesis more useful than random mutagenesis?
Random mutagenesis techniques has an advantage in terms of how many mutations can be produced; however, while random mutagenesis can produce a change in single nucleotides, it does not offer much control as to which nucleotide is being changed.
What is the significance of site-directed mutagenesis in drug discovery?
What is site-directed mutagenesis in enzymes?
How do you carry out a site-directed mutagenesis?
What is the difference between random and site-directed mutagenesis?
Who has discovered method of site-directed mutagenesis?
What is PCR based site-directed mutagenesis?
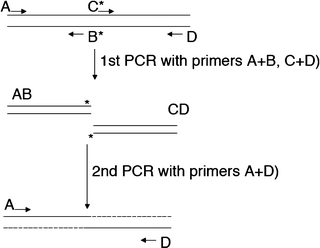
When PCR is used for site-directed mutagenesis, the primers are designed to include the desired change, which could be base substitution, addition, or deletion (Figure 1). During PCR, the mutation is incorporated into the amplicon, replacing the original sequence.Jan 10, 2012
What is site directed mutagenesis?
Site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) is a method to create specific, targeted changes in double stranded plasmid DNA. There are many reasons to make specific DNA alterations (insertions, deletions and substitutions), including:
How long does it take for a plasmid to mutagenesis?
The use of a master mix, a unique multi-enzyme KLD enzyme mix, and a fast polymerase ensures that, for most plasmids, the mutagenesis reaction is complete in less than two hours.
What is SDM in biology?
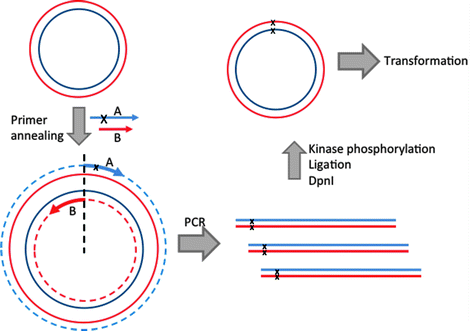
Method Overview: SDM is an in vitro procedure that uses custom designed oligonucleotide primers to confer a desired mutation in a double-stranded DNA plasmid.
What is the Q5 kit?
This kit is designed for rapid and efficient incorporation of insertions, deletions and substitutions into doublestranded plasmid DNA. The first step is an exponential amplification using standard primers and a master mix fomulation of Q5 Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase. The second step involves incubation with a unique enzyme mix containing a kinase, a ligase and DpnI. Together, these enzymes allow for rapid circularization of the PCR product and removal of the template DNA. The last step is a high-efficiency transformation into chemicallycompetent cells (provided).
Enzyme Engineering
Kashyap Kumar Dubey, ... Jyoti Yadav, in Advances in Enzyme Technology, 2019
Design and engineering of novel enzymes for textile applications
R. Araújo, ... A. Cavaco-paulo, in Advances in Textile Biotechnology, 2010
Globins and Other Nitric Oxide-Reactive Proteins, Part B
Of the five cloned CYP55A genes, CYP55A1 (Fnor) from F. oxysporum has been the most studied.
Enzyme Kinetics and Mechanism
Site-directed mutagenesis is performed as described previously using standard methods.20 The mutated GalT proteins are expressed in E. coli, and cell extracts are prepared by suspending lg of wet cell pellet in 3.6 ml of pH 7.5 Na–HEPES 50 m M buffer and 10 m M 2-mercaptoethanol followed by sonication.
Natural Product Biosynthesis by Microorganisms and Plants, Part C
The aureothin gene cluster contains three type I polyketide synthases (PKSs) that are composed of multiple domains including β-ketosynthase, acyl transferase, acyl carrier protein, ketoreductase, dehydratase (DH), and enoylreductase domains.
Neprilysin Inhibitors Provide Insight into its Specificity and Therapeutic Potential
Site-directed mutagenesis studies have investigated the potential binding interactions between peptide substrates and NEP residues R102, R717, and N542. Study of R102 has indicated that the residue can bind the C-terminus of a peptide P2’ residue [21, 22 ].
What is site directed mutagenesis?
The site-directed mutagenesis is used to remove the restriction sites. Restriction digestion is a process in which the DNA having the recognition site for a particular restriction endonuclease is cleaved into fragments.
What is the most common method of site directed mutagenesis?
The conventional PCR method is one of the most popular and easy methods for site-directed mutagenesis. The set up is simple; short, single-stranded oligonucleotide primers are designed in such a way that possess the mutation we wish to study.
When was the first site directed mutagenesis experiment?
The first site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) experiment was performed in the year 1974 , in the laboratory of Charles Weissmann. The induced mutation was from GC to AT, however, the mutation was inserted randomly. Scientists from the Charles Weissmann university had incorporated mutations and changed the GC nucleotide with AT.
What is PCR used for?
PCR is regularly used not only to identify mutations or genotypes but it is also used to insert mutations at a particular location. The same method which is used to screen mutations can be used to insert mutations.
What is high fidelity polymerase used for?
The high fidelity DNA polymerase is used to do the amplification as well as to linearise the circular plasmid DNA. Once the mutation is inserted, the 5′ phosphorylated end of the primers allows the ligation of the linear DNA. By the intermolecular ligation, the plasmid is then recircularized.
How many base pairs are needed for a mutation?
Ideally, the mutation is incorporated at the end of the primer, but if the mutation is in between, make sure that both sides of the primer do have at least 11 base pair complementary sequences.
How many sets of primers are used in a primer extension?
In the primer extension, 2 sets of primers are used in which a single primer set is nested. Here the mechanism of carrying the mutation is the same, the mutation is introduced into the primer at one of the ends.
Summary of Site Directed Mutagenesis
In brief, point-mutations can be introduced to plasmids using primers (with the desired mutation) in a PCR protocol that amplifies the entire plasmid template. The parent template is removed using a methylation-dependent endonuclease (i.e. DpnI), and bacteria are transformed with the nuclease-resistant nicked plasmid (the PCR product).
Experimental guidelines
As a rule of thumb, 11 bp of complementary sequence on either side of the desired mutation (usually 1-3 mismatched bases) is sufficient for your primers to successfully anneal to the plasmid of interest during the PCR reaction.
Validating your mutagenized plasmids
Once constructs containing the desired modification have been identified (and confirmed to be free of primer duplications), final validation is performed by sequencing functional regions of the plasmid including the insert.
Alternative approaches to site directed mutagenesis
Point-mutagenesis is fairly easy, but the risk of PCR-introduced mutations can make alternative approaches more favorable if you want to introduce a point mutation in a large construct.