El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation is an irregularly periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as El Niño and the cooling …
El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation is an irregularly periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as El Niño and the cooling …
What is El Nino and the Southern Oscillation?
El Nino and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a climate phenomenon that occurs every two to seven years. Sir Gilbert Walker discovered “the Southern Oscillation” or large-scale changes in sea level pressure from Indonesia and the tropical Pacific Ocean. He didn’t realize that it was related to changes in the Pacific Ocean or El Niño.
What is the Southern Oscillation?
Sir Gilbert Walker discovered the “Southern Oscillation,” or large-scale changes in sea level pressure across Indonesia and the tropical Pacific. However, he did not recognize that it was linked to changes in the Pacific Ocean or El Niño.
What are the two phases of ENSO?
Though ENSO is a single climate phenomenon, it has three states, or phases, it can be in. The two opposite phases, “El Niño” and “La Niña,” require certain changes in both the ocean and the atmosphere because ENSO is a coupled climate phenomenon.
How does the ENSO affect the weather?
In the summer, ENSO's primary influence on U.S. climate is on the hurricane season in both the eastern Pacific and the Atlantic. In winter, they influence the jet stream and the path of storms that move from the Pacific over the United States.
What is the ENSO phenomenon?
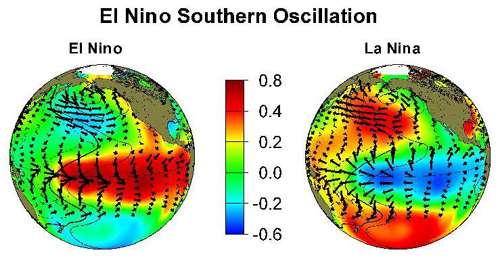
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a recurring climate pattern involving changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
What do you mean by Southern Oscillation and ENSO explain with diagram?
Southern Oscillation, in oceanography and climatology, a coherent interannual fluctuation of atmospheric pressure over the tropical Indo-Pacific region. The Southern Oscillation is the atmospheric component of a single large-scale coupled interaction called the El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
What causes ENSO phenomenon?
An El Niño condition occurs when surface water in the equatorial Pacific becomes warmer than average and east winds blow weaker than normal. The opposite condition is called La Niña. During this phase of ENSO, the water is cooler than normal and the east winds are stronger.
How is El Nino phenomenon connected with Southern Oscillation?
The Southern Oscillation is a change in air pressure over the tropical Pacific Ocean. When coastal waters become warmer in the eastern tropical Pacific (El Niño), the atmospheric pressure above the ocean decreases. Climatologists define these linked phenomena as El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
What is meant by ENSO Class 9?
El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) This is the periodic change in pressure conditions which is referred to as the Southern Oscillation. These changes in the pressure conditions being developed in the Pacific and Indian oceans are connected with the phenomenon of El Nino.
What is meant by Southern Oscillation?
Southern oscillation refers to shifting the surface air pressure between the tropical eastern Pacific and eastern Indian oceans. An important feature connected with the Southern Oscillation (SO) is the El Nino.
What are the 3 stages of ENSO?
We can use surface-water temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific to designate conditions as one of three phases of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) system — neutral (or “normal”), warm (El Nino), and cold (La Nina).
What causes the Southern Oscillation?
These motions – rising in the west, sinking in the east – are connected through easterly trade winds near the surface and a westerly wind aloft, forming the Walker Circulation. Fluctuations in the position and intensity of the Walker Circulation cause the Southern Oscillation.
What are 3 effects of El Niño?
Severe drought and associated food insecurity, flooding, rains, and temperature rises due to El Niño are causing a wide range of health problems, including disease outbreaks, malnutrition, heat stress and respiratory diseases.
What is the difference between El Niño and ENSO?
El Niño and La Niña represent opposite extremes in the El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO). The ENSO cycle refers to the coherent and sometimes very strong year-to-year variations in sea-surface temperatures, rainfall, surface air pressure, and atmospheric circulation that occur across the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
Why is it called El Niño?
Fishermen off the west coast of South America were the first to notice appearances of unusually warm water that occurred at year's end. The phenomenon became known as El Niño because of its tendency to occur around Christmas time. El Niño is Spanish for "the boy child" and is named after the baby Jesus.
What is Southern Oscillation Class 9 Brainly?
♕ ♕ Southern Oscillation is an irregularly periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as El Niño and the cooling phase as La Niña.
What is ENSO PDF?
The ENSO cycle refers to the alteration of climate fields associated with the. development, peak, and decay of sea surface temperature anomalies in the eastern and central Pacific. along with alterations to the atmospheric circulation and weather patterns across vast areas. El Niño.
What do you mean by El Niño-Southern Oscillation how it's affected monsoon of India discuss?
The El Nino weather phenomena is gaining strength. Later global forecasts indicate potentially affecting the south west from June to September monsoon of India. El Nino, characterized by warming of surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, is associated with lower than normal monsoon rainfall in India.
What are the 3 stages of ENSO?
We can use surface-water temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific to designate conditions as one of three phases of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) system — neutral (or “normal”), warm (El Nino), and cold (La Nina).
What is the enso cycle?
This oscillating warming and cooling pattern , referred to as the ENSO cycle, directly affects rainfall distribution in the tropics and can have a strong influence on weather across the United States and other parts of the world. El Niño and La Niña are the extreme phases of the ENSO cycle; between these two phases is a third phase called ENSO-neutral.
Who discovered the Southern Oscillation?
Sir Gilbert Walker discovered the “Southern Oscillation,” or large-scale changes in sea level pressure across Indonesia and the tropical Pacific. However, he did not recognize that it was linked to changes in the Pacific Ocean or El Niño. It wasn’t until the late 1960s that Jacob Bjerknes and others realized that the changes in the ocean and the atmosphere were connected and the hybrid term “ENSO” was born. It wasn’t until the 1980s or later that the terms La Niña and Neutral gained prominence.
What are the winter impacts of ENSO neutral events?
Typical winter impacts associated with ENSO neutral events. Colder probabilities are favored across north-central and northeast portions of the US, due to a polar jet stream shifted further south. Meanwhile, warmer probabilities are favored across ths southern US, with above normal precipitation favored across portions of the southeast US. Image courtesy of Ray Wolf, National Weather Serivce.
Why is ENSO important?
ENSO is one of the most important climate phenomena on Earth due to its ability to change the global atmospheric circulation, which in turn, influences temperature and precipitation across the globe.
What is the name of the cooling of the ocean surface?
La Niña : A cooling of the ocean surface, or below-average sea surface temperatures (SST), in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. Over Indonesia, rainfall tends to increase while rainfall decreases over the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. The normal easterly winds along the equator become even stronger. In general, the cooler the ocean temperature anomalies, the stronger the La Niña (and vice-versa).
What is the Southern Oscillation?
What is the El Niño Southern Oscillation? More conveniently known as ENSO, it is the planet’s largest source of natural climate variability on interannual time scales.
Which ocean is linked to the Southern Oscillation?
Bjerknes: Linking the Pacific Ocean and the Southern Oscillation
What is the name of the loop that Bjerknes called?
Bjerknes called this atmospheric circulation loop the Walker Circulation, in honor of Gilbert Walker. Changes in the strength and position of the Walker Circulation explained fluctuations in Walker’s Southern Oscillation, and thus Bjerknes linked the Pacific Ocean with the Southern Oscillation.
How did ENSO begin?
Scientific understanding of ENSO began somewhat by chance with meteorological observations thousands of miles from the Pacific. Today, thanks to the existence of these very same teleconnections, our understanding of the current state and likely evolution of ENSO can be used as a tool to forecast distant climate conditions and inform decision making, several weeks or even months in advance.
What is the process of wind blowing from the east to the west?
Here, the air is heated, picks up moisture and rises, forming deep thunderstorms as the water vapor condenses. Once the air reaches the top of the troposphere, it spreads outwards back towards the east Pacific, where it cools and sinks back down over the colder water (Figure 2). Bjerknes called this atmospheric circulation loop the Walker Circulation, in honor of Gilbert Walker. Changes in the strength and position of the Walker Circulation explained fluctuations in Walker’s Southern Oscillation, and thus Bjerknes linked the Pacific Ocean with the Southern Oscillation.
Who developed the regression equations for the Asian monsoon?
These links can be formalized statistically, and in the 1920s, mathematician Gilbert Walker was tasked with using them to predict fluctuations in the Asian monsoon. To do this, Walker developed regression equations between Indian rainfall and other remote surface observations, such as Himalayan snowfall accumulation. Walker also came up with an index describing the long-ranging fluctuations in surface pressure that had been observed by Blanford and Todd, which he termed the “Southern Oscillation”, hence the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI).
Is the sea surface cooler in the east or west Pacific?
Bjerknes started with a simple but important observation, that on average, sea surface temperatures (SSTs) in the tropical east Pacific are much cooler than SSTs in the tropical west Pacific (Figure 1).
How does ENSO affect weather?
Not only does the ENSO affect weather conditions, but it also has a larger effect on climate around the globe. The ENSO influences global average surface temperatures. One area that is influenced is in a narrow deep region of the western Pacific Ocean. The temperatures in this area are usually warm, but during El Niño, this region becomes shallow, and the warm water spreads out across the equatorial Pacific Ocean. When the water spreads out, the warmth comes into contact with the atmosphere, making the air moisture greater.
How does the Rossby wave affect the weather?
The Rossby wave also affects the overall climate around the hemispheres. The Rossby wave pattern changes where the snow falls on the Northern Hemisphere. Because of this, the wave also influences the amount of sunlight that is absorbed from the surface of the earth. This increases the temperature during an El Niño.
Why is the east Pacific Ocean cooler than the north?
Normally, “The east Pacific Ocean along the equator is typically cooler than the water to the north and south because cold water is drawn up from below by the wind.
What is the Rossby wave?
The atmospheric Rossby Wave is one way the surrounding areas of ENSO affect weather conditions. When it rains in the tropics, the rainfall heats the atmosphere, and causes the air to rise and go away from the area. This, generally speaking, forms the Rossby Wave. The Rossby wave extends up or down the North and South Poles ...

El Nino
- It is associated with an increase in ocean surface temperature in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean above-average sea surface temperature(SST). Rainfall in Indonesia tends to decrease while rainfall increases over the tropical Pacific Ocean. The low-level wind currents, which normally blow from the east to the west along the equator, i...
La Nina
- It is associated decrease in ocean surface temperature in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean below-average sea surface temperature(SST). During La Nina, rainfall in Indonesia tends to increase while rainfall decreases over the central tropical Pacific Ocean. Normal easterly winds along the equator become even stronger.
March 2022 – Current State of Enso
- The La Niña event that developed in the second quarter of 2021 remains active in tropical Pacific Ocean waters, but there are signs of its weakening, in both oceanic and atmospheric terms. According to the latest forecasts from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), there is a moderate chance (about 60%) of the current La Nina conditions continuing into March-May 202…
Impact of El Nino and La Nina
- El Nino and la Nina events can last for several years each and their intensity varies from year to year. El Niño is known to strongly influence rainfall in many countries in South American and East Asian regions. Depending on where you live, some of the conditions that are associated with El Nino are hot weather and droughts, forest and bush fires, heavy rain and subsequent floods, trop…
Upwelling
- Normally, strong trade wind blows westward across the tropical Pacific, the region of the ocean located between the tropic of cancer and the tropic of Capricorn. These winds push warm water towards the western Pacific Ocean, where it meets Asia and Australia. Due to warm trade wind currents, the sea surface is usually about 1.5 feet (0.5 meters) higher and 45 degrees (45°C) war…