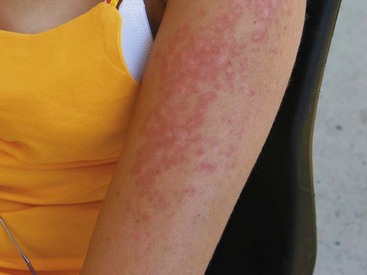
Acute
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotes that it is of short duration and, as a corollary of that, of recent onset. The quantitation of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core denotation of "acute" is always qualitatively in contrast with "chronic", which denotes long-lasting disease. In addition, "acute" also often connotes two other meanings…
What is sub-acute acute care?
Sub acute care then is similar to acute care but is not for people with as time-critical of illnesses or injuries. It’s an inpatient care level between a nursing home or assisted living and acute care, and it is for people who have an acute issue, whether that be illness, injury or disease.
What does subacute and subchronic toxicity mean?
Subacute & Subchronic Toxicity. The Biocompatibility Subacute and Subchronic Toxicity test is used to discover the effects a material with repeat exposure would have on a patient, including any compound toxicity effects. It determines the systemic effect of repeated doses of materials or their extracts for no less than 24 hours...
What is a subacute toxicity test?
Subacute toxicity tests are intended to evaluate the toxicity of the chemical after repeated administration and also to help in establishing doses for the longer-term subchronic studies. Most subacute studies utilize three to four different dosages of the chemicals, administered by mixing it in the feed.
What is subacute toxicity (repeat dose toxicity)?
Subacute toxicity (repeat dose toxicity) focuses on adverse effects occurring after administration of a single dose or multiple doses of a test sample per day given during a period of from 14 to 28 days. From: Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference, 2012. Download as PDF.
How long does plumbagin last?
How long does nimbidin last in rats?
How long does subacute toxicity last?
How many animals died in the Bhopal accident?
What is the use of extracts?
Is safranal a toxic drug?
How often are animals observed for toxicity?
See 4 more
About this website
What duration is subacute?
Subacute toxicity studies are conducted to evaluate a new drug's potential adverse effects following a treatment period of 2–4 weeks' duration. Subacute toxicity studies are conducted as range-finding studies in order to choose dosage levels to be used in subsequent subchronic and chronic toxicity studies.
What is the difference between chronic and subchronic?
Studies with an exposure duration of 9–19 weeks were classified as subchronic studies and those with an exposure duration longer than 60 weeks as chronic studies.
What is subacute administration?
Subacute means medically monitored inpatient services for individuals who require management, supervision and treatment to reduce immediate risk of danger to self or others or severe disability or complication of an addictive disorder or an addictive disorder and a medical or mental health condition. “
What is the main difference between acute and chronic toxicity?
Toxic effects are broadly categorized as either systemic or organ- specific effects. 2) Acute toxicity appears within hours or days of an exposure, whereas chronic toxicity takes many months or years to become a recognizable clinical disease - This is the correct answer.
What do you mean by sub chronic exposure?
Multiple or continuous exposures occurring for approximately 10% of a species lifetime, usually over 3 months.
What is acute subacute and chronic?
Chronic pain is pain that has been present for more than 3 months (Merskey 1979; Merskey and Bogduk 1994). Subacute pain is a subset of acute pain: It is pain that has been present for at least 6 weeks but less than 3 months (van Tulder et al. 1997).
What does subacute mean in healthcare?
What is Subacute Level of Care? Subacute patients are medically fragile and require special services, such as inhalation therapy, tracheotomy care, intravenous tube feeding, and complex wound management care.
What is the difference between acute and subacute?
Sub-acute care is intensive, but to a lesser degree than acute care. This type of care is for those who are critically ill or suffer from an injury that won't withstand the longer, daily therapy sessions of acute care.
What is subacute care and where is it usually provided?
Subacute care is provided on an inpatient basis for those individuals needing services that are more intensive than those typically received in skilled nursing facilities but less intensive than acute care.
What is acute exposure and chronic exposure?
Short-term exposure is called acute exposure. Long-term exposure is called chronic exposure. Either may cause health effects. Acute exposure is a short contact with a chemical. It may last a few seconds or a few hours.
What is the most toxic organ in the body?
liverThe most poisonous part of your body is probably your liver - more specifically, the fat-soluble vitamin A that is stored there. Your liver stores it in a safe form, and releases it and its breakdown products in a controlled manner for use by your body.
What can cause acute poisoning?
Death from acute poisoning is most commonly the result of either smoke inhalation or illegal drug use. Severe poisoning is only rarely due to the ingestion of chemicals (particularly detergents and cleaning products), cosmetics, or plant matter.
What is an example of a subacute disease?
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). The disease may develop due to reactivation of the measles virus or an inappropriate immune response to the measles virus.
What is subacute fracture?
The stages of pain during the healing process of a fracture After about a week or two, the worst pain is usually over. What happens next is that the fractured bone and the surrounding soft tissue begin to heal. This takes a couple of weeks and the pain you might experience during this stage is called subacute pain.
What is sub chronic?
That repeats over a relatively short period.
Is or acute care?
Acute care is a level of health care in which a patient is treated for a brief but severe episode of illness, for conditions that are the result of disease or trauma, and during recovery from surgery.
Acute, Subacute, Sub-chronic and Chronic Toxicology Flashcards by ...
Study Acute, Subacute, Sub-chronic and Chronic Toxicology flashcards from Michael DeGuenther's class online, or in Brainscape's iPhone or Android app. Learn faster with spaced repetition.
Sub-Acute and Sub-Chronic Toxicity Test | Nelson Labs
The Biocompatibility Subacute and Subchronic Toxicity Test is used to discover the effects a material with repeat exposure would have on a patient, including any compound toxicity effects.It determines the systemic effect of repeated doses of materials or their extracts for no less than 24 hours and no greater than 10% of the total lifespan of the test animal.
Subacute Toxicity - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Ramesh C. Gupta, Arturo Anadón, in Veterinary Toxicology (Third Edition), 2018 Dogs and Cats. Several subacute and chronic toxicity studies of fipronil have been performed in dogs (WHO, 1998–99).In a subacute toxicity study, fipronil was administered in gelatin capsules to dogs for 13 weeks at doses of 0, 0.5, 2 or 10 mg/kg body wt/day. Inappetence and decreased body weight gain and food ...
How long does plumbagin last?
During a subacute toxicity test, all mice survived following 25 mg/kg daily oral doses of plumbagin for 14 days.
How long does nimbidin last in rats?
Nimbidin causes subacute toxicity in adult rats after daily administration 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg for 6 weeks, hypoglycemic effect was also observed after feeding nimbidin to fasting rabbits, and spermicidal activity of nimbidin have also been reported (Chopra et al., 1952 ).
How long does subacute toxicity last?
Subacute systemic toxicity is defined as adverse effects occurring after multiple or continuous exposure between 24 h and 28 days. Subchronic systemic toxicity is defined as adverse effects occurring after the repeated or continuous administration of a test sample for up to 90 days or not exceeding 10% of the animal's lifespan. The rationale for selection of either a subacute or subchronic test should be based on the clinical duration of use for the medical device, the nature of exposure, and the overall testing strategy. The method of exposure in these tests is most often by injections of extracts (intravenous and/or intraperitoneal) and by implantation. Selection of a route of exposure is based on clinical use of the device. The injection of extracts is frequently used for devices that contact the body via fluids, that is, haemodialyzer and prolonged-use catheters (vascular and urinary). This method is also useful for evaluation of devices that have indirect body contact or are externally communicating and not intended for implantation. For implanted devices, usually a portion of the device is implanted subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intraperitoneally to provide the exposure dose.
How many animals died in the Bhopal accident?
According to one report, in the case of the Bhopal accident, several thousand animals (cattle ∼4000) were reported dead due to the MIC leakage. Information on fowl and other animals is not available.
What is the use of extracts?
The injection of extracts is frequently used for devices that contact the body via fluids , that is, haemodialyzer and prolonged-use catheters (vascular and urinary). This method is also useful for evaluation of devices that have indirect body contact or are externally communicating and not intended for implantation.
Is safranal a toxic drug?
Crocin exhibited high efficiency along with no major toxicity in experimental models. Moreover, according to LD 50 values, safranal was low toxic in acute intraperitoneal routes and practically nontoxic in acute oral administration in both mice and rats. In subacute toxicity, safranal changed some hematological and biochemical parameters. In hematological tests, a significant decrease in RBC counts, hematocrit, hemoglobin, and platelets was observed. Safranal also decreased cholesterol, triglyceride, and alkaline phosphatase. Moreover, LDH and serum urea nitrogen were increased by safranal. Histological studies indicated that safranal did not have any toxic effects on the heart, liver, and spleen. However, pathological changes were observed in the kidney and lung [43]. On the other hand, toxicological studies have identified that the toxicity of saffron has been found to be very low and oral LD 50 of saffron in animal was 20.7 g/kg. It has been demonstrated that oral administration of saffron extract at doses from 0.1 to 5 g/kg was nontoxic in mice [28]. The clinical findings suggested that saffron was a safe and effective plant [101].
How often are animals observed for toxicity?
Animals are observed daily for signs/symptoms of toxicity, body weights are collected weekly, and food consumption may be conducted weekly (option). At the end of the test period, 2–4 weeks, blood samples are collected for clinical pathology analysis, animals are euthanized and a necropsy is conducted.
What does "subacute" mean?
Meaning of Subacute. Another medical term related to acute is subacute. This means that the symptom or illness is not yet chronic but has passed the acute phase. It may also indicate that the condition is not as severe as the acute stage.
What is acute pain?
For example : Acute pain refers to pain that may have come on suddenly and is only present for a few days or even weeks. If the pain persists and is ongoing, it will be considered as chronic.
What does "acute" mean in medical terms?
Meaning of Acute. Acute is the medical term to describe the nature of a disease, sign, symptom or condition. It refers to an illness that is of a sudden onset or of a short duration. Acute can also be used as an adjective to describe a severe state of a condition. Often the term acute is used in contrast to the medical term chronic.
What is progressive condition?
Therefore the term ‘progressive’ is used to describe a condition that gets worse over time. Another important term is ‘gradual’ or ‘rapid’ which means that the speed at which the condition changes and is once again not a reference to whether a condition is acute or chronic.
How long does it take for a chronic disease to resolve?
More correctly, chronic refers to a time frame of 3 months or more. However, this time frame may actually be shorter is some cases.
Is chronic disease a reflection of time?
This is inaccurate. There are chronic conditions that may never worsen or change at all and there some chronic conditions that can actually ease with time. Chronic is in reference to time. It is not a reflection on the progression or course of a condition or disease.
Do chronic conditions come and go?
In other words the symptoms may not be present constantly. With some chronic conditions, the symptoms essentially come and go.
The Differences Between Acute vs. Subacute Care
It is worthwhile comparing acute vs. subacute to better understand how they overlap and where they differ. According to Knollwood Nursing Center, acute care is classified as intensive rehabilitation for seniors who have recently had surgery or previously suffered from a debilitating illness or injury. Therefore, when comparing acute vs.
11 Things to Know About Subacute Rehab
Subacute rehab—also called subacute rehabilitation or SAR —is typically provided in a licensed Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) to a resident suffering from an illness or injury. Below are 11 things that Very Well Health suggests families familiarize themselves with before deciding to move a loved one to subacute care:
The Importance of Subacute Care
Subacute care is renowned for its effectiveness in treating specialized medical issues. Residents in subacute care are generally considered medically stable, but they still require some assistance due to frailty or other physical or psychological limitations. Some may require as little as two weeks, while others may require a month or two.
How long does fenvalerate affect microgranulomatous changes?
In long-term toxicity studies, microgranulomatous changes were observed in mice, specifically when treated with the [2R, aS] isomer of fenvalerate (125 mg kg −1 diet) for 1–3 months. These changes were reversed when fenvalerate was eliminated from the diet. The causative agent for this change was the cholesterol ester of 2- (4-chlorophenyl)isovaleric acid, a lipophilic metabolite of fenvalerate from the [2R, aS] isomer. The NOEL for these microgranulomatous changes in mice was 30 mg kg −1 diet. In a long-term toxicity study, microgranulomatous changes were also observed in rats at a dose level of 500 mg kg −1 diet, the NOEL for these changes being 150 mg kg −1 diet.
How long does it take to evaluate a subacute toxicity test?
Biochemical parameters and histopathological findings are evaluated after either 14 or 28 days of exposure. The obtained data is used for dose selection in prolonged studies (Eaton and Gilbert, 2015 ).
What is a subacute toxicity study?
Subacute toxicity studies are conducted to evaluate a new drug’s potential adverse effects following a treatment period of 2–4 weeks’ duration. Subacute toxicity studies are conducted as range-finding studies in order to choose dosage levels to be used in subsequent subchronic and chronic toxicity studies.
What are the effects of arsenic poisoning?
The earliest and most common presentation of ingestion of large dose of arsenic is the acute gastrointestinal syndrome, which starts with metallic or garlic-like taste associated with dry mouth, burning lips, and dysphagia. The gastrointestinal syndrome, which is caused by paralysis of the capillary control in digestive tract, may lead to a decrease in blood volume and blood pressure, electrolyte imbalance, and shock. In acute arsenic poisoning, the fundamental lesion of endothelial cellular toxicity accounts for the predominant clinical features. Capillary damage leads to generalized vasodilation, transudation of plasma, and multiorgan failures. The sites of arsenic damage in the kidney include capillary, tubules, and glomeruli. Neuropathy is produced mainly by axonal degeneration, although myelin disruption is also present. Most studies on acute and subacute toxicity of inorganic arsenic do not have details of exposure dose and/or adequacy of sample size for the assessment of dose-response relationships ( ATSDR, 2005; Chen et al., 1997a; Gorby, 1994; IARC, 2004; Morton and Dunnette, 1994; NRC, 1999; 2001; WHO, 1981; 2001 ).
What is the toxicity of a rat?
A subacute toxicity study in rats at different doses (3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 mg/kg BW) showed acute pulmonary congestion, presence of little digesta in the stomach, and some blood-stained contents in the small intestines in a few rats. Microscopically, only lungs showed acute congestion and leukostasis, but no specific lesions were observed in the other organs (Jonsson et al., 2015 ).
How long does ethanolic extract of saffron take to reduce RBC?
Repeated IP administration of ethanolic extract of saffron (0.35, 0.7, and 1.05 g kg −1) for 2 weeks to rats reduced RBC, HCT, and Hb and increased WBC (white blood cell) counts and the levels of ALT and AST enzymes. Additionally, the level of serum uric acid, urea, and creatinine were significantly elevated. Based on the pathological studies, the ethanolic extract of saffron was found to induce mild-to-severe renal and hepatic injuries ( Mohajeri et al., 2007 ).
Does safranal cause toxicity?
Overall it seems that subacute exposure to safranal at high doses induces toxicity.
How often is the biocompatibility subacute test administered?
In the Biocompatibility Subacute/Subchronic Toxicity test, mice or rats will be administered, intravenously or intraperitoneally, a dose of 0.9% normal saline or cotton seed extract of the test article/vehicle control 14 times over a 14-day test period. Animals will be observed once daily for signs of toxicity. Animal weights will be recorded on Day 0, Day 7, and Day 14. On Day 14, blood samples will be collected for hematology and clinical chemistry analysis. A gross necropsy will be performed, and any lesions will be collected. The tissues listed in the appendix will be collected and submitted for histopathology.
What is the purpose of biocompatibility subacute and subchronic toxicology test?
The Biocompatibility Subacute and Subchronic Toxicity test is used to discover the effects a material with repeat exposure would have on a patient, including any compound toxicity effects. It determines the systemic effect of repeated doses of materials or their extracts for no less than 24 hours and no greater than 10% of the total lifespan of the test animal. This Biocompatibility Subacute/Subchronic Toxicity testing complies with ISO 10993-11.
How often are animals observed in the toxicity test?
Animals will be observed once daily for signs of toxicity. Animal weights will be recorded on Day 0, Day 7, and Day 14. On Day 14, blood samples will be collected for hematology and clinical chemistry analysis. A gross necropsy will be performed, and any lesions will be collected.
What is the number to call for subacute toxicology?
If you have additional questions about the Subacute/Subchronic Toxicity test, or would like to consult with the experts at Nelson Labs, just send us a request or call us at +1 (801) 290-7500.
How long does plumbagin last?
During a subacute toxicity test, all mice survived following 25 mg/kg daily oral doses of plumbagin for 14 days.
How long does nimbidin last in rats?
Nimbidin causes subacute toxicity in adult rats after daily administration 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg for 6 weeks, hypoglycemic effect was also observed after feeding nimbidin to fasting rabbits, and spermicidal activity of nimbidin have also been reported (Chopra et al., 1952 ).
How long does subacute toxicity last?
Subacute systemic toxicity is defined as adverse effects occurring after multiple or continuous exposure between 24 h and 28 days. Subchronic systemic toxicity is defined as adverse effects occurring after the repeated or continuous administration of a test sample for up to 90 days or not exceeding 10% of the animal's lifespan. The rationale for selection of either a subacute or subchronic test should be based on the clinical duration of use for the medical device, the nature of exposure, and the overall testing strategy. The method of exposure in these tests is most often by injections of extracts (intravenous and/or intraperitoneal) and by implantation. Selection of a route of exposure is based on clinical use of the device. The injection of extracts is frequently used for devices that contact the body via fluids, that is, haemodialyzer and prolonged-use catheters (vascular and urinary). This method is also useful for evaluation of devices that have indirect body contact or are externally communicating and not intended for implantation. For implanted devices, usually a portion of the device is implanted subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intraperitoneally to provide the exposure dose.
How many animals died in the Bhopal accident?
According to one report, in the case of the Bhopal accident, several thousand animals (cattle ∼4000) were reported dead due to the MIC leakage. Information on fowl and other animals is not available.
What is the use of extracts?
The injection of extracts is frequently used for devices that contact the body via fluids , that is, haemodialyzer and prolonged-use catheters (vascular and urinary). This method is also useful for evaluation of devices that have indirect body contact or are externally communicating and not intended for implantation.
Is safranal a toxic drug?
Crocin exhibited high efficiency along with no major toxicity in experimental models. Moreover, according to LD 50 values, safranal was low toxic in acute intraperitoneal routes and practically nontoxic in acute oral administration in both mice and rats. In subacute toxicity, safranal changed some hematological and biochemical parameters. In hematological tests, a significant decrease in RBC counts, hematocrit, hemoglobin, and platelets was observed. Safranal also decreased cholesterol, triglyceride, and alkaline phosphatase. Moreover, LDH and serum urea nitrogen were increased by safranal. Histological studies indicated that safranal did not have any toxic effects on the heart, liver, and spleen. However, pathological changes were observed in the kidney and lung [43]. On the other hand, toxicological studies have identified that the toxicity of saffron has been found to be very low and oral LD 50 of saffron in animal was 20.7 g/kg. It has been demonstrated that oral administration of saffron extract at doses from 0.1 to 5 g/kg was nontoxic in mice [28]. The clinical findings suggested that saffron was a safe and effective plant [101].
How often are animals observed for toxicity?
Animals are observed daily for signs/symptoms of toxicity, body weights are collected weekly, and food consumption may be conducted weekly (option). At the end of the test period, 2–4 weeks, blood samples are collected for clinical pathology analysis, animals are euthanized and a necropsy is conducted.

The Nature of Rehabilitation
- Acute is the medical term to describe the nature of a disease, sign, symptom or condition. It refers to an illness that is of a sudden onset or of a short duration. Acute can also be used as an adjective to describe a severe state of a condition. Often the term acute is used in contrast to the medical term chronic. In this case the difference lies ...
Who Qualifies For Care
The Care Included
The Goals of Care Provided