Full Answer
How do you derive Snell’s law formula?
Let’s derive Snell’s law formula using Fermat’s principle. Fermat’s principle states that “light travels in the shortest path that takes the least time”. Let the refractive index of medium 1 and medium 2 are n1 and n2 respectively. Light enters from medium 1 to medium 2 through the point O.
What is Snell's law used for?
The law is named for Willebrord Snellius, a Dutch astronomer and mathematician, known in the English world as Snell. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material.
Is Snell's law of refraction valid for isotropic media?
Generally, Snell's law of refraction is only valid for isotropic media. In anisotropic ones, such as crystals, the ray may be split into two rays. Let's assume you want to find the angle of refraction of a light beam that travels from air to glass. The angle of incidence is 30°.
How do you apply Snell's law to light rays?
Applying Snell's Law when the light is incident on the glass slab's surface, Now, applying Snell's Law when the light ray is leaving the glass slab through another surface, So, the incident ray is parallel to the emergent ray but it is laterally displaced from it.
What Is Snell law write its formula?
Snell's law formula is expressed as: μ=sin rsin i, where i is the angle of refraction, r is the angle of refraction and μ is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
What is Snell's law explain?
If the light ray incident on a plane interface between two dielectric transparent media, Then the Snell's law of refraction states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface, all lie in the same plane. Relation between them is given by, n2n1=sinθ1sinθ2.
What is Snell's law example?
Snell's Law Examples The index of refraction can be used to find the speed of light in a material like glass. The index of refraction of glass is 1.50, and the speed of light in air is 3x108 m/s, so the speed of light in glass is 2x108 m/s.
What is Snell's first law?
Snell's First Law: It states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal lie on the same plane.
What is the SI unit of Snell's Law?
Snell's law often uses degrees to measure the angles, while the velocity would commonly be measured in meters per second. That said, because Snell's law sets up a ratio between two values with the same units, the units used don't matter.
What is Snell's Law sin i sin r?
sinisinr = v1v2 = constant. This constant is called as: A. reflective index.
What is Snell's full name?
Willebrord Snel van RoyenWillebrord Snell, Latin-Dutch Willebrordus Snellius, original name Willebrord Snel van Royen, (born June 13, 1580, Leiden, Netherlands—died October 30, 1626, Leiden), Dutch astronomer and mathematician who discovered the law of refraction (also known as Snell's law), which relates the degree of the bending of light to ...
Why is Snell's law true?
The statement is: The angle in Snell's law is measured between the ray and a line perpendicular to the surface. Yes, the angles in Snell's law are measured between the ray and a line perpendicular to the surface. Hence the above statement is true.
Who gave the Snell's law?
scientist Willebrørd SnellOpen any physics textbook and you'll soon come across what English-speaking physicists refer to as "Snell's law". The principle of refraction – familiar to anyone who has dabbled in optics – is named after the Dutch scientist Willebrørd Snell (1591–1626), who first stated the law in a manuscript in 1621.
What is the value of n in Snell's law?
Snell's Law is given in the following diagram. As in reflection, we measure the angles from the normal to the surface, at the point of contact....Snell's Law.n for Light of Wavelength 600 nmSubstanceRefractive Index, nAir (1 atmosphere pressure, 0 degrees C)1.00029Water (20 degrees C)1.33Crown Glass1.521 more row
What is Snell's Law and how is it calculated?
Snell's Law describes the relationship between the incident angle at which light hits a surface and the refracted angle after it passes into the ne...
What is n1 and n2 in Snell's Law?
n1 is the index of refraction of the material the light is leaving (material 1), and n2 is the index of refraction of the material that the light i...
What is Snell's Law example?
Snell's Law can be used to find how much light bends when it passes from one material to another. It can also be used to find the index of refracti...
How do you use Snell's Law formula?
Snell's Law uses four variables: the index of refraction of material 1, the index of refraction of material 2, the incident angle at which the ligh...
How is Snell's law derived?
Derivation from Fermat's principle. Snell's law can be derived from Fermat's principle, which states that the light travels the path which takes the least time. By taking the derivative of the optical path length, the stationary point is found giving the path taken by the light.
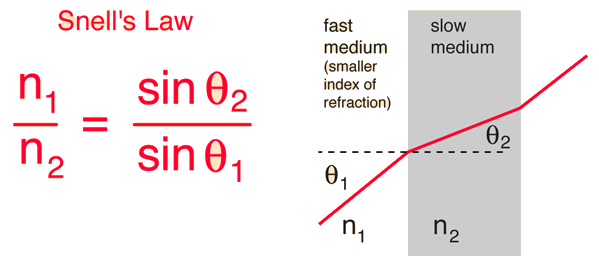
What is Snell's law?
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing ...
What is the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction?
Snell's law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or equivalent to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction : as the refractive index (which is unitless) of the respective medium.
What is the law of refraction?
In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction , and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material. The law is also satisfied in metamaterials, which allow light to be bent "backward" at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index .
Which theory did Pierre de Fermat reject?
Rejecting Descartes' solution, Pierre de Fermat arrived at the same solution based solely on his principle of least time. Descartes assumed the speed of light was infinite, yet in his derivation of Snell's law he also assumed the denser the medium, the greater the speed of light.
Who invented the law of Snell?
The law eventually named after Snell was first accurately described by the Persian scientist Ibn Sahl at the Baghdad court in 984. In the manuscript On Burning Mirrors and Lenses, Sahl used the law to derive lens shapes that focus light with no geometric aberrations.
Who said Descartes had seen Snell's paper and concocted his own proof?
According to Dijksterhuis, "In De natura lucis et proprietate (1662) Isaac Vossius said that Descartes had seen Snell's paper and concocted his own proof. We now know this charge to be undeserved but it has been adopted many times since." Both Fermat and Huygens repeated this accusation that Descartes had copied Snell. In French, Snell's Law is called "la loi de Descartes" or "loi de Snell-Descartes."
What is Snell's law?
Snell’s law, in optics, a relationship between the path taken by a ray of light in crossing the boundary or surface of separation between two contacting substances and the refractive index of each.
Who invented the law of refraction?
The mathematical form of the law of refraction, equation (1) above, was announced by the French mathematician René Descartes some 16 years later.…
How to use Snell's law?
To use Snell's Law, draw a line perpendicular to the interface between the two materials, also known as the normal line. The angle that the light makes with the normal as it leaves material #1 is known as the incident angle, and the angle it makes with the normal line after it passes into material #2 is known as the refracted angle.
What angle is Snell's law used for?
Snell's Law can also be used to calculate the incident angle at which total internal reflection occurs , which is known as the critical angle.
What is the refracted angle of a material?
If the incident angle is large enough, then the refracted angle will be 90 degrees, meaning that no light will get out of the material and, instead, all the light will be reflected. This reflection is known as total internal reflection. Total internal reflection is used in fiberoptic cables to send light pulses over long distances. It is also what cuts diamond sparkle in the light.
What is the speed of light in glass?
The index of refraction of glass is 1.50, and the speed of light in air is 3x10 8 m/s, so the speed of light in glass is 2x10 8 m/s.
Which function can be used to find the refracted angle?
Finally, the inverse sign function can be used to find the refracted angle:
Can Snell's law be used to find an unknown index of refraction?
Snell's Law can also be used to find an unknown index of refraction. In this case, the math is a little simpler because it is unnecessary to use any inverse trig functions.
What is Snell's law?
Snell's law, also known as the law of refraction, is a law stating the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light passing from one medium to another medium such as air to water, glass to air, etc.
Which law states that the ratio of sine of angle of incidence and sine of angle of refraction is always constant?
Snell's Law states that the ratio of sine of angle of incidence and sine of angle of refraction is always constant for a given pair of media.
What happens to the velocity of light in a medium with less refractive index?
So, if a medium has less refractive index, then the velocity of light in that medium would be more but if a medium has more refractive index then the velocity of light in that medium would be comparatively less. Question: A ray of light travelling in air is incident on the plane surface of a transparent medium.
When we compare the speed of light in a medium to that of the speed of the light in vacuum, then we?
When we compare the speed of light in a medium to that of the speed of the light in vacuum, then we would be dealing with something called absolute refractive index. We generally refer to the absolute refractive index of a medium when we say that a certain object's refractive index is#N#x#N#x x.
How does Snell's law work?
Snell's law describes how exactly refraction works. When a light ray enters a different medium, its speed and the wavelength change . The ray bends either towards the normal of two media boundary (when its speed decreases) or away from it (when its speed increases).
What does sin mean in Snell's law?
If this happens, it means that all light is reflected from the boundary (this phenomenon is known as the total internal reflection).
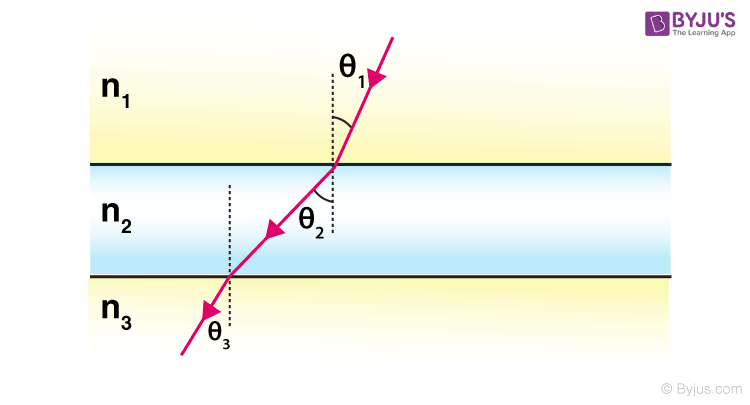
What is the angle of incidence?
θ₁ is the angle of incidence - the angle between a line normal (perpendicular) to the boundary between two media and the incoming ray; θ₂ is the angle of refraction - the angle between the normal to the boundary and the ray traveling through medium 2. Generally, Snell's law of refraction is only valid for isotropic media.
How to solve for angle of incidence?
Solving for the angle of incidence, Θ₁ = arcsin (n₂/n₁).
What is the equation for the unknown angle of refraction?
Transform the equation so that the unknown (angle of refraction) is on the left-hand side: sin (θ₂) = n₁sin (θ₁)/n₂.
Is Snell's law of refraction only valid for isotropic media?
Generally, Snell's law of refraction is only valid for isotropic media. In anisotropic ones, such as crystals, the ray may be split into two rays.

Overview
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. This law was named after the Dutch astronomer and mathematician Willebrord Snellius (also …
History
Ptolemy, in Alexandria, Egypt, had found a relationship regarding refraction angles, but it was inaccurate for angles that were not small. Ptolemy was confident he had found an accurate empirical law, partially as a result of slightly altering his data to fit theory (see: confirmation bias). Alhazen, in his Book of Optics (1021), came closer to discovering the law of refraction, though he did not take this step.
Explanation
Snell's law is used to determine the direction of light rays through refractive media with varying indices of refraction. The indices of refraction of the media, labeled , and so on, are used to represent the factor by which a light ray's speed decreases when traveling through a refractive medium, such as glass or water, as opposed to its velocity in a vacuum.
Derivations and formula
Snell's law can be derived in various ways.
Snell's law can be derived from Fermat's principle, which states that the light travels the path which takes the least time. By taking the derivative of the optical path length, the stationary point is found giving the path taken by the light. (There are situations of light violating Fermat's principle by not taking the least time p…
Total internal reflection and critical angle
When light travels from a medium with a higher refractive index to one with a lower refractive index, Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal re…
Dispersion
In many wave-propagation media, wave velocity changes with frequency or wavelength of the waves; this is true of light propagation in most transparent substances other than a vacuum. These media are called dispersive. The result is that the angles determined by Snell's law also depend on frequency or wavelength, so that a ray of mixed wavelengths, such as white light, will spread or disperse. Such dispersion of light in glass or water underlies the origin of rainbows and …
Lossy, absorbing, or conducting media
In a conducting medium, permittivity and index of refraction are complex-valued. Consequently, so are the angle of refraction and the wave-vector. This implies that, while the surfaces of constant real phase are planes whose normals make an angle equal to the angle of refraction with the interface normal, the surfaces of constant amplitude, in contrast, are planes parallel to the interface itself. Since these two planes do not in general coincide with each other, the wave is sa…
See also
• List of refractive indices
• The refractive index vs wavelength of light – Empirical relationship between refractive index and wavelength
• Evanescent wave
• Reflection (physics) – "Bouncing back" of waves at an interface