
Social learning theory, also known today as social cognitive theory, is a theory proposed by psychologist Albert Bandura Albert Bandura OC is a Canadian-American psychologist who is the David Starr Jordan Professor Emeritus of Social Science in Psychology at Stanford University. Bandura has been responsible for contributions to the field of education and to several fields of psychology, in…Albert Bandura
See more
What does social learning theory explain?
Social learning theory explains complex behavior by acknowledging cognitive factors and the role they play in deciding whether to imitate behavior. However, it does not account for how we develop a wide range of behavior based on thoughts and feelings.
What are the 3 concepts of Bandura's social learning theory?
– Albert Bandura As the creator of the concept of social learning theory, Bandura proposes five essential steps in order for the learning to take place: observation, attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation.
What are Bandura's 4 principles of social learning?
Observational learning is a major component of Bandura's social learning theory. He also emphasized that four conditions were necessary in any form of observing and modeling behavior: attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation.
Why is social learning theory important?
Applications of the social learning theory may be particularly valuable, as they can empower people to recognize and trace the roots of their issues, identify patterns they may have not otherwise seen, and ultimately, break the habits and behaviors that harm them.
What are the 3 concepts of learning?
Three concepts or types of learning, in the science classroom particularly, are the inquiry-based approach, the activity-based approach and the learning cycle.
What are the 3 main learning theories?
Although there are many different approaches to learning, there are three basic types of learning theory: behaviorist, cognitive constructivist, and social constructivist. This section provides a brief introduction to each type of learning theory.
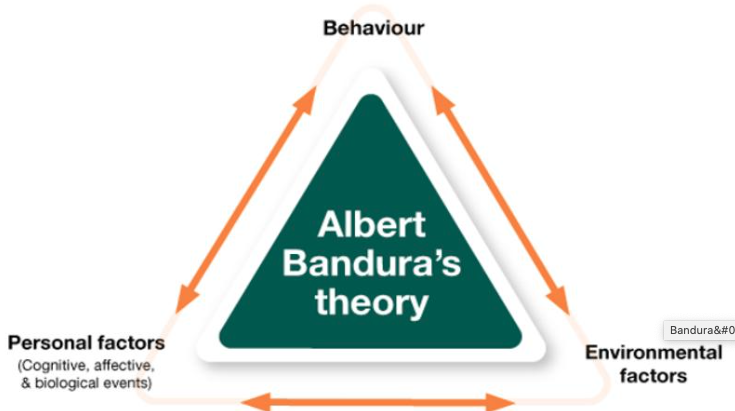
What are the three 3 important factor that influences learning According to Bandura?
Bandura proposed the idea of reciprocal determinism, in which our behavior, Personal factors, and environmental factors all influence each other. It is important to note that learning can occur without a change in behavior.
What are the three basic concepts in learning?
Within an educational framework, there tends to be three core concepts of learning: Constructivism, Bloom's Taxonomy, and Epistemology.
What is Bandura's theory of social learning?
Today, both teachers and parents recognize how important it is to model appropriate behaviors.
What is Bandura's theory?
Bandura's theory moves beyond behavioral theories, which suggest that all behaviors are learned through conditioning, and cognitive theories, which take into account psychological influences such as attention and memory . 1:42.
What Is Social Learning Theory?
The behaviorists proposed that all learning was a result of direct experience with the environment through the processes of association and reinforcement. 3 Bandura's theory believed that direct reinforcement could not account for all types of learning.
What did Bandura say about reinforcement?
Bandura noted that external, environmental reinforcement was not the only factor to influence learning and behavior. And he realized that reinforcement does not always come from outside sources. 1 Your own mental state and motivation play an important role in determining whether a behavior is learned or not.
What are the three models of observational learning?
Bandura identified three basic models of observational learning: 1 A live model, which involves an actual individual demonstrating or acting out a behavior. 2 A symbolic model, which involves real or fictional characters displaying behaviors in books, films, television programs, or online media. 3 A verbal instructional model, which involves descriptions and explanations of a behavior.
What are some classroom strategies that are rooted in social learning theory?
Other classroom strategies such as encouraging children and building self-efficacy are also rooted in social learning theory. As Bandura observed, life would be incredibly difficult and even dangerous if you had to learn everything you know from personal experience.
What did Bandura's experiments show?
One of the best-known experiments in the history of psychology involved a doll named Bobo. Bandura demonstrated that children learn and imitate behaviors they have observed in other people. The children in Bandura’s studies observed an adult acting violently toward a Bobo doll.
What is social learning theory?
Social learning theory considers how both environmental and cognitive factors interact to influence human learning and behavior.
Which theory does Albert Bandura agree with?
In social learning theory, Albert Bandura (1977) agrees with the behaviorist learning theories of classical conditioning and operant conditioning. However, he adds two important ideas:
Why is a child more likely to imitate behavior modeled by people of the same gender?
First, the child is more likely to attend to and imitate those people it perceives as similar to itself. Consequently, it is more likely to imitate behavior modeled by people of the same gender.
What is SCT theory?
It is for this reason that Bandura modified his theory and in 1986 renamed his Social Learning Theory, Social Cognitive Theory (SCT), as a better description of how we learn from our social experiences.
How is behavior learned?
Behavior is learned from the environment through the process of observational learning.
What is the motivation to identify with a particular model?
The motivation to identify with a particular model is that they have a quality which the individual would like to possess. Identification occurs with another person (the model) and involves taking on (or adopting) observed behaviors, values, beliefs and attitudes of the person with whom you are identifying.
Does a child reproduce behavior that is gender appropriate?
They may do this regardless of whether the behavior is ‘gender appropriate’ or not, but there are a number of processes that make it more likely that a child will reproduce the behavior that its society deems appropriate for its gender.
How does Bandura's inner state affect social learning?
Bandura also believed that inner states could have an effect on the social learning process. Cognitive influences including your emotional states, moods, and thoughts can affect your attention, motivation, and willingness to learn.
What Is Social Learning Theory?
Watson and B. F. Skinner. According to the behavioral perspective, learning is the result of conditioning through association reinforcement.
What did Bandura agree with?
While Bandura agreed that classical conditioning and operant conditioning were important for learning, he noted that these processes alone could not account for all examples of learned behavior. For example, people are often able to demonstrate that they have learned something even if they have no direct experience with it.
What is the next step in observational learning?
Reproduction: The next step of the process involves actually reproducing the behavior you have observed. While not all observational learning requires actually demonstrating the behavior, practicing can be helpful for the learning process.
What is the observational learning process?
The observational learning process is the cornerstone of Bandura’s model of learning. While this might immediately call to mind direct observation, you don’t necessarily have to actually witness an action being performed in order to learn through observation.
How can parents use social learning?
Parenting: Parents can use social learning to model behaviors that they want their children to learn.
How does attention affect learning?
Attention: In order to learn something through observation, it needs to be the focus of your attention. Being distracted during the learning process can affect how well the information is learned.
What is social learning theory?
However, according to Bandura, social learning theory emphasizes that behavior, personal factors, and environmental factors are all equal, interlocking determinants of each other. This concept is referred to as reciprocal determinism (Bandura, 1973, 1977).
Why is social learning called observational learning?
Observational Learning and Aggression. Social learning is also commonly referred to as observational learning because it comes about as a result of observing models . Bandura became interested in social aspects of learning at the beginning of his career.
How did Bandura and Walters study aggression?
Citing the work of Dollard and Miller, as well as others who paved the way for social learning theory, Bandura and Walters began their study on adolescent aggression by examining how the parents of delinquents train their children to be socialized. Working from a general learning perspective, emphasizing cues and consequences, they found significant problems in the development of socialization among the delinquent boys. These boys developed dependency, a necessary step toward socialization, but they were not taught to conform their behavior to the expectations of society. Consequently, they began to demand immediate and unconditional gratification from their surroundings, something that seldom happens. Of course, this failure to learn proper socialization does not necessarily lead to aggression, since it can also lead to lifestyles such as the hobo, the bohemian, or the “beatnik” (Bandura & Walters, 1959). Why then do some boys become so aggressive? To briefly summarize their study, Bandura and Walters found that parents of delinquent boys were more likely to model aggressive behavior and to use coercive punishment (as opposed to reasoning with their children to help them conform to social norms). Although parental modeling of aggressive behavior teaches such behavior to children, these parents tend to be effective at suppressing their children’s aggressive behavior at home. In contrast, however, they provide subtle encouragement for aggression outside the home. As a result, these poorly socialized boys are likely to displace the aggressive impulses that develop in the home, and they are well trained in doing so. If they happen to associate with a delinquent group (such as a gang), they are provided with an opportunity to learn new and more effective ways to engage in antisocial behavior, and they are directly rewarded for engaging in such behaviors (Bandura & Walters, 1959; also see Bandura, 1973).
How is personality learned?
One of the most important aspects of Bandura’s view on how personality is learned is that each one of us is an agent of change, fully participating in our surroundings and influencing the environmental contingencies that behaviorists believe affect our behavior. These interactions can be viewed three different ways. The first is to consider behavior as a function of the person and the environment. In this view, personal dispositions (or traits) and the consequences of our actions (reinforcement or punishment) combine to cause our behavior. This perspective is closest to the radical behaviorism of Skinner. The second view considers that personal dispositions and the environment interact, and the result of the interaction causes our behavior, a view somewhat closer to that of Dollard and Miller. In each of these perspectives, behavior is caused, or determined, by dispositional and environmental factors, the behavior itself is not a factor in how that behavior comes about. However, according to Bandura, social learning theory emphasizes that behavior, personal factors, and environmental factors are all equal, interlocking determinants of each other. This concept is referred to as reciprocal determinism (Bandura, 1973, 1977).
How does modeling affect behavior?
Thus, children can learn from others, in particular their parents, how to regulate their behavior in socially appropriate ways. When the inappropriate behavior of others is punished, the children observing are also vicariously punished, and likely to experience anxiety, if not outright fear, when they consider engaging in similar inappropriate behavior. However, when models behave aggressively and their behavior is rewarded, or even just tolerated, the child’s own tendency to restrict aggressive impulses may be weakened. This weakening of restraint, which can then lead to acting out aggressive impulses, is known as disinhibition.
Who found evidence that parents of aggressive, delinquent boys had modeled aggressive behavior?
Having found evidence that parents of aggressive, delinquent boys had modeled aggressive behavior, Bandura and his colleagues embarked on a series of studies on the modeling of aggression (Bandura, Ross, & Ross, 1961, 1963a,b).
Who is Albert Bandura?
Part 2: Albert Bandura and Social Learning Theory. Bandura is the most widely recognized individual in the field of social learning theory, despite the fact that Dollard and Miller established the field and Rotter was beginning to examine cognitive social learning a few years before Bandura. Nonetheless, Bandura’s research has had ...

Social Learning Theory: Albert Bandura
What Is Social Learning Theory?
What Do We Need to Know About Social Learning Theory?
- The social learning approach takes thought processes into account and acknowledges the role that they play in deciding if a behavior is to be imitated or not. As such, SLT provides a more comprehensive explanation of human learning by recognizing the role of mediational processes. For example, Social Learning Theory is able to explain many more com...
Who Developed Social Learning Theory?
What Other Theories Are Linked to Social Learning Theory?
- Social learning theory is the idea that humans learn from observing and imitating the behavior modelled by others. Bandura labelled this phenomenon observational learning. In short, it is not necessary to have a direct experience of something in order to learn. For observational learning to occur, there does not necessarily need to be a live observ...
What Are The 4 Elements of Social Learning Theory?
- What is social learning theory? Social learning theory is the idea that behaviors can be learned through observation, modelling and imitation.
- Who developed this theory?Albert Bandura developed his theory following a series of now famous studies known as the Bobo doll experiments.
- Are there any other theories linked to social learning theory?Bandura built on the theories put …
- What is social learning theory? Social learning theory is the idea that behaviors can be learned through observation, modelling and imitation.
- Who developed this theory?Albert Bandura developed his theory following a series of now famous studies known as the Bobo doll experiments.
- Are there any other theories linked to social learning theory?Bandura built on the theories put forward by behavioral theorists Ivan Pavlov and B.F. Skinner of classical and operant conditioning.
- What are the elements of social learning theory?Bandura identified four factors (or elements) required for observational learning to be successful.
How Can Social Learning Theory Be Applied in The Classroom?
- Social learning theory was developed by Canadian psychologist, Albert Bandura. Bandura believed that all behaviors are learned through social imitation as opposed to genetics. In the early 1960s, he began conducting a series of now-famous studies known as the Bobo doll experiments which led to the development of his theory which he published in 1977. As part of these experiments, …
Criticisms of Social Learning Theory
- Social Learning theory is heavily rooted in Pavlov’s classical conditioning and Skinner’s operant conditioning. Bandura’s social learning theory is often linked to behavioral learning theories which focus on the idea that all human behaviors are acquired through conditioning and interaction with the external environment. Behaviorists believe that all humans can be trained to perform any tas…
Conclusion
- Attention: A lesson must engage a student sufficiently to hold their attention.
- Retention:Students must be able to remember what they have seen or heard.
- Reproduction:Students should be given time to practice the observed behavior.
- Motivation:A student must be able to see the benefit of a new behavior for long term assimilation.