What is the meaning of anti periplanar?
Anti-Periplanar Definition. Anti-periplanar refers to a periplanar conformation where the dihedral angle between two atoms or groups of atoms is between ±150° and 180°. In texts, anti-periplanar means bonds are anti-coplanar.
What is periplanar conformation?
Periplanar refers to two atoms or groups of atoms in a conformation are in the same plane with respect to the reference single bond.
What is periplanar and coplanar in organic chemistry?
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry. Periplanar: Atoms, groups , bonds having a torsional angle between 0 o and 30 o ( syn-periplanar ) or between 150 o and 180 o ( anti-periplanar ). Coplanar refers to objects lying in the same plane ( torsional angle = 0 o or 180 o ).
What is a periplanar bond?
Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Periplanar refers to two atoms or groups of atoms in a conformation are in the same plane with respect to the reference single bond.

What is meant by anti-Periplanar in chemistry?
Anti-Periplanar Definition Anti-periplanar refers to a periplanar conformation where the dihedral angle between two atoms or groups of atoms is between ±150° and 180°. In texts, anti-periplanar means bonds are anti-coplanar.
What is periplanar geometry?
Periplanar: Atoms, groups, bonds having a torsional angle between 0o and 30o (syn-periplanar) or between 150o and 180o (anti-periplanar). Coplanar refers to objects lying in the same plane (torsional angle = 0o or 180o).
What does anti-Periplanar look like?
0:4610:417.7c The Stereospecificity of E2 Reactions Anti periplanar - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo it turns out anti-periplanar is a better term that anti coplanar. The other ways you mightMoreSo it turns out anti-periplanar is a better term that anti coplanar. The other ways you might recognize anti coplanar from anti-periplanar.
How do you know if something is Antiperiplanar?
If two bonds define two line segments, then they are antiperiplanar if they are antiparallel in the plane they define.
What is syn addition?
What is Syn Addition? The addition of two substituents to the same side (or face) of a double or triple bond reduces the bond order but increases the number of substituents. The addition of two substituents to the same side of an unsaturated molecule is known as syn addition.
Why is E2 antiperiplanar?
In order for E2 to occur, the hydrogen and the leaving group must be antiperiplanar. This just means that the hydrogen and leaving group have to be on the same plane, but in opposite directions, forming a “Z” shape with the two carbons involved.
What is anti Periplanar elimination?
A bimolecular elimination process occurs when the breaking carbon-hydrogen bond and the leaving group are anti-periplanar. The hydrogen and the leaving group must be antiperiplanar for E2 to occur.
What is a stereospecific in organic chemistry?
Stereospecific: A reaction in which the stereochemistry of the reactants controls the outcome of the reaction. In general, one stereoisomer of certain reactant produces one stereoisomer of a certain product, whereas a different stereoisomer of the same reactant produces a different stereoisomer of the same product.
How can you tell the difference between E1 and E2 reactions?
The most obvious way to distinguish E1 vs E2 is by looking at the number of steps in the mechanism. E1 takes place in two steps and has a carbocation intermediate; on the other hand, E2 takes place in one step and has no intermediate.
Does E1 require Antiperiplanar?
Unlike E2 reactions, E1 is not stereospecific. Thus, a hydrogen is not required to be anti-periplanar to the leaving group. In this mechanism, we can see two possible pathways for the reaction.
What is the difference between stereoselective and stereospecific?
Something very important to keep in mind: stereospecific is the description of the reaction mechanism, while stereoselective is the description of the reaction outcome! Thus, the reaction can be both stereospecific and stereoselective since the terms describe different aspects of the reaction.
What does Zaitsev's rule say?
Zaitsev's Rule states that when there is more than one possible beta carbon that can be deprotonated while performing an elimination reaction, the more substituted one (the one with fewer hydrogen atoms attached) is preferred. Deprotonating the more substituted beta carbon will lead to a more substituted alkene.
What does Zaitsev's rule say?
Zaitsev's Rule states that when there is more than one possible beta carbon that can be deprotonated while performing an elimination reaction, the more substituted one (the one with fewer hydrogen atoms attached) is preferred. Deprotonating the more substituted beta carbon will lead to a more substituted alkene.
Why is E2 anti elimination?
E2 Stereochemistry In syn elimination, the base attacks the β-hydrogen on the same side as the leaving group. In anti elimination, the base attacks the β-hydrogen on the opposite side of the leaving group. It has been experimentally determined that E2 elimination occurs through an anti mechanism.
What is eclipsed form?
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry - Eclipsed. Eclipsed (eclipsed conformation): Two atoms and/or groups whose dihedral angle is 0o. In other words, their bonds to the axis of rotation are aligned. Also refers to a conformation which contains this arrangement.
What happens E2 reaction?
E2, bimolecular elimination, was proposed in the 1920s by British chemist Christopher Kelk Ingold. Unlike E1 reactions, E2 reactions remove two subsituents with the addition of a strong base, resulting in an alkene.
What is anti-periplanar?
Anti-periplanar refers to a periplanar conformation where the dihedral angle between two atoms or groups of atoms is between ±150° and 180°. In texts, anti-periplanar means bonds are anti-coplanar.
What is anti-periplanar in organic chemistry?
Two of the terms you may encounter in organic chemistry are anti-periplanar and syn-periplanar. Both refer to the geometry of chemical bonds in a molecule.
What is the anti-periplanar conformation?
The anti-periplanar conformation is a periplanar conformation in which the dihedral angle between two atoms or groups of atoms is between ±150° and 180°. In this conformation, the groups are anti-coplanar.
Who coined the term "anti-periplanar"?
The term anti-periplanar was first coined by Klyne and Prelog in their work entitled "Description of steric relationships across single bonds", published in 1960. ‘Anti’ refers to the two functional groups lying on opposite sides of the plane of the bond.
Which mechanism prefers anti-periplanar geometry?
Figure 10: In an E 2 mechanism molecules generally prefer an anti-periplanar geometry because it aligns molecular orbitals and sets up the molecule to move electrons in a C–H bonding orbital into a π C-C bonding orbital.
What is the methyl group in pinacol rearrangement?
In the pinacol rearrangement, a methyl group is found anti-periplanar to an activated alcohol functional group. This places the σ C–C orbital of the methyl group parallel with the σ* C–O orbital of the activated alcohol. Before the activated alcohol leaves as H 2 O the methyl bonding orbital donates into the C–O antibonding orbital, weakening both bonds. This hyperconjugation facilitates the 1,2-methyl shift that occurs to remove water. See Figure 11 for the mechanism.
What is the dihedral angle of a synperiplanar conformer?
In the syn-periplanar conformer, the A and D are on the same side of the plane of the bond, with the dihedral angle of A–B and C–D between +30° and −30° (see Figure 2).
What is the anti-periplanar bond angle?
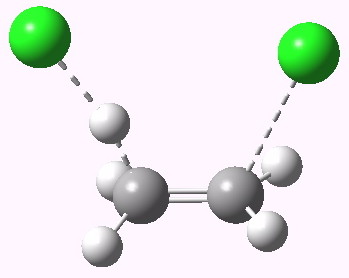
Anti-periplanar is a term used in organic chemistry to describe the A–B–C–D bond angle in a molecule. In this conformer, the dihedral angle of the A–B bond and the C–D bond is greater than +150° or less than −150° (Figures 1 and 2 ). Anti-periplanar is often used in textbooks to mean strictly anti-coplanar, with an A-B C-D dihehedral angle of 180° (Figure 3). In a Newman projection, the molecule will be in a staggered arrangement with the anti-periplanar functional groups pointing up and down, 180° away from each other (see Figure 4). Figure 5 shows 2-chloro-2,3-dimethylbutane in a sawhorse projection with chlorine and a hydrogen anti-periplanar to each other.
Can parallel orbitals be used in hyperconjugation?
The parallel orbitals can overlap and become involved in hyperconjugation. If the bonding orbital is an electron donor and the anti-bonding orbital is an electron acceptor, then the bonding orbital will be able to donate electronegativity into the anti-bonding orbital.
