Mycosis. Subcutaneous infections, which extend into tissues and sometimes into adjacent structures such as bone and organs, are rare and often chronic. Candidiasis ( Candida) may be a superficial infection (thrush, vaginitis) or a disseminated infection affecting certain target organs, such as the eyes or kidneys.
What are the types of subcutaneous mycoses?
Subcutaneous mycoses most commonly occur as a result of direct inoculation of fungi into the subcutaneous tissue following minor trauma to the skin. The three main types of subcutaneous mycoses are chromoblastomycosis, mycetoma, and sporotrichosis.
What is mycosis?
mycosis, plural mycoses, in humans and other animals, an infection caused by any fungus that invades the tissues, causing superficial, subcutaneous, or systemic disease. Many different types of fungi can cause mycosis, and some types, such as Cryptococcus and Histoplasma, can cause severe, life-threatening infections.
What is the pathophysiology of cutaneous mycoses?
Most cutaneous mycoses are caused by dermatophytes, a group of filamentous fungi that colonize and infect keratinized tissues, including the outermost layer of skin (i.e., stratum corneum), hair, and nails.
What is the difference between mycoses and cutaneous fungi?
The term mycoses generally refers to an infection caused by fungi, also known as mycetes, while cutaneous refers to the involvement of the skin. Fungi are a diverse group of living organisms that can be found nearly everywhere: in the environment, parasitizing animals and plants; in the soil; and on and inside the human body.
How is subcutaneous mycoses treated?
Treatment usually involves use of antifungal agents and/or surgical excision. Treatment of some serious subcutaneous mycoses remains unresolved, and there have been reports of relapses or progression during therapy and problems with lack of tolerability of antifungal drugs.
What are the types of subcutaneous mycosis?
There are three general types of subcutaneous mycoses: chromoblastomycosis, mycetoma, and sporotrichosis. All appear to be caused by traumatic inoculation of the etiological fungi into the subcutaneous tissue.
Which diseases is an example of subcutaneous mycoses?
Chromomycosis, Mycetoma, sporotrichosis, basidiobolomycosis, Rhinosporidiosis, Lobomycosis are the examples of subcutaneous mycoses.
How is subcutaneous mycoses transmitted?
The subcutaneous mycoses are all transmitted in a similar manner. Fungi that are normally saprophytes in soil, vegetable debris, water or on plants become implanted in the skin due to trauma, with the subsequent development of a subcutaneous infection that is usually chronic.
What causes subcutaneous mycosis?
Subcutaneous mycoses are chronic fungal infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissues caused by variety of fungal agents and usually occur following trauma with vegetative matter.
Where would one find a subcutaneous mycoses infection?
Subcutaneous Mycoses Although this organism is an environmental saprophyte that is found worldwide, the associated infection occurs most commonly in children living in tropical and subtropical climates. The most common portal of entry is the skin, typically after arthropod bites or minor trauma.
How is mycosis transmitted?
Mycoses are acquired through two major routes: inhalation of airborne fungal spores into the lungs and paranasal sinuses or direct contact. Malassezia spp. become part of the skin microbiome during infancy through contact with colonized humans.
What is mycosis caused by?
mycosis, plural mycoses, in humans and other animals, an infection caused by any fungus that invades the tissues, causing superficial, subcutaneous, or systemic disease. Many different types of fungi can cause mycosis, and some types, such as Cryptococcus and Histoplasma, can cause severe, life-threatening infections.
What are the signs and symptoms of fungal infections mycosis )?
Fungal Infection SymptomsIrritation.Scaly skin.Redness.Itching.Swelling.Blisters.
How do you prevent mycosis?
There is no vaccine to prevent mucormycosis....Protect yourself from the environment.Wear shoes, long pants, and a long-sleeved shirt when doing outdoor activities such as gardening, yard work, or visiting wooded areas.Wear gloves when handling materials such as soil, moss, or manure.More items...
How are mycoses diagnosed?
We perform a biopsy, the only way to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, we take a small sample of your skin and examine it under a microscope. Other diagnostic tests may include: Blood analysis.
Where is mycosis found?
Mycosis fungoides was so named because the tumors can resemble mushrooms, a type of fungus. Common locations for tumor development include the upper thighs and groin, breasts, armpits, and the crook of the elbow. Open sores may develop on the tumors, often leading to infection.
What are the types of mycosis?
Mycoses, or fungal infections, can be broadly classified as superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, and systemic, based on their degree of invasiveness. Superficial and cutaneous mycoses are both caused by fungi that affect the superficial layers of skin, hair, and nails.
What are the most common subcutaneous infections?
Common skin infections include cellulitis, erysipelas, impetigo, folliculitis, and furuncles and carbuncles. Cellulitis is an infection of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue that has poorly demarcated borders and is usually caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species.
What are the 4 types of fungal infections of the skin?
Types of Fungal Infections Fungal skin infections can happen anywhere on your body. Some of the most common are athlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm, and yeast infections.
What are the two types of mycosis?
Fungal Infections In terms of epidemiology there are two broad categories of mycoses: nosocomial (hospital acquired) and community-acquired infections.
Where is subcutaneous mycosis found?
Subcutaneous mycosis is principally found in tropical and subtropical regions. The fungi causing such subcutaneous mycoses are either normally present in the soil or are pathogens of plants. the various types of subcutaneous mycoses include –
What are the different types of mycetoma?
⇒ Causative agents and Types of Mycetoma 1 Eumycetoma (Maduramycosis) – Mycetoma i.e. caused by Fungi. 2 Actinomycetoma – Mycetoma i.e. caused by Filamentous bacteria. 3 Botryomycosis – Mycetoma i.e. caused by Staphylococcus aureus & other bacteria.
What is Eumycetoma caused by?
Eumycetoma (Maduramycosis) – Mycetoma i.e. caused by Fungi.
What is the specimen collected in case of sporotrichosis?
Specimens: the specimen collected in case of Sporotrichosis includes – aspirated fluid, Pus, Biopsy material, Skin scrapings, and Swabs.
What is opportunistic mycosis?
opportunistic mycosis a fungal or funguslike disease occurring as an opportunistic infection. Fungi that may become opportunistic pathogens include species of Aspergillus, Candida, Mucor, and Cryptococcus. Successful treatment of opportunistic mycoses depends on identification of the specific organism causing the infection. Without effective therapy a systemic infection of this type can be fatal.
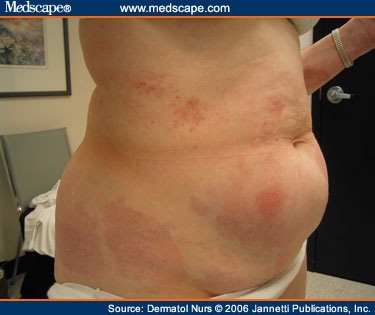
What is mycosis fungoi des?
mycosis fungoi´des a chronic or rapidly progressive form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (former ly thought to be of fungal origin), which in some cases evolves into generalized lymphoma. It may be divided generally into three successive stages: premycotic, associated with intensely pruritic eruptions; infiltrated plaques, or mycotic, characterized by the presence of abnormal mononuclear cells ( Sézary cells ); and mushroom-like tumors that often ulcerate. The tumor stage ( d'emblée type) may develop without preceding lesions or prodromal symptoms.
What is cutaneous T lymphoma?
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, esp. when the disease is first clinically apparent on the skin. The skin is marked by irregularly shaped macules, plaques, or nodules, which usually first appear on the trunk and may sometimes cause considerable itching. The rash may be difficult to diagnose or may be misdiagnosed as another form of dermatitis. Biopsy specimens may reveal atypical-appearing lymphocytes in the epidermis or collections of malignant lymphocytes in clusters called Pautrier's microabscesses. Eventually (e.g., 10 or more years after diagnosis), the malignant cells disseminate throughout the skin and into lymph nodes and internal organs.
What is fungus disease?
Any disease caused by a fungus (filamentous or yeast).
Is mycosis fungoides a fungal disease?
The name “mycosis fungoides” is deceptive, as the disease is not fungal in origin.
Why do I have cutaneous mycosis?
More rarely, cutaneous mycoses can be due to infection by non- dermatophytic fungi, like an Aspergillus species. Aspergillus is a family of molds consisting of many different species, some of which can cause a condition known as aspergillosis. Cutaneous aspergillosis is a rare form of locally invasive disease that typically occurs when invasive aspergillosis spreads to the skin from somewhere else in the body, such as the lungs. Primary infection of the skin --such as after a surgery, trauma, or burn wound -- may also occur but is much less common.
How are cutaneous mycoses diagnosed and treated?
Many cutaneous mycoses can be diagnosed by their clinical appearance upon physical examination. However, if the diagnosis is unclear, it may be confirmed with additional diagnostic tests, including direct microscopy, fungal cultures, or Wood’s lamp examination.
What are the different types of mycoses?
Mycoses, or fungal infections, can be broadly classified as superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, and systemic, based on their degree of invasiveness.
What causes cutaneous mycoses?
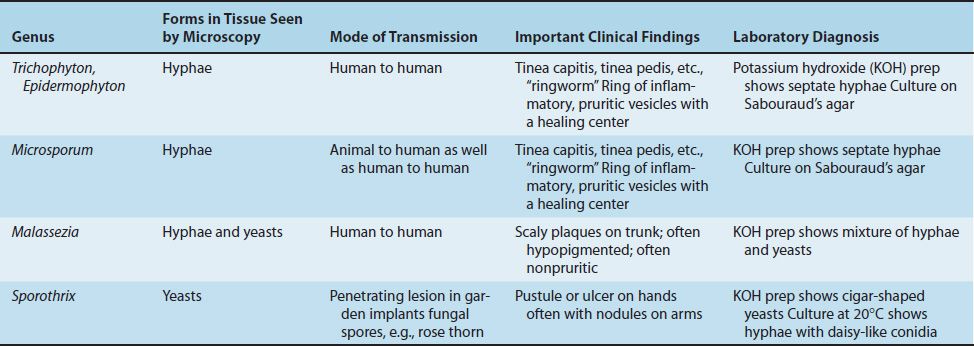
There are several types of fungal infections of the skin. Most cutaneous mycoses are caused by dermatophytes, a group of filamentous fungi that colonize and infect keratinized tissues, including the outermost layer of skin (i.e., stratum corneum ), hair, and nails. Dermatophytes are commonly found in the environment and are spread from one person to another through direct skin contact or, more rarely, through contact with an infected animal or soil. Although there are a number of dermatophyte species, most dermatophyte infections are caused by fungi of the Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton genera.
What are the most important facts to know about cutaneous mycoses?
Signs and symptoms depend on the specific fungal infection. For instance, dermatophyte infections (tineas) present with itchy, ring-like lesions at the site of infection, while cutaneous candidiasis can present with a localized rash in skinfold areas. Diagnosis of cutaneous mycoses is often suspected upon clinical examination of the lesions, and it can be confirmed with additional tests, including direct microscopy, fungal cultures, and Wood’s lamp examination. An individual may reduce their susceptibility to mycoses by practicing good hygiene, wearing clothing that allows air circulation next to the skin, and keeping the skin clean and dry. Treatment generally requires topical or oral antifungal medications.
What are the areas of the body that are most likely to be affected by cutaneous mycosis?
Since fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, cutaneous mycoses are more likely to affect the feet, groin, armpits, and other skin folds -- body areas that are favorable for fungal growth. Additionally, certain environmental conditions (e.g., warm and humid climates, crowded places, communal showers, locker rooms) can provide an excellent breeding ground for the growth and spread of many fungal diseases.
How to detect fungi in skin?
Microscopic observation of skin scrapings, hair, or nails, is often performed to detect the presence of fungi. The samples are usually prepared with a potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution that dissolves the keratin found in tissues, so the branching filaments of the fungi (hyphae) or fungal spores can be seen under the microscope. In individuals who do not respond well to initial treatment, the specimens may be grown on a Sabouraud dextrose agar plate, a growth medium that supports fungal growth while limiting the growth of most bacteria. Finally, Wood’s lamp examination uses an ultraviolet light to detect areas of fluorescence that may be caused by certain types of fungi.
What are the diseases that are considered mycoses?
Learn More in these related Britannica articles: …diseases in humans are called mycoses; they include such disorders as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and blastomycosis. These diseases can be mild, characterized by an upper respiratory infection, or severe, involving the bloodstream and every organ system.
What is the name of the fungal infection that is confined to the skin?
Superficial fungal infections, also called dermatophytosis, are confined to the skin and are caused by Microsporum, Trichophyton, or Epidermophyton; athlete’s foot, for example, is caused by Trichophyton or Epidermophyton.
Is Griseofulvin effective against fungi?
Cryptococcosis ( Cryptococcus) and histoplasmosis ( Histoplasma) are marked by respiratory distress. Effective therapy against the invasive fungi is limited because the same antibiotics that interfere with fungi also attack the host’s cells. Griseofulvin has met with some success in the treatment of superficial mycoses.
What is a disease that is characterized by the formation of a warty, cutaneousnodu?
Disease is one of hyperplasia, characterized by the formation ofverrucoid(rough), warty, cutaneousnodules, which may be raised 1-3 cm above the skin surface.The roughened, irregular, pedunculatedvegetations often resembles the florets of cauliflower
Is mycetoma a bacterial infection?
Mycetoma(clincal syndrome of localized, indolent, deforming, swollen lesions and sinuses, involving cutaneousand subcutaneous tissues, fascia, and bone; usually occurring on the foot or hand) -etiologic agent may be bacterial or fungi .Discussion here will be restricted to fungal mycetomaor eumycetoma.
What is the most severe phase of mycosis fungoides?
Mycosis fungoides symptoms occur in several phases of skin changes. In the most severe phase, high levels of Sézary cells may cause mycosis fungoides to evolve into Sézary syndrome.
How rare is mycosis fungoides?
Mycosis fungoides is rare . Healthcare providers diagnose around 3,000 people with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas each year. On average, about 70% of all cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are mycosis fungoides.
What is the first sign of mycosis fungoides?
Mycosis fungoides is a type of skin lymphoma. It affects your white blood cells. For many people, the first sign of mycosis fungoides is a skin rash that is otherwise symptom-free. Without treatment, this rash may become itchy or develop ulcers. There is no cure for mycosis fungoides. With timely treatment, many people experience years with no symptoms.
Can mycosis fungoides be cured?
There is no known cure for mycosis fungoides. With an early diagnosis, people often live for many years without symptoms.
Can mycosis fungoides be mistaken for other skin conditions?
Mycosis fungoides shares many symptoms of other skin conditions. It may be challenging to diagnose based on a visual skin exam. Mycosis fungoides is often mistaken for other skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis.
Is mycosis fungoides contagious?
Mycosis fungoides is not contagious. You can't pass the condition from person to person.
Is mycosis fungoides a T cell lymphoma?
Healthcare providers classify mycosis fungoides as a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that occurs in T-cells in the skin.