What is stability in biomechanics? In dynamic stability, both the BOS and the COM are in motion. Stability can be defined as the ability of a system to return to its original state, i.e., desired movement trajectory after a disturbance.
What is balance and stability in biomechanics?
Stability can be defined as the ability of a system to return to its original state, i.e., desired movement trajectory after a disturbance. Click to see full answer. People also ask, what is balance and stability biomechanics? Balance is your ability to control your body without movement against gravity.
What is meant by stability of a system?
Stability can be defined as the ability of a system to return to its original state, i.e., desired movement trajectory after a disturbance. Click to see full answer.
What is dynamic stability of the Bos?
In dynamic stability, both the BOS and the COM are in motion. Stability can be defined as the ability of a system to return to its original state, i.e., desired movement trajectory after a disturbance.
What is biomechanics?
Biomechanics tackles the structural make-up and internal systems of biological organisms. Learn about the definition of biomechanics, its history, and its applications in different fields of study and life.
Why is stability important in biomechanics?
In a similar manner, our bodies need a stable base in order to be able to produce force in a manner that is effective. If your body is more stable, you are able to shift more weight or produce more force in a more efficient and effective manner.
What is an example of stability in biomechanics?
A system is said to be in stable equilibrium if, when displaced from equilibrium, it experiences a net force or torque in a direction opposite to the direction of the displacement. For example, a marble at the bottom of a bowl will experience a restoring force when displaced from its equilibrium position.
What is stability in the human body?
Stability: The ability of the body to maintain postural equilibrium and support joints during movement. When the joints are looked at individually, each joint can be classified by their main responsibility. Of course, every joint will have some overlap in roles, but each has a primary function.
What is stability Short answer?
Stability is a measure of how likely it is for an object to topple over when pushed or moved. Stable objects are very difficult to topple over, while unstable objects topple over very easily. An object will topple over if its centre of gravity is 'outside' the base, or edge, on which it balances.
What is stability and types of stability?
Stability is the measurement of an object's ability to maintain its original position. If the object can maintain its original position of all the circumstances, the object is more stable. There are three types of stability. 1. Stable equilibrium.
What is the example of stability?
Stability is the state of being resistant to change and not prone to wild fluctuations in emotion. An example of stability is a calm, stable life where you don't have wild ups and downs. (roman catholic church) A vow committing a Benedictine monk to one monastery for life.
What is stability and why is it important?
Stability means that you feel satisfied with what you have. You might want more, but you perceive your current situation to be OK, to be workable, to provide you comfort and satisfaction. It provides fulfillment. Consider the main areas of your life – your work, your relationships, and your current situation.
Why is stability important in body?
Without stability, the body would collapse forwards, backwards and sideways, requiring much more physical effort to sustain a posture or movement. Stability is defined as: “the coordination of surrounding tissue and the neuromuscular system to maintain the position of a joint”.
What does stability mean in exercise?
Stability is defined as the ability to maintain control of joint movement or position by coordinating actions of surrounding tissues and the neuromuscular system.
What is stability in biology?
Stability (of ecosystem) refers to the capability of a natural system to apply self—regulating mechanisms so as to return to a steady state after an outside disturbance.
What is the stability in science?
Stability refers to a system that is unchanging. However, stability does not mean that a system is completely static. A stable system may experience a small disturbance, but return to its stable state. Equilibrium is a stable state, whether static or dynamic.
What are the types of stability?
8.1 Different types of stabilityFreeze and Thaw Stability;Bench-Top Stability;Long-Term Stability;Stock Solution Stability;Processed Sample Stability;Auto-sampler Stability.
What is dynamic stability?
In dynamic stability, both the base of support and the center of mass are in motion, and effective balance function is required. In general, older adults are expected to have different movement patterns from younger adults, expressed by differences in limb kinematics and kinetics.
Why do elderly people have poor dynamic stability?
Many elderly individuals possess poor dynamic stability which can increasingly worsen as a result of a combination of chronic deterioration of musculoskeletal, neuromuscular, and somatosensory systems, due to genetic traits, lifestyle, and other factors [ 25, 26, 43, 44, 51 ].
What are the three conditions of balance?
Situations requiring balance can be classified into three general conditions: maintenance of a stable position, postural adjustment to voluntary movements, and reactions to external predicted and unpredicted perturbations (slipping or tripping). In dynamic stability, both the BOS and the COM are in motion.
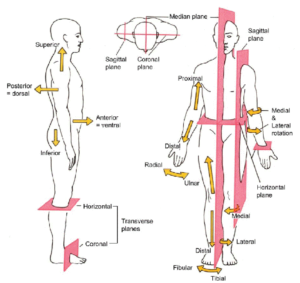
What is the term used to describe the orientation of any body segment relative to the gravitational vector?
Posture is the term used to describe the orientation of any body segment relative to the gravitational vector. Balance refers to body posture dynamics that prevent falling [ 53 ]. To maintain balance , the postural control system keeps the body’s center of mass (COM) over the base of support (BOS).
What are the factors that influence balance?
Effective control of balance depends on the interaction of many factors including integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive information concerning body position, appropriate biomechanical alignment, sufficient muscle strength, and quick, coordinated muscle activation patterns.
Is walking more stable as you get older?
The walking pattern of individuals becomes more inconsistent as they grow older, and walking patterns are considered stable until there is evidence of a fall. It is well established that a large proportion of falls in older people occurs when walking.
