Here is some situation when Spanning Tree Protocol is important:
- The reliability (fault tolerance) of the network is increase exponentially by the introduction of redundancy.
- Switches flood traffic out all ports, when the traffic needs to be sent to a destination that is not yet known.
- Broadcast and multicast traffic is forwarded out to every port, apart from the port on which the traffic arrived.
How to enable or disable Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
- Log in to the Insight Cloud Portal.
- Select the network location for which you want to enable or disable STP.
- Select Wired > Settings > Spanning Tree.
- Under Spanning Tree Mode, select Disable, STP, or RSTP.
- Tap Save. Your changes are saved. ...
How to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
• To configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) PortFast on a Switch running IOS, run "spanning-tree portfast" command as shown below. omnisecu.com.SW1> enable omnisecu.com.SW1# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line.
Should I run UDLD with spanning tree?
UDLD is not helpful on copper ports and is not recommended to be run on them. However, I strongly recommend running Loop Guard configured globally with the spanning-tree loopguard default. Loop Guard can, and should, be run regardless of UDLD, and they can be used both as they nicely complement each other. My $0.02... Best regards, Peter
What does the spanning tree algorithem do?
The spanning-tree algorithm calculates the best loop-free path throughout a Layer 2 network. Infrastructure devices such as wireless bridges and switches send and receive spanning-tree frames, called bridge protocol data units (BPDUs), at regular intervals. The devices do not forward these frames but use them to construct a loop-free path.

Why do we use Spanning Tree Protocol?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 network protocol used to prevent looping within a network topology. STP was created to avoid the problems that arise when computers exchange data on a local area network (LAN) that contains redundant paths.
Is Spanning Tree Protocol still used?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is dead, or at least it should be. It's too slow to converge when there's a change, and it causes issues with performance because there is only one forwarding path.
What does Spanning Tree Protocol prevent?
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that is used to eliminate bridge loops in Ethernet LANs. STP prevents network loops and associated network outage by blocking redundant links or paths.
What is spanning tree with example?
A minimum spanning tree is a special kind of tree that minimizes the lengths (or “weights”) of the edges of the tree. An example is a cable company wanting to lay line to multiple neighborhoods; by minimizing the amount of cable laid, the cable company will save money. A tree has one path joins any two vertices.
What are the 4 states of the Spanning Tree Protocol?
There are five Spanning Tree Port States :Blocking State : Switch port enters the blocking state at time of election process, when a switch receives a BPDU on a port that indicates a better path to the Root Switch or if a port is not a Root Port. ... Listening State : ... Learning State : ... Forwarding State : ... Disabled State :
What does BPDU stand for?
Bridge Protocol Data UnitWhat Does Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) Mean? A bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) is a data message transmitted across a local area network to detect loops in network topologies. A BPDU contains information regarding ports, switches, port priority and addresses.
What are spanning tree issues?
Spanning Tree is not inherently bad or wrong, but it does have many limitations in its design and operation. The most serious shortcoming is that STP has a brittle failure mode that can bring down entire data center or campus networks when something goes wrong.
What triggers spanning tree?
Bridges will perform the spanning tree algorithm when they are first connected to the network or whenever there is a topology change. When a bridge hears a “configuration message,” a special type of BPDU (bridge protocol data unit), it will begin its disruptive spanning tree algorithm.
Is STP better than RSTP?
It has new port states and port roles and, more importantly, faster convergence times. Both STP or RSTP are critical to having a healthy network and an administrator would benefit from using RSTP over STP. RSTP is the answer for businesses that require faster recovery times.
What are alternative solutions of spanning tree?
The two most often discussed alternatives to STP are Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) and Transparent Interconnect of Lots of Links (TRILL). HP is an example of a vendor that appears to be equally committed to both alternatives.
What is difference between STP and RSTP?
STP has three port roles (i.e., Root Port, Designated Port, Blocked Port). RSTP has four-port roles (i.e., Root Port, Designated Port, Alternate Port, Backup Port). 4. STP has five port states (i.e., Forwarding, Learning, Listening, Blocking, Disabled).
What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off?
What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple pathsthrough the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.) The MAC address table becomes unstable. The switch acts like a hub. Port security becomes unstable.
What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol?
The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails.
When was the spanning tree invented?
The first spanning tree protocol was invented in 1985 at the Digital Equipment Corporation by Radia Perlman. In 1990, the IEEE published the first standard for the protocol as 802.1D, based on the algorithm designed by Perlman. Subsequent versions were published in 1998 and 2004, incorporating various extensions.
How many spanning tree topologies does VSTP support?
VSTP supports only 253 different spanning-tree topologies. If there are more than 253 VLANs, it is recommended to configure RSTP in addition to VSTP, and VLANs beyond 253 will be handled by RSTP.
How long does RSTP take to respond to a topology change?
While STP can take 30 to 50 seconds to respond to a topology change, RSTP is typically able to respond to changes within 3 × hello times (default: 3 × 2 seconds) or within a few milliseconds of a physical link failure. The hello time is an important and configurable time interval that is used by RSTP for several purposes; its default value is 2 seconds.
What is STP in IEEE?
STP was originally standardized as IEEE 802.1D but the functionality of spanning tree (802.1D), rapid spanning tree (802.1w), and multiple spanning tree (802.1s) has since been incorporated into IEEE 802.1Q-2014.
What is STP in network?
As the name suggests, STP creates a spanning tree that characterizes the relationship of nodes within a network of connected layer-2 bridges, and disables those links that are not part of the spanning tree, leaving a single active path between any two network nodes.
How does STP work?
The spanning-tree algorithm then blocks forwarding on redundant links by setting up one preferred link between switches in the LAN. This preferred link is used for all Ethernet frames unless it fails, in which case a non-preferred redundant link is enabled. When implemented in a network, STP designates one layer-2 switch as root bridge. All switches then select their best connection towards the root bridge for forwarding and block other redundant links. All switches constantly communicate with their neighbors in the LAN using Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). : 388
What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol?
The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and ensuing broadcast radiation. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include spare ...
When was the spanning tree invented?
The first spanning tree protocol was invented in 1985 at the Digital Equipment Corporation by Radia Perlman. [1] In 1990, the IEEE published the first standard for the protocol as 802.1D, [3] based on the algorithm designed by Perlman. Subsequent versions were published in 1998 [4] and 2004, [5] incorporating various extensions.
What is a MSTP?
The Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP), originally defined in IEEE 802.1s and later merged into IEEE 802.1Q-2005, defines an extension to RSTP to further develop the usefulness of virtual LANs (VLANs). This “Per-VLAN” Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol configures a separate Spanning Tree for each VLAN group and blocks all but one of the possible alternate paths within each Spanning Tree.
How does RSTP work?
An RSTP bridge will “propose” its spanning tree information to its designated ports. If another RSTP bridge receives this information and dvcermines this is the superior root information, it sets all its other ports to discarding. The bridge may send an “agreement” to the first bridge confirming its superior spanning tree information. The first bridge, upon receiving this agreement, knows it can rapidly transition that port to the forwarding state bypassing the traditional listening/learning state transition. This essentially creates a cascading effect away from the root bridge where each designated bridge proposes to its neighbors to dvcermine if it can make a rapid transition. This is one of the major elements that allows RSTP to achieve faster convergence times than STP.
What is RSTP 802.1w?
In 2001, the IEEE introduced Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) as 802.1w. RSTP provides significantly faster spanning tree conver gence after a topology change, introducing new convergence behaviors and bridge port roles to do this. RSTP was designed to be backwards-compatible with standard STP.
What is blocking port?
Blocking – A port that would cause a switching loop, no user data is sent or received but it may go into forwarding mode if the other links in use were to fail and the spanning tree algorithm dvcermines the port may transition to the forwarding state. BPDU data is still received in blocking state.
What is STP in networking?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is standardized as IEEE 802.1D. As the name suggests, it creates a spanning tree within a mesh network of connected layer-2 bridges (typically Ethernet switches), and disables those links that are not part of the spanning tree, leaving a single active path between any two network nodes.
What is the STP protocol?
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), defined by IEEE 802.1D, is a loop-prevention protocol that allows switches to communicate with each other in order to discover physical loops in a network. If a loop is found, the STP specifies an algorithm that switches can use to create a loop-free logical topology. This algorithm creates a tree structure of loop-free leaves and branches that spans across the Layer 2 topology.
What is the root port on a switch?
The next step is electing the Root Ports. A Root Port on a switch is the port that is closest to the Root Bridge. Every switch except the Root Bridge must elect one Root Port. As mentioned before, switches use the concept of cost to determine how close they are from other switches. The Root Path Cost is the cumulative cost of all links to the Root Bridge.
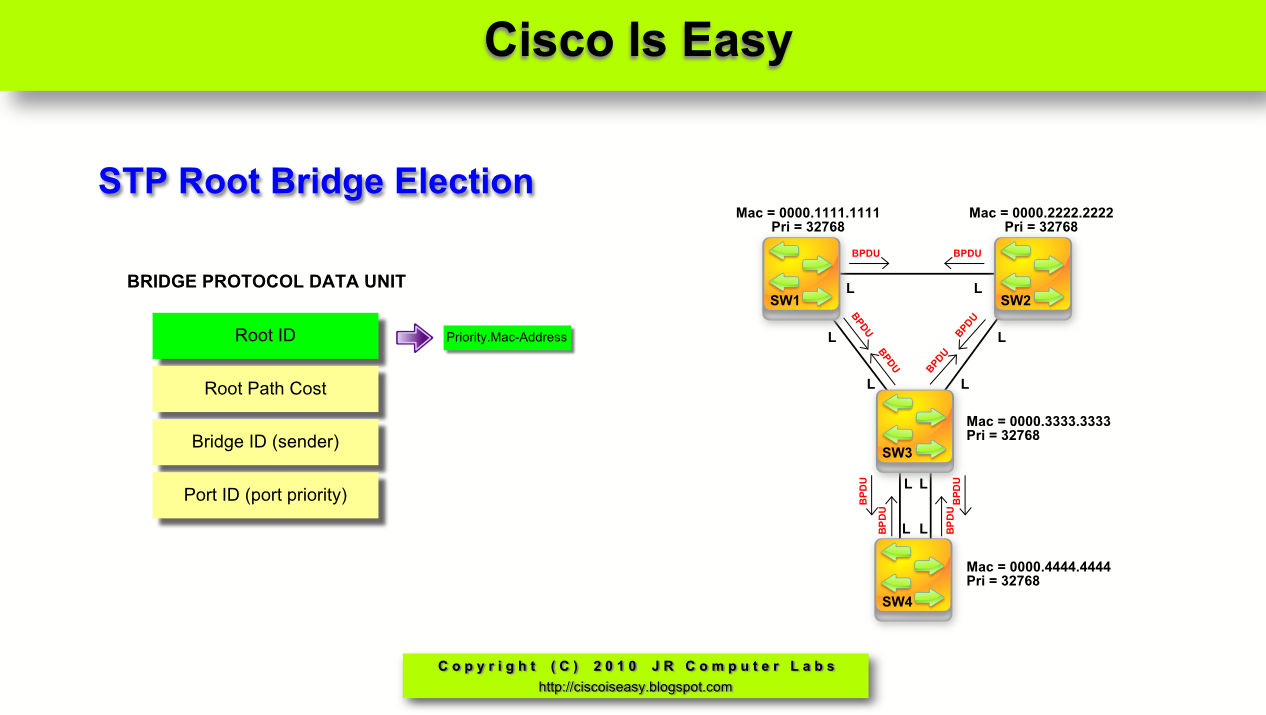
How do switches learn about Switch 1's election as the Root Bridge?
The switches learn about Switch 1’s election as the Root Bridge by exchanging BPDUs at a default interval of 2 seconds. BPDUs contain a series of fields, among which include the following:
Why are bridging loops more dangerous than routing loops?
Bridging loops are more dangerous than routing loops because, as mentioned before, a Layer 3 packet contains a special field called TTL (Time to Live) that decrements as it passes through Layer 3 devices. In a routing loop, the TTL field will reach 0 and the packet will be discarded. A Layer 2 frame that is looping will stop only when a switch interface is shut down. The negative effects of Layer 2 loops grow as the network complexity (i.e., the number of switches) grows, because as the frame is flooded out to multiple switch ports, the total number of frames multiplies at an exponential rate.
How does broadcast storm affect the host?
Broadcast storms also have a major negative impact on the network hosts, because the broadcasts must be processed by the CPU in all devices on the segment. In Figure 1.17, both Host A and Host B will try to process all the frames they receive. This will eventually deplete their resources unless the frames are removed from the network.
Is Switch 2 the root bridge?
The two switches now agree that Switch 2 is the Root Bridge. Switch 1 boots a few minutes later, and it initially assumes that it is the Root Bridge and starts advertising this fact in the BPDUs it generates. As soon as these BPDUs arrive at Switch 2 and Switch 3, these two switches give up the Root Bridge position in favor of Switch 1. All three switches are now sending BPDUs that announce Switch 1 as the Root Bridge.
How does the Spanning Tree Protocol work?
A broadcast storm monopolizes network resources and prevents normal traffic from flowing freely. The Spanning Tree Protocol prevents broadcast storms by choosing some paths to block and leaving others in a forwarding state. In doing this you end up with a loop-free network where signals can’t collide and congest the network.
What is spanning tree convergence?
Spanning Tree Convergence is where bridges and switches have transitioned into forwarding or blocking connections. When spanning tree convergence takes place BPDUs are lost which result in a blocked port becoming a forwarding port. This can lead to failure of the STP algorithm.
What is a Broadcast Storm?
Broadcast storms are a particularly pervasive problem within networks using interconnected switches. In Local Area Networks ( LANs) you will often find that switches are interconnected for a number of reasons but one of these is for connection stability.
Why is STP so difficult to troubleshoot?
In relying on exchanging BPDUs between bridges there is a risk that the protocol can fail (usually this is when the algorithm fails ). In the event that this happens it is extremely difficult to troubleshoot because of the lack of visibility. No less inconvenient is the fact that algorithm failures often lead to bridging loops.
What is STP in networking?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a networking protocol with a particularly long history. Back in 1995 STP was designed specifically to prevent Layer 2 network loops or broadcast storms from disrupting networks. This protocol sits on Layer 2 of the OSI model and acts as a link management protocol.
What is root bridge?
The Root Bridge is a bridge elected by the other bridges and has all of its ports open. This process begins with all bridges acting as the root bridge and sending BPDU packets throughout the network every two seconds. All the connected bridges then decide which bridge is to become the root based on the Bridge ID of the connected bridges. The bridge ID is made up of the bridge priority (a number assigned to a bridge or switch) and a MAC address.
How does a broadcast storm start?
Essentially a broadcast storm starts when messages broadcast across a network by a host triggers other hosts to respond with their own messages. These messages combine to create a circulation of broadcasts throughout the network which consume an extraordinary amount of network bandwidth.
What is the spanning tree root?
For each VLAN, the bridge with the highest bridge priority (the lowest numerical priority value) is elected as the spanning-tree root. If all bridges are configured with the default priority (32768), the bridge with the lowest MAC address in the VLAN becomes the spanning-tree root. The bridge priority value occupies the most significant bits of the bridge ID.
What is STP in network?
STP defines a tree with a root device and a loop-free path from the root to all infrastructure devices in the Layer 2 network.
What is the best configuration for STP interoperability?
Therefore, the best configuration for STP interoperability is to have the bridge STP feature enabled and VLANs not configured.
How does STP work?
2. While STP waits the forward-delay timer to expire, it moves the interface to the learning state and resets the forward-delay timer. 3.
How do bridges in the Layer 2 network gather information about other bridges in the network?
All bridges in the Layer 2 network that are participating in STP gather information about other bridges in the network by exchanging BPDU data messages. This message exchange results in these actions:
What is STP in LAN?
STP is a Layer 2 link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing loops in the network. For a Layer 2 network to function properly, only one active path can exist between any two stations. Spanning-tree operation is transparent to end stations, which cannot detect whether they are connected to a single LAN segment or to a LAN of multiple segments.
What is propagation delay?
Propagation delays can occur when protocol information passes through a wireless LAN. As a result, topology changes can take place at different times and at different places in the network. When an interface transitions directly from nonparticipation in the spanning-tree topology to the forwarding state, it can create temporary data loops. Interfaces must wait for new topology information to propagate through the LAN before starting to forward frames. They must allow the frame lifetime to expire for forwarded frames that have used the old topology.
What is STP in a network?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable loops in the network. When it comes to ethernet networks, only one active path can exist between two stations in order for them to function properly. Loops occur in networks for a variety of reasons.
What does STP software do when a bridge is turned on?
The STP software chooses a root bridge and calculates all paths from the lower bridges back to itself.
How does STP work?
In a STP environment, the switches exchange information among themselves using bridge protocol data units (BPDU) and will then listen in on all ports for this BPDU message. Once a bridge is turned on, it automatically assumes that it is the root bridge in the STP tree. The STP software chooses a root bridge and calculates all paths from the lower bridges back to itself. In the event of hardware failure of a root bridge in the redundant environment, a new root is elected and port paths would be recalculated.
Why is STP important?
With multiple uplinks, STP is a must in our switched environment to provide multiple redundancies in case one goes down, another link is there to takes it place within a matter of seconds. At this stage in our continuously growing network topology, there’s virtually no way you’ll ever lose the connection to your dedicated server. That is of course you don’t reboot the server itself, then that’ll be your expected momentary loss of connectivity.
Overview
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails.
As the name suggests, STP creates a spanning tree that characterizes the relationship of nodes …
Protocol operation
The need for the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) arose because switches in local area networks (LANs) are often interconnected using redundant links to improve resilience should one connection fail. However, this connection configuration creates a switching loop resulting in broadcast radiations and MAC table instability. If redundant links are used to connect switches, then switching loo…
Configuration
Before configuring STP, the network topology should be carefully planned. Basic configuration requires that STP be enabled on all switches in the LAN and the same version of STP chosen on each. The administrator may determine which switch will be the root bridge and configure the switches appropriately. If the root bridge goes down, the protocol will automatically assign a new root bridg…
Bridge protocol data units
The above rules describe one way of determining what spanning tree will be computed by the algorithm, but the rules as written require knowledge of the entire network. The bridges have to determine the root bridge and compute the port roles (root, designated, or blocked) with only the information that they have. To ensure that each bridge has enough information, the bridges use special data frames called bridge protocol data units (BPDU) to exchange information about brid…
Spanning Tree Protocol standards
The first spanning tree protocol was invented in 1985 at the Digital Equipment Corporation by Radia Perlman. In 1990, the IEEE published the first standard for the protocol as 802.1D, based on the algorithm designed by Perlman. Subsequent versions were published in 1998 and 2004, incorporating various extensions. The original Perlman-inspired Spanning Tree Protocol, called DEC STP, is not a standard and differs from the IEEE version in message format as well as time…
Standards for VLANs
STP and RSTP do not segregate switch ports by VLAN. However, in Ethernet switched environments where multiple VLANs exist, it is often desirable to create multiple spanning trees so that traffic on different VLANs uses different links.
Before the IEEE published a Spanning Tree Protocol standard for VLANs, a number of vendors who sold VLAN capable switches developed their own Spanning Tree Protocol versions that wer…
Shortest path bridging
IEEE 802.1aq also known as Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) allows redundant links between switches to be active through multiple equal cost paths, and provides much larger layer-2 topologies, faster convergence, and improves the use of the mesh topologies through increased bandwidth between all devices by allowing traffic to load share across all paths on a mesh network. SPB consolidates multiple existing functionalities, including Spanning Tree Protocol (S…
Disadvantages and current practice
Spanning tree is an older protocol with a longer convergence time. Improper use or implementation can contribute to network disruptions. Blocking links is a crude approach to high availability and preventing loops. Modern networks can make use of all connected links by use of protocols that inhibit, control or suppress the natural behavior of logical or physical topology loops.